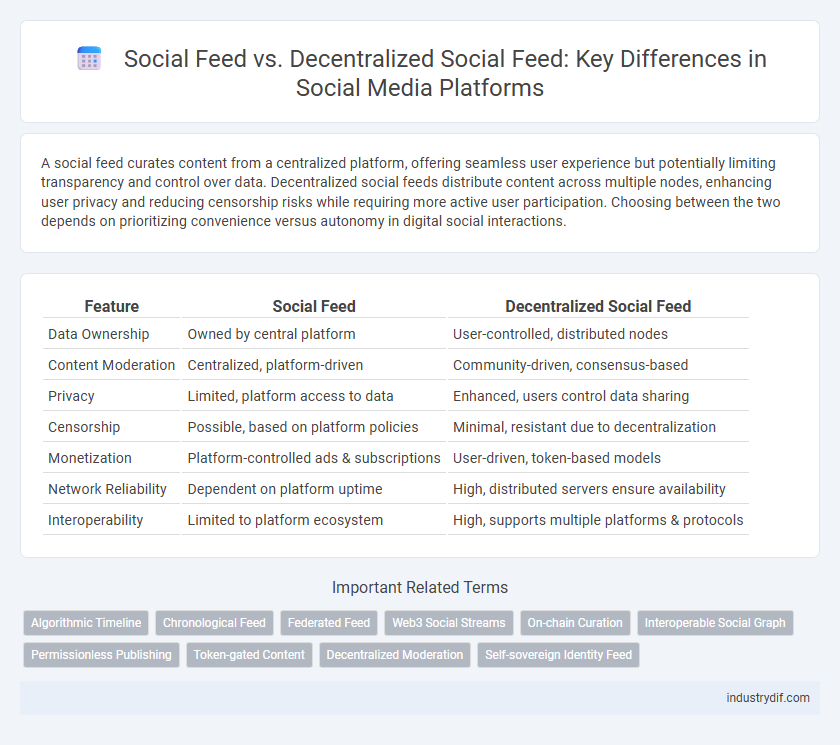
A social feed curates content from a centralized platform, offering seamless user experience but potentially limiting transparency and control over data. Decentralized social feeds distribute content across multiple nodes, enhancing user privacy and reducing censorship risks while requiring more active user participation. Choosing between the two depends on prioritizing convenience versus autonomy in digital social interactions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Social Feed | Decentralized Social Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Owned by central platform | User-controlled, distributed nodes |
| Content Moderation | Centralized, platform-driven | Community-driven, consensus-based |
| Privacy | Limited, platform access to data | Enhanced, users control data sharing |
| Censorship | Possible, based on platform policies | Minimal, resistant due to decentralization |
| Monetization | Platform-controlled ads & subscriptions | User-driven, token-based models |
| Network Reliability | Dependent on platform uptime | High, distributed servers ensure availability |
| Interoperability | Limited to platform ecosystem | High, supports multiple platforms & protocols |
Understanding Social Feeds: Traditional Platforms Explained
Traditional social feeds on platforms like Facebook and Twitter rely on centralized servers to curate and display content, often using proprietary algorithms that prioritize engagement metrics. These feeds aggregate posts, updates, and multimedia from users within a controlled environment, where platform owners dictate data access and content visibility. The centralized nature raises concerns over privacy, data ownership, and potential manipulation of the information users receive.
What Is a Decentralized Social Feed?
A decentralized social feed is a social media platform where content distribution and data ownership are controlled by users rather than a central authority, enhancing privacy and censorship resistance. Unlike traditional social feeds managed by centralized servers, decentralized feeds use blockchain or peer-to-peer networks to ensure transparency and user autonomy. This structure empowers users to curate their own feeds, fostering trust and eliminating single points of failure in content moderation.
Core Differences: Centralized vs Decentralized Social Feeds
Centralized social feeds rely on a single platform to control data, content distribution, and user interactions, often leading to algorithm-driven visibility and potential censorship. Decentralized social feeds operate on blockchain or peer-to-peer networks, giving users ownership of their data, transparency in content moderation, and resistance to centralized control. This fundamental difference enhances privacy, user agency, and content diversity in decentralized social feeds compared to traditional centralized models.
User Privacy and Data Ownership
Social feeds on traditional platforms centralize user data, often leading to privacy concerns and limited control over personal information. Decentralized social feeds prioritize user privacy by enabling data ownership through blockchain or peer-to-peer networks, ensuring users retain full control and transparency of their digital footprint. This shift enhances data security, reduces censorship risks, and empowers users to manage their social interactions without reliance on centralized authorities.
Content Moderation and Censorship
Social feeds on centralized platforms rely heavily on authoritative content moderation, often resulting in algorithm-driven censorship that prioritizes engagement and advertiser interests over user expression. Decentralized social feeds offer community-driven moderation frameworks, enhancing transparency and reducing unilateral censorship by distributing control across a wider network of users. This shift promotes diverse perspectives and mitigates the risk of biased suppression inherent in centralized systems.
Algorithmic Influence on Social Feed Visibility
Algorithmic influence on social feed visibility directs content exposure based on user behavior, often creating echo chambers by prioritizing engagement and popular posts. In contrast, decentralized social feeds distribute control across users or nodes, reducing algorithmic bias and promoting diverse content visibility. This shift enhances transparency and user autonomy while mitigating manipulation by centralized platforms.
Monetization and Rewards for Content Creators
Decentralized social feeds empower content creators with direct monetization options through blockchain-based tokens and smart contracts, ensuring transparent and fair rewards without intermediary fees. Traditional social feeds rely on platform-controlled ad revenue sharing, often limiting creators' earnings and control over their content. Decentralized platforms promote increased financial incentives and ownership, fostering a more equitable digital social economy.
Community Governance and Platform Control
Decentralized social feeds prioritize community governance by distributing decision-making power among users, reducing reliance on centralized platform control that often dictates content visibility and moderation. This structure enables transparent algorithms and democratic moderation processes, fostering a more equitable and user-driven social experience. In contrast, traditional social feeds concentrate control within a single entity, limiting user influence over platform policies and content management.
Security and Risk Factors in Social Feeds
Social feeds controlled by centralized platforms often present significant security risks, including data breaches and unauthorized content manipulation due to single points of failure. Decentralized social feeds leverage blockchain technology and distributed networks to enhance data integrity, reduce censorship, and mitigate risks related to centralized control and single points of vulnerability. Users in decentralized feeds benefit from increased privacy, control over personal data, and resistance to hacking incidents that commonly compromise traditional social media platforms.
Future Trends in Social Feed Technology
Future trends in social feed technology emphasize the shift from centralized algorithms to decentralized social feeds that enhance user control and data privacy. Innovations like blockchain integration enable transparent content curation and reduce censorship risks, fostering trust and authenticity within online communities. Predictive AI models will further personalize experiences while maintaining decentralization, balancing relevancy with user empowerment.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Timeline
Algorithmic Timelines in social feeds prioritize content based on user behavior and engagement metrics, often leading to echo chambers and reduced content diversity. Decentralized Social Feeds distribute content through peer-to-peer networks with transparent, customizable algorithms, enhancing user control and fostering diverse information exposure.
Chronological Feed
A traditional social feed typically uses algorithmic sorting to prioritize content based on user engagement metrics, often creating echo chambers and reducing visibility for recent posts. In contrast, a decentralized social feed employs a chronological feed model that ensures transparency and fairness by displaying posts in real-time order, empowering users with control over their content consumption without algorithmic bias.
Federated Feed
A Federated Feed operates across multiple interconnected servers, enabling users to share and receive content without relying on a single central authority, which enhances data privacy and reduces censorship risks. Compared to traditional Social Feeds, Federated Feeds offer greater user control over personal data and promote a more resilient, decentralized social networking experience by leveraging protocols like ActivityPub.
Web3 Social Streams
Web3 social streams leverage decentralized social feeds to enhance user control, privacy, and data ownership by distributing content across blockchain networks instead of relying on centralized platforms. This approach fosters transparent interactions and censorship resistance, enabling users to curate authentic social experiences while directly monetizing their contributions.
On-chain Curation
On-chain curation enables decentralized social feeds to leverage blockchain technology for transparent content moderation and reward distribution, enhancing trust and user accountability. Unlike traditional social feeds, decentralized platforms prioritize user-driven content discovery and governance through immutable on-chain records.
Interoperable Social Graph
A decentralized social feed leverages an interoperable social graph to enable users to maintain control over their data and interactions across multiple platforms, enhancing privacy and reducing central authority. This interoperability allows seamless content sharing and consistent social connections, fostering a more open and user-centric social networking experience compared to traditional centralized social feeds.
Permissionless Publishing
Social feeds on centralized platforms restrict content through algorithmic curation and permission-based publishing, limiting user autonomy and content diversity. Decentralized social feeds enable permissionless publishing, allowing users to share content freely without centralized control, fostering open access and enhanced content variety.
Token-gated Content
Token-gated content in decentralized social feeds enhances user engagement by enabling exclusive access based on token ownership, fostering a more secure and transparent way to monetize and distribute content compared to traditional social feeds. This approach leverages blockchain technology to create verifiable scarcity and incentivizes community participation, driving innovative social interactions and value exchange.
Decentralized Moderation
Decentralized social feeds empower users with community-driven moderation, reducing centralized control and censorship often seen on traditional social platforms. This approach enhances transparency and accountability by distributing content governance across diverse participants rather than relying on a single authority.
Self-sovereign Identity Feed
Social feeds typically rely on centralized platforms that control user data and content distribution, limiting user ownership and privacy. Decentralized social feeds leverage Self-sovereign Identity (SSI) frameworks, empowering users with full control over their personal data and enabling secure, transparent content sharing without intermediaries.
Social Feed vs Decentralized Social Feed Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com