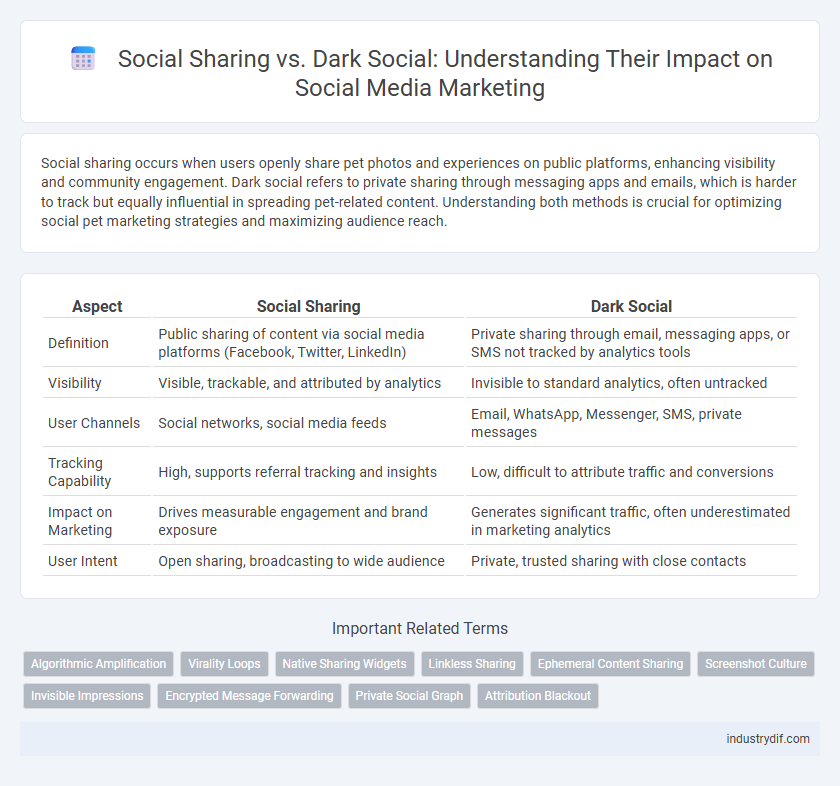
Social sharing occurs when users openly share pet photos and experiences on public platforms, enhancing visibility and community engagement. Dark social refers to private sharing through messaging apps and emails, which is harder to track but equally influential in spreading pet-related content. Understanding both methods is crucial for optimizing social pet marketing strategies and maximizing audience reach.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Social Sharing | Dark Social |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Public sharing of content via social media platforms (Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn) | Private sharing through email, messaging apps, or SMS not tracked by analytics tools |
| Visibility | Visible, trackable, and attributed by analytics | Invisible to standard analytics, often untracked |
| User Channels | Social networks, social media feeds | Email, WhatsApp, Messenger, SMS, private messages |
| Tracking Capability | High, supports referral tracking and insights | Low, difficult to attribute traffic and conversions |
| Impact on Marketing | Drives measurable engagement and brand exposure | Generates significant traffic, often underestimated in marketing analytics |
| User Intent | Open sharing, broadcasting to wide audience | Private, trusted sharing with close contacts |
Understanding Social Sharing: Definition and Examples
Social sharing refers to the public distribution of content on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, enabling users to broadcast messages, links, and media to their network. It differs from dark social, which consists of private sharing through channels such as messaging apps, email, and SMS that are harder to track by marketers. Examples of social sharing include posting a news article on a Facebook timeline or tweeting a video link, whereas dark social involves sending the same content via WhatsApp or private email conversations.
What Is Dark Social and Why Does It Matter?
Dark social refers to the sharing of content through private channels such as messaging apps, email, and text messages, making it difficult for marketers to track and analyze through traditional web analytics tools. This hidden sharing accounts for a significant portion of online content distribution, often surpassing public social sharing on platforms like Facebook and Twitter. Understanding dark social is crucial for brands to accurately measure engagement and optimize their content strategies for deeper, organic reach.
Key Differences Between Social Sharing and Dark Social
Social sharing involves openly posting content on visible platforms like Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram, enabling measurable engagement through likes, shares, and comments. Dark social refers to private content sharing via channels such as messaging apps, email, and text messages, where tracking and analytics are limited or unavailable. The key differences lie in visibility, data tracking capabilities, and the platforms used for content distribution.
Platforms Driving Social Sharing
Platforms driving social sharing include Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and Instagram, which facilitate public content distribution and engagement through likes, comments, and shares. Dark social refers to content shared via private channels like email, messaging apps, and SMS, making tracking and attribution challenging for marketers. Understanding the distinction between public social sharing platforms and dark social channels is crucial for accurate measurement of content reach and audience behavior.
How Dark Social Impacts Data Analytics
Dark social significantly challenges data analytics by obscuring the true origin of traffic, as shares occur through private channels like messaging apps, emails, and text messages. This lack of attribution leads to underreported referral sources and skews overall data accuracy, complicating efforts to measure campaign effectiveness. Consequently, marketers must rely on indirect metrics and advanced tracking solutions to better understand user behavior influenced by dark social sharing.
Pros and Cons of Social Sharing
Social sharing allows content to reach a broad audience quickly, increasing brand visibility and engagement through measurable metrics like shares and likes. However, it often exposes content to algorithmic limitations and public scrutiny, potentially reducing message control and authenticity. While social sharing drives traffic and fosters community interaction, it may also lead to reduced privacy and increased competition for audience attention.
Challenges Presented by Dark Social
Dark Social presents significant challenges in tracking and measuring content reach due to its private nature, as shares occur via encrypted messaging apps, email, and SMS, which are often invisible to traditional analytics tools. This lack of visibility complicates marketers' ability to attribute traffic and engagement accurately, limiting insights into user behavior and campaign effectiveness. Furthermore, the spread of content through Dark Social hinders targeting strategies and personalized marketing efforts, making it difficult to optimize outreach and engagement.
Strategies to Track Dark Social Traffic
Implementing UTM parameters and unique tracking codes in URLs helps identify and measure dark social traffic from private messaging apps, emails, and other non-public channels. Using social listening tools and sentiment analysis provides insights into content engagement and user behavior beyond traditional social sharing metrics. Encouraging direct user interactions with branded links and leveraging analytics platforms with deep-linking capabilities enhance the accuracy of tracking dark social traffic for refined marketing strategies.
Leveraging Both for Effective Marketing
Social sharing through public platforms like Facebook and Twitter amplifies brand visibility by encouraging users to share content openly, driving organic reach and engagement. Dark social, including private messaging apps and email forwarding, accounts for a significant portion of traffic and is critical for targeting personalized, trust-based interactions often missed in traditional analytics. Leveraging both strategies enhances marketing effectiveness by combining measurable public engagement with the impactful yet covert reach of dark social channels.
Future Trends in Social and Dark Sharing
Future trends in social sharing emphasize increased encryption and privacy controls, driving a shift toward dark social channels like private messaging apps and closed groups. Emerging technologies such as AI-powered content discovery and blockchain-based data verification will enhance trust and personalization while limiting public data exposure. As user demand for intimate, secure communication grows, marketers must develop strategies tailored to dark social networks, leveraging seamless, authentic engagement tools and indirect analytics.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Amplification
Social sharing leverages algorithmic amplification by platforms to boost content visibility through public posts and shares, increasing reach via user engagement signals. Dark social, comprising private messages and untrackable shares, bypasses these algorithms, limiting measurable amplification despite its significant role in content distribution.
Virality Loops
Virality loops in social sharing harness public platforms like Facebook and Twitter to amplify content reach, while dark social relies on private channels such as messaging apps and email, making tracking and optimization more challenging. Understanding the interplay between open social sharing and dark social is crucial for maximizing engagement and the organic spread of content through repetitive, self-sustaining user interactions.
Native Sharing Widgets
Native sharing widgets streamline content distribution by enabling users to share directly within apps or websites, boosting visibility on social platforms and increasing organic reach. While social sharing through these widgets provides measurable engagement metrics, dark social--shares via private channels like messaging apps and email--remains difficult to track but significantly impacts viral growth and referral traffic.
Linkless Sharing
Linkless sharing in dark social channels facilitates private content distribution through messaging apps, email, and SMS, making it harder to track compared to traditional social sharing with visible URLs. This form of sharing significantly drives website traffic and user engagement, yet challenges marketers' ability to measure and optimize content reach accurately.
Ephemeral Content Sharing
Ephemeral content sharing thrives in dark social channels, where temporary posts disappear after viewing, fostering intimate and authentic interactions away from public social sharing platforms. These transient messages drive organic engagement through private messaging apps, SMS, and encrypted platforms, making them essential for marketers targeting genuine user connections and timely content consumption.
Screenshot Culture
Screenshot culture fuels dark social by enabling private, untraceable sharing of content across messaging apps and closed groups, bypassing traditional social sharing metrics. This phenomenon challenges marketers to adapt strategies, as valuable user engagement occurs beyond public social platforms and standard analytics.
Invisible Impressions
Invisible impressions in dark social channels like private messaging apps and email often surpass visible social sharing metrics, making traditional analytics underestimate true content reach. Dark social drives significant, untrackable engagement that shapes brand awareness and consumer behavior beyond public shares and likes.
Encrypted Message Forwarding
Encrypted message forwarding in dark social channels significantly enhances user privacy by allowing content to be shared without tracking or public exposure, contrasting with traditional social sharing on platforms like Facebook or Twitter where data is often collected and analyzed. This form of private sharing through messaging apps, email, and encrypted platforms drives a substantial volume of unseen traffic that challenges marketers' ability to measure engagement accurately.
Private Social Graph
Private social graph emphasizes connections formed through dark social channels like private messaging, email, and closed groups, where content is shared discreetly without public visibility. Unlike social sharing on public platforms, dark social interactions represent a more authentic and trusted exchange between close networks, significantly impacting brand reach and user engagement analytics.
Attribution Blackout
Social sharing enables content distribution through visible channels like Facebook and Twitter, allowing marketers to track engagement and attribute traffic effectively. Dark social occurs when users share content via private channels such as messaging apps and email, creating an attribution blackout that complicates accurate measurement of referral sources.
Social Sharing vs Dark Social Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com