Incident Management provides a structured approach to resolving individual issues through defined roles and escalation paths, ensuring accountability and timely resolution. The Swarming Support Model promotes collaborative efforts among support agents who simultaneously address the problem, accelerating resolution and enhancing knowledge sharing. Choosing between these models depends on organizational priorities such as efficiency, communication, and complexity of incidents.
Table of Comparison
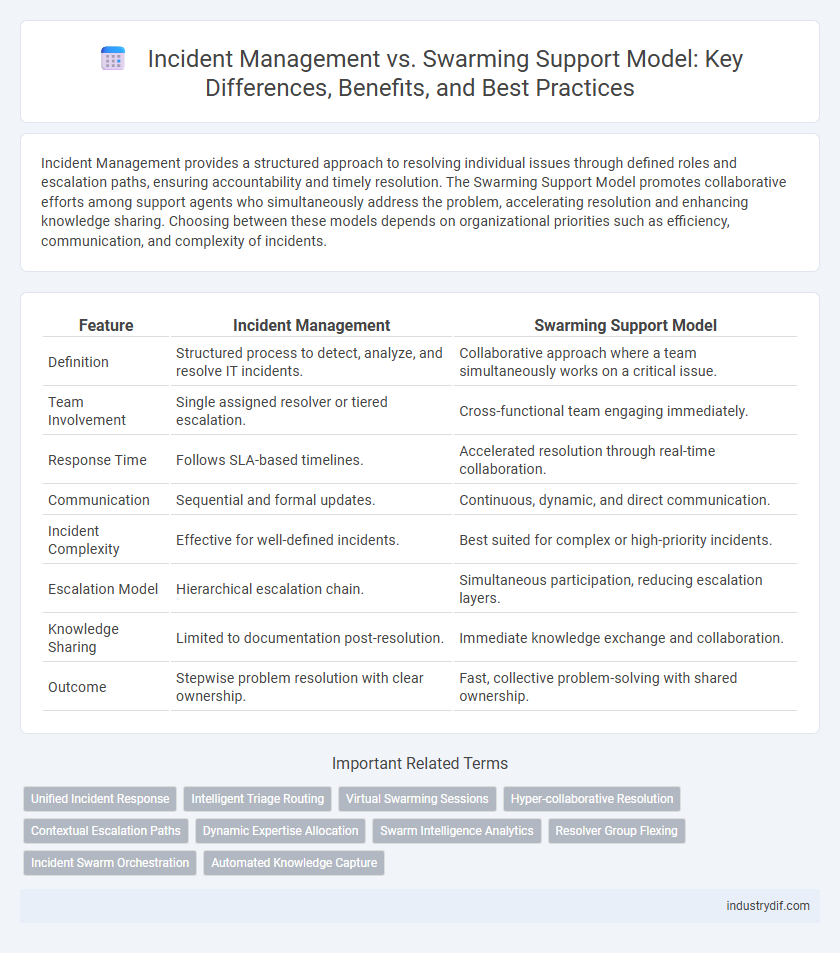
| Feature | Incident Management | Swarming Support Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured process to detect, analyze, and resolve IT incidents. | Collaborative approach where a team simultaneously works on a critical issue. |
| Team Involvement | Single assigned resolver or tiered escalation. | Cross-functional team engaging immediately. |
| Response Time | Follows SLA-based timelines. | Accelerated resolution through real-time collaboration. |
| Communication | Sequential and formal updates. | Continuous, dynamic, and direct communication. |
| Incident Complexity | Effective for well-defined incidents. | Best suited for complex or high-priority incidents. |
| Escalation Model | Hierarchical escalation chain. | Simultaneous participation, reducing escalation layers. |
| Knowledge Sharing | Limited to documentation post-resolution. | Immediate knowledge exchange and collaboration. |
| Outcome | Stepwise problem resolution with clear ownership. | Fast, collective problem-solving with shared ownership. |
Introduction to Incident Management and Swarming Support
Incident Management involves a structured process for identifying, analyzing, and resolving IT service disruptions to restore normal operations quickly and minimize impact. Swarming Support is a collaborative approach where cross-functional teams simultaneously address complex incidents, accelerating resolution through shared expertise. Both models aim to enhance service reliability but differ in coordination style and resource allocation, optimizing response times and customer satisfaction.
Key Principles of Incident Management
Incident Management centers on structured processes aimed at quickly restoring normal service operations by identifying, analyzing, and resolving incidents based on predefined severity levels and escalation protocols. Key principles include thorough incident detection, accurate classification, prioritization aligned with business impact, and coordinated communication among stakeholders to minimize downtime and prevent recurrence. This contrasts with the Swarming Support Model, which relies on collaborative, real-time problem-solving across multiple teams without formalized escalation paths.
Core Concepts of the Swarming Support Model
The Swarming Support Model centers on rapid, collaborative problem-solving where cross-functional experts converge to address incidents in real-time, enhancing efficiency and reducing resolution time. Unlike traditional Incident Management, swarming relies on collective ownership and dynamic team formation that prioritizes immediate knowledge sharing and continuous communication. This approach leverages collective intelligence to quickly isolate root causes and implement solutions, fostering agility and minimizing service disruptions.
Roles and Responsibilities in Incident Management vs Swarming
Incident Management assigns specific roles such as Incident Manager, Technical Lead, and Communications Lead, each responsible for defined tasks like incident detection, escalation, resolution, and stakeholder communication. In contrast, the Swarming Support Model emphasizes a collaborative approach where cross-functional team members work simultaneously on the incident without strict role delineation, promoting faster knowledge sharing and problem-solving. Clear role definitions in Incident Management ensure accountability, while Swarming enables agility and collective ownership during complex issue resolution.
Escalation Processes: Traditional vs Swarming
The traditional Incident Management escalation process follows a hierarchical structure where issues are escalated through predefined tiers until resolution, often causing delays and communication gaps. In contrast, the Swarming Support Model employs a collaborative, real-time approach where multiple experts converge immediately to address incidents, reducing resolution time and improving knowledge sharing. This agile escalation process enhances efficiency, minimizes downtime, and fosters continuous learning within support teams.
Collaboration and Communication Approaches
Incident Management relies on structured escalation paths and defined roles to ensure clear communication and efficient resolution, emphasizing documentation and handoffs. The Swarming Support Model fosters real-time collaboration among cross-functional teams, encouraging spontaneous knowledge sharing and direct communication channels. Both models prioritize responsiveness but differ in the approach to teamwork and interaction dynamics during incident resolution.
Handling Complex Incidents: Which Model Excels?
Incidents involving multiple interdependent systems benefit from the swarming support model, which enables rapid collaboration among specialized experts to diagnose and resolve issues efficiently. In contrast, the incident management model operates through a structured tier-based escalation, ideal for routine or well-defined problems but often slower in addressing complex, multi-faceted incidents. Organizations managing high-severity, complex outages gain improved resolution times and reduced downtime by adopting swarming, promoting cross-functional teamwork and real-time communication.
Impact on Customer Experience and Resolution Time
Incident Management follows a structured, tiered approach that ensures systematic tracking and resolution, often leading to longer wait times but thorough documentation. The Swarming Support Model emphasizes real-time collaboration among experts, significantly accelerating resolution time and improving customer satisfaction by providing immediate, comprehensive responses. Customers benefit from faster problem-solving and reduced frustration when swarming, whereas traditional incident management may delay resolution but offer a more formal escalation path.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Model
Incident Management often faces challenges such as delayed resolution due to rigid escalation paths and limited collaboration across teams, which can hinder quick problem diagnosis. Swarming Support Model can encounter limitations with coordination complexity and potential resource overuse, as multiple experts simultaneously engage without structured prioritization. Both models require careful balance between efficiency and resource allocation to optimize incident response outcomes.
Choosing the Right Support Model for Your Organization
Choosing the right support model depends on your organization's incident frequency, team size, and complexity of issues. Incident Management offers structured escalation paths and clear accountability, ideal for predictable workflows and regulated environments. Swarming Support Model promotes collaborative problem-solving with cross-functional teams, enhancing response time for complex or high-impact incidents requiring diverse expertise.
Related Important Terms
Unified Incident Response
Unified Incident Response integrates Incident Management with the Swarming Support Model by enabling real-time collaboration among cross-functional teams to rapidly identify, assess, and resolve incidents. This approach streamlines communication, reduces resolution time, and enhances overall service reliability through collective expertise and coordinated efforts.
Intelligent Triage Routing
Intelligent triage routing in incident management enables automatic classification and prioritization of issues based on severity and impact, ensuring rapid assignment to specialized teams. The swarming support model enhances this by promoting collaborative, real-time problem-solving among cross-functional experts, accelerating resolution and reducing escalation cycles.
Virtual Swarming Sessions
Virtual swarming sessions enhance incident management by enabling real-time collaboration among cross-functional experts to quickly identify root causes and implement resolutions, reducing downtime and improving service reliability. This dynamic approach contrasts traditional tiered support structures by fostering immediate, collective problem-solving and minimizing escalation delays.
Hyper-collaborative Resolution
Incident Management emphasizes structured workflows and defined roles to resolve issues efficiently, while the Swarming Support Model fosters hyper-collaborative resolution by mobilizing cross-functional teams simultaneously for faster problem-solving and knowledge sharing. This agile approach reduces resolution times and enhances customer satisfaction by leveraging diverse expertise in real-time collaboration.
Contextual Escalation Paths
Incident Management utilizes predefined escalation paths based on incident severity and service impact, ensuring a structured response through designated tiers of support personnel. Swarming Support Model adopts dynamic contextual escalation paths, enabling rapid collaboration across cross-functional teams to resolve complex issues efficiently without rigid hierarchy.
Dynamic Expertise Allocation
Incident Management relies on predefined roles and escalation paths to resolve issues, often leading to slower response times. Swarming Support Model leverages dynamic expertise allocation by assembling cross-functional teams in real-time, enabling faster problem resolution through collaborative knowledge sharing.
Swarm Intelligence Analytics
Swarm Intelligence Analytics enhances incident resolution by leveraging real-time collaboration among multidisciplinary experts, enabling faster identification and remediation of issues compared to traditional Incident Management's linear escalation process. This model uses collective knowledge and adaptive problem-solving strategies to improve response accuracy and reduce downtime through dynamic, decentralized decision-making.
Resolver Group Flexing
Resolver group flexing in Incident Management enables dynamic reassignment of incidents to specialized teams based on priority and expertise, improving resolution efficiency. The Swarming Support Model enhances this flexibility by promoting real-time collaboration among cross-functional experts, reducing response time and increasing incident resolution quality.
Incident Swarm Orchestration
Incident Swarm Orchestration enhances the traditional Incident Management approach by enabling rapid, collaborative problem-solving through dynamic, cross-functional team engagement. This model prioritizes real-time communication and coordinated expertise allocation, significantly reducing resolution times and improving service reliability in complex support environments.
Automated Knowledge Capture
Automated knowledge capture in Incident Management systematically documents resolutions during ticket processing, enhancing future incident resolution efficiency. In contrast, the Swarming Support Model promotes real-time, collaborative problem-solving but may lack structured knowledge consolidation, potentially limiting long-term learning.
Incident Management vs Swarming Support Model Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com