IT Support traditionally relies on in-person assistance and on-site troubleshooting, which can delay response times and restrict flexibility. Remote-first Support leverages advanced technology to provide immediate, location-independent solutions, enhancing efficiency and user satisfaction. This shift enables businesses to maintain continuous support while reducing operational costs and downtime.
Table of Comparison
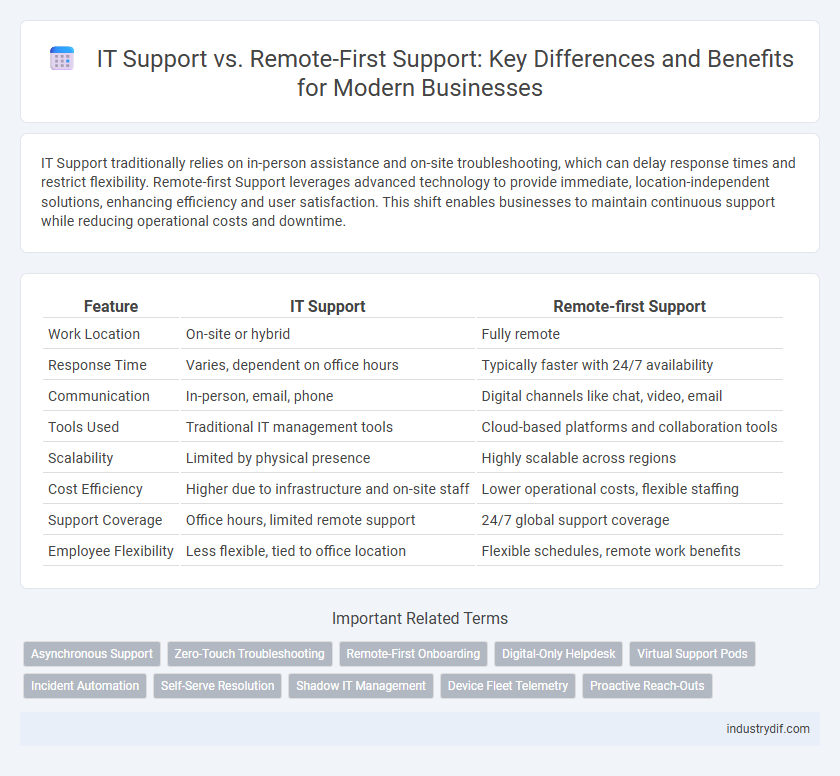
| Feature | IT Support | Remote-first Support |
|---|---|---|
| Work Location | On-site or hybrid | Fully remote |
| Response Time | Varies, dependent on office hours | Typically faster with 24/7 availability |
| Communication | In-person, email, phone | Digital channels like chat, video, email |
| Tools Used | Traditional IT management tools | Cloud-based platforms and collaboration tools |
| Scalability | Limited by physical presence | Highly scalable across regions |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher due to infrastructure and on-site staff | Lower operational costs, flexible staffing |
| Support Coverage | Office hours, limited remote support | 24/7 global support coverage |
| Employee Flexibility | Less flexible, tied to office location | Flexible schedules, remote work benefits |
Understanding IT Support: Traditional Models
Traditional IT support models rely heavily on on-site assistance, where technicians physically troubleshoot hardware and network issues within an organization's premises. This approach involves scheduled visits, direct interaction with users, and immediate access to physical infrastructure, which can delay resolution times if availability is limited. Understanding these constraints highlights the differences when compared to the flexibility and scalability offered by remote-first support models.
What is Remote-first Support?
Remote-first support prioritizes delivering IT assistance primarily through remote channels, enabling technicians to resolve issues without needing physical presence. This model leverages tools like remote desktop software, cloud-based ticketing systems, and instant communication platforms to ensure quick and efficient problem-solving. Emphasizing scalability and accessibility, remote-first support reduces response times and operational costs while maintaining high service quality.
Key Differences Between IT Support and Remote-first Support
IT Support traditionally centers on in-person troubleshooting, hardware maintenance, and onsite user assistance, ensuring direct interaction with physical infrastructure. Remote-first Support emphasizes cloud-based tools, virtual communication, and proactive monitoring, enabling IT professionals to resolve issues without being physically present. Key differences include the scope of access, with remote-first support providing scalable, flexible solutions across multiple locations, while traditional IT Support often depends on localized, hands-on service delivery.
Advantages of Traditional IT Support
Traditional IT Support offers immediate, on-site assistance that ensures rapid resolution of hardware and network issues, minimizing downtime. It provides personalized, face-to-face interaction for more accurate troubleshooting and tailored solutions. Access to physical resources and direct control over infrastructure enhances security and compliance management in enterprise environments.
Benefits of Remote-first Support Approaches
Remote-first IT support enhances flexibility by allowing technicians to resolve issues from any location, reducing downtime and accelerating response times. This approach leverages cloud-based tools, ensuring seamless collaboration and real-time system monitoring across distributed teams. Companies adopting remote-first support models experience increased scalability and cost efficiency compared to traditional on-site IT support setups.
Common Challenges in Both Support Models
Both IT Support and Remote-first Support face common challenges such as maintaining effective communication, ensuring data security, and providing timely technical assistance. Troubleshooting hardware and software issues remotely requires robust diagnostic tools and clear protocols. Employee training and access management remain critical to minimize downtime and enhance productivity across both support environments.
Security Considerations: Onsite vs Remote
IT Support onsite offers direct control over physical security, reducing risks of unauthorized access to sensitive data compared to remote-first support. Remote-first support relies heavily on secure VPNs, multi-factor authentication, and endpoint protection to safeguard data transmitted over potentially unsecured networks. Organizations must implement strict access controls and continuous monitoring to mitigate vulnerabilities inherent in remote environments versus the controlled setting of onsite support.
Cost Implications: IT Support vs Remote-first Support
IT support often incurs higher overhead costs due to on-site staffing, physical infrastructure, and maintenance expenses, whereas remote-first support leverages cloud-based tools and virtual communication to reduce these costs significantly. Remote-first models lower travel, office space, and equipment expenditures, enabling organizations to allocate budgets more efficiently while maintaining service quality. The cost savings of remote-first support directly impact overall operational expenses, making it a financially strategic option for scalable IT service delivery.
Scalability and Flexibility in Support Strategies
IT Support typically offers scalable solutions by expanding on-site teams and resources as demand grows, while Remote-first Support leverages cloud technologies and distributed workforces to dynamically adjust to fluctuating workloads and geographic dispersion. Scalability in Remote-first Support is enhanced through instant access to a global talent pool and automation tools, facilitating rapid response and issue resolution without physical constraints. Flexibility in Remote-first Support enables 24/7 coverage and personalized service across time zones, surpassing traditional IT Support models limited by fixed office hours and locations.
Choosing the Right Support Model for Your Business
Selecting the right IT support model depends on your business size, technical needs, and operational flexibility. Traditional IT support typically offers on-site assistance and immediate troubleshooting, ideal for companies requiring direct hardware interaction. Remote-first support leverages cloud-based tools and virtual access, providing scalable, cost-effective solutions that enhance efficiency for distributed teams.
Related Important Terms
Asynchronous Support
IT Support traditionally relies on synchronous interactions, requiring real-time availability to resolve issues, whereas Remote-first Support prioritizes asynchronous support, enabling users to submit requests and receive assistance without time zone constraints. Asynchronous support enhances flexibility, boosts productivity, and accelerates response times by allowing support teams to manage multiple queries simultaneously across diverse locations.
Zero-Touch Troubleshooting
Zero-touch troubleshooting revolutionizes IT support by enabling remote-first teams to diagnose and resolve issues without physical intervention, significantly reducing downtime and operational costs. This approach leverages automated diagnostics, remote monitoring, and cloud-based management tools to streamline problem resolution, enhancing efficiency compared to traditional IT support models.
Remote-First Onboarding
Remote-first onboarding streamlines IT support by enabling employees to access comprehensive setup resources and troubleshooting directly from any location, reducing downtime and accelerating productivity. Leveraging cloud-based tools and virtual assistance, remote-first support ensures seamless integration and immediate resolution without the need for physical IT intervention.
Digital-Only Helpdesk
Digital-only helpdesk solutions enhance IT support by enabling remote-first support models that deliver instant, scalable assistance through cloud-based platforms, reducing downtime and operational costs. Leveraging AI-driven ticketing systems and real-time chat tools, digital-only helpdesks optimize issue resolution efficiency and improve user satisfaction in hybrid and fully remote work environments.
Virtual Support Pods
Virtual Support Pods enhance IT Support by forming specialized, agile teams that collaborate remotely, improving response times and expertise sharing. These pods leverage cloud-based tools and real-time communication platforms to deliver seamless Remote-first Support, reducing downtime and increasing customer satisfaction.
Incident Automation
Incident automation in IT Support streamlines issue resolution by automatically detecting, categorizing, and prioritizing incidents, reducing response times and manual intervention. Remote-first Support leverages cloud-based automation tools to enable instant incident tracking and resolution from any location, enhancing scalability and minimizing downtime for distributed teams.
Self-Serve Resolution
IT Support often requires direct technician intervention to resolve issues, whereas Remote-first Support emphasizes self-serve resolution through comprehensive knowledge bases and automated troubleshooting tools, significantly reducing downtime and increasing user autonomy. By leveraging AI-driven chatbots and interactive guides, Remote-first Support empowers employees to diagnose and fix common technical problems independently without waiting for live assistance.
Shadow IT Management
IT Support traditionally involves on-site troubleshooting and direct management of Shadow IT risks, whereas Remote-first Support emphasizes proactive monitoring and remote control tools to detect and mitigate unauthorized applications and devices effectively. Integrating advanced security protocols with cloud-based asset management enhances Shadow IT management by ensuring compliance and safeguarding organizational data across dispersed work environments.
Device Fleet Telemetry
Device Fleet Telemetry in IT Support enables real-time monitoring and diagnostics of hardware performance across all endpoints, ensuring swift issue resolution and minimized downtime. Remote-first Support leverages this telemetry data to proactively manage device health remotely, enhancing efficiency and user experience without the need for on-site interventions.
Proactive Reach-Outs
IT Support often relies on reactive problem-solving, addressing issues only after users report them, whereas Remote-first Support emphasizes proactive reach-outs, identifying and resolving potential problems before they impact workflow. This proactive approach reduces downtime, enhances user satisfaction, and aligns with dynamic, distributed work environments by leveraging continuous monitoring and automated alerts.
IT Support vs Remote-first Support Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com