Onsite support provides hands-on assistance, allowing technicians to physically inspect and repair pet-related equipment or infrastructure, ensuring immediate and precise problem resolution. Remote troubleshooting offers convenience and quick diagnostics through virtual tools, minimizing downtime and reducing the need for travel. Choosing the right approach depends on the complexity of the issue, urgency, and available resources for effective pet support.
Table of Comparison
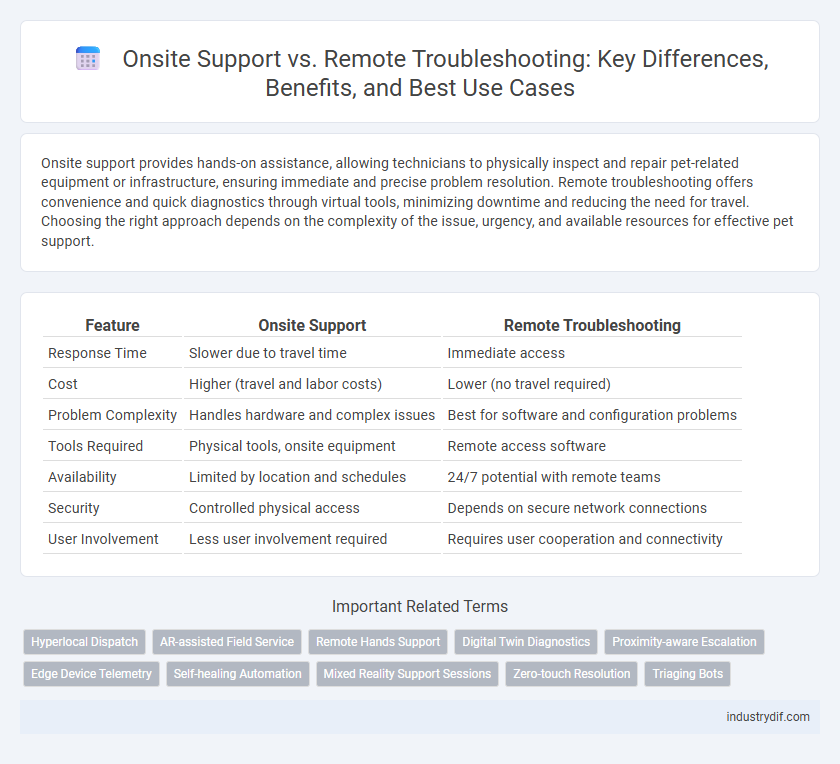
| Feature | Onsite Support | Remote Troubleshooting |
|---|---|---|
| Response Time | Slower due to travel time | Immediate access |
| Cost | Higher (travel and labor costs) | Lower (no travel required) |
| Problem Complexity | Handles hardware and complex issues | Best for software and configuration problems |
| Tools Required | Physical tools, onsite equipment | Remote access software |
| Availability | Limited by location and schedules | 24/7 potential with remote teams |
| Security | Controlled physical access | Depends on secure network connections |
| User Involvement | Less user involvement required | Requires user cooperation and connectivity |
Understanding Onsite Support: Definition and Scope
Onsite support refers to technical assistance provided directly at the customer's location, addressing hardware issues, network setups, and equipment installations that require physical presence. This service scope includes preventive maintenance, urgent repairs, and system upgrades, ensuring minimal downtime for critical infrastructure. Understanding the boundaries and capabilities of onsite support helps organizations allocate resources effectively and enhances overall service reliability.
Remote Troubleshooting Explained: Processes and Tools
Remote troubleshooting leverages advanced diagnostic tools and secure remote access software to identify and resolve technical issues without the need for onsite presence, enhancing efficiency and reducing downtime. Key processes involve real-time system monitoring, remote desktop control, and utilizing virtual private networks (VPNs) to maintain data security during interventions. Tools such as TeamViewer, LogMeIn, and remote command-line utilities enable support teams to perform detailed error analysis and implement fixes swiftly across diverse hardware and software environments.
Key Differences Between Onsite and Remote Support
Onsite support involves a technician physically present to diagnose and resolve issues, offering hands-on access to hardware and immediate interaction with users. Remote troubleshooting utilizes internet-based tools to address technical problems without geographic constraints, enabling faster initial response times and reducing travel costs. Key differences include the level of physical access, speed of deployment, and suitability for complex hardware repairs versus software or configuration issues.
Cost Implications: Onsite vs Remote Assistance
Onsite support generally incurs higher costs due to travel expenses, technician time, and potential downtime, while remote troubleshooting significantly reduces these expenses by enabling immediate access without physical presence. Organizations benefit from remote assistance through lower operational costs and faster issue resolution, making it a cost-effective alternative for routine and minor technical problems. However, onsite support remains essential for complex hardware failures or network infrastructure issues that require physical intervention.
Speed and Response Time: Which Support is Faster?
Onsite support typically involves longer response times due to travel and scheduling but offers immediate physical access to hardware and network systems for faster resolution of complex issues. Remote troubleshooting enables quicker initial response through instant connectivity, allowing technicians to diagnose and fix many problems without delay. For urgent issues requiring immediate intervention, remote support is usually faster, while onsite support excels in resolving hardware failures that cannot be addressed remotely.
Security Considerations: Onsite vs Remote Services
Onsite support allows direct control over physical security of hardware and data, reducing risks associated with remote access vulnerabilities. Remote troubleshooting demands robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and secure VPN connections to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Organizations must balance convenience and speed of remote services with strict compliance requirements and sensitive data protection inherent in onsite interventions.
Customer Experience: Personal Touch vs Convenience
Onsite support delivers a personalized, face-to-face experience that fosters trust and immediate, hands-on problem resolution, enhancing customer satisfaction through direct interaction. Remote troubleshooting offers unparalleled convenience and speed by resolving issues without travel delays, catering to customers who prioritize efficiency and accessibility. Balancing the personal touch of onsite visits with the quick accessibility of remote support can optimize customer experience based on specific needs and preferences.
When to Choose Onsite Over Remote Troubleshooting
Onsite support is essential when hardware issues require physical inspection or replacement, or when network problems demand direct access to equipment for accurate diagnostics. Complex system failures that cannot be resolved remotely, especially in environments with sensitive data or strict security protocols, also necessitate onsite intervention. Choosing onsite support ensures faster resolution in cases where remote troubleshooting is limited by connectivity constraints or insufficient technical visibility.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Support Model
Onsite support faces limitations such as longer response times and higher operational costs due to travel and physical presence requirements, while remote troubleshooting struggles with challenges like limited access to hardware, potential security risks, and dependency on stable internet connectivity. Onsite interventions are essential for complex hardware repairs and situations requiring direct inspection, but they can disrupt workflows due to the need for scheduling and physical access. Remote support excels in quick issue diagnosis and software updates, yet it may be inadequate for resolving hardware malfunctions or intricate network problems beyond the technician's virtual reach.
Future Trends in Technical Support: Onsite and Remote Integration
Future trends in technical support emphasize seamless integration between onsite support and remote troubleshooting, leveraging AI-powered diagnostics and augmented reality tools to enhance real-time problem resolution. Hybrid models combining remote monitoring with targeted onsite interventions are improving efficiency and reducing downtime in enterprise environments. Cloud-based support platforms and IoT connectivity facilitate proactive maintenance, enabling faster response times and predictive issue detection.
Related Important Terms
Hyperlocal Dispatch
Onsite support ensures immediate, hands-on resolution by deploying technicians directly to the problem location, enhancing service quality through hyperlocal dispatch that reduces travel time and response delays. Remote troubleshooting leverages advanced diagnostic tools and real-time communication to quickly identify and resolve issues without physical presence, optimizing operational efficiency while hyperlocal dispatch remains critical for escalated or hardware-related cases.
AR-assisted Field Service
AR-assisted field service enhances onsite support by enabling technicians to receive real-time guidance and access detailed equipment data remotely, reducing downtime and travel costs. This technology integrates augmented reality to overlay diagnostic information, improving accuracy and accelerating problem resolution compared to traditional remote troubleshooting methods.
Remote Hands Support
Remote Hands Support offers 24/7 access to skilled technicians who can perform physical tasks such as equipment reboots, cable management, and hardware inspections without onsite presence, reducing downtime and operational costs. This service is essential for data centers and IT environments requiring rapid response and minimal disruption, complementing traditional Onsite Support by enabling faster issue resolution through remote management tools.
Digital Twin Diagnostics
Digital Twin Diagnostics enhances both onsite support and remote troubleshooting by creating real-time virtual replicas of physical assets, enabling precise fault detection and predictive maintenance. This approach reduces downtime and operational costs by allowing technicians to simulate repairs remotely, minimizing the need for physical presence while ensuring accurate diagnostics.
Proximity-aware Escalation
Proximity-aware escalation enhances onsite support by rapidly assigning local technicians to resolve issues requiring physical intervention, reducing downtime and increasing customer satisfaction. Remote troubleshooting leverages real-time diagnostics and expert collaboration from a distance but escalates to onsite support when proximity factors indicate faster or more effective resolution through direct hardware access.
Edge Device Telemetry
Onsite support provides hands-on access to edge devices, enabling technicians to physically inspect hardware and capture comprehensive telemetry data for accurate diagnostics. Remote troubleshooting leverages real-time edge device telemetry via secure IoT platforms to quickly analyze performance metrics and resolve issues without the need for physical presence.
Self-healing Automation
Self-healing automation enhances remote troubleshooting by automatically detecting and resolving issues without human intervention, reducing downtime and support costs. In contrast, onsite support provides physical presence for complex hardware repairs but lacks the immediacy and scalability of automated remote fixes.
Mixed Reality Support Sessions
Mixed Reality support sessions combine the advantages of onsite support's hands-on assistance with remote troubleshooting's real-time expertise, enabling technicians to guide users through complex tasks using interactive 3D visualizations. This hybrid approach reduces downtime by enhancing problem diagnosis accuracy and streamlining communication between on-field operators and remote specialists.
Zero-touch Resolution
Zero-touch resolution streamlines support by enabling automated issue detection and repair without technician presence, significantly reducing downtime and operational costs. Remote troubleshooting leverages advanced diagnostics and real-time remote access tools, offering faster problem resolution compared to traditional onsite support.
Triaging Bots
Onsite support provides direct interaction for triaging bots, allowing technicians to physically assess hardware and network conditions that influence bot performance. Remote troubleshooting offers faster response times using diagnostic tools and real-time data analysis, enhancing efficiency in identifying and resolving bot-related issues.
Onsite Support vs Remote Troubleshooting Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com