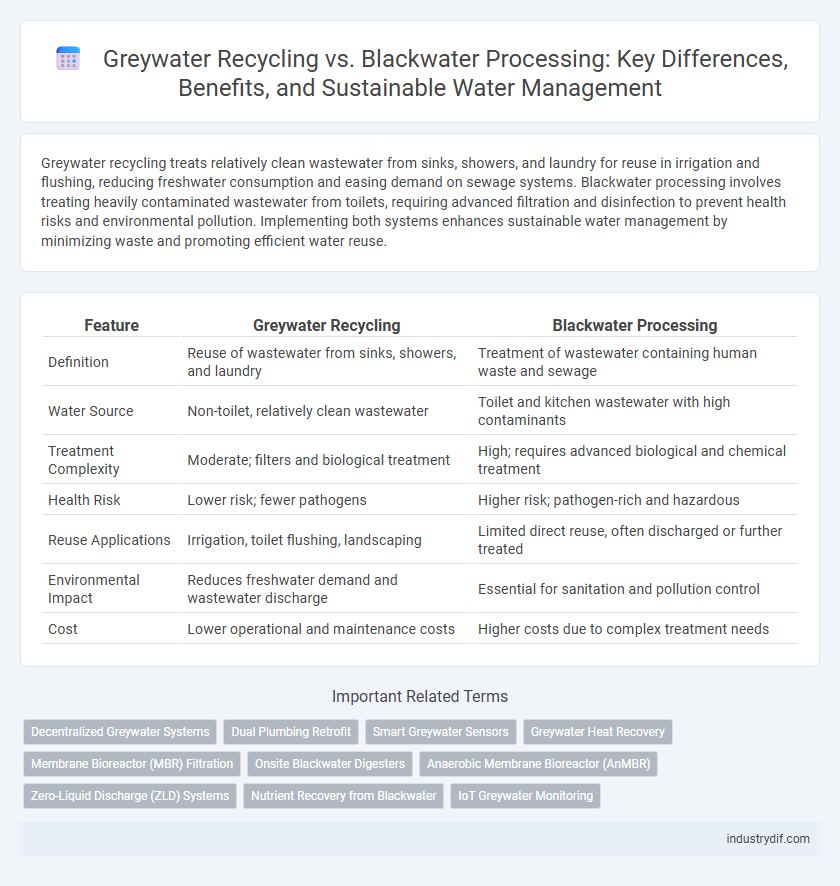
Greywater recycling treats relatively clean wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry for reuse in irrigation and flushing, reducing freshwater consumption and easing demand on sewage systems. Blackwater processing involves treating heavily contaminated wastewater from toilets, requiring advanced filtration and disinfection to prevent health risks and environmental pollution. Implementing both systems enhances sustainable water management by minimizing waste and promoting efficient water reuse.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Greywater Recycling | Blackwater Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reuse of wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry | Treatment of wastewater containing human waste and sewage |
| Water Source | Non-toilet, relatively clean wastewater | Toilet and kitchen wastewater with high contaminants |
| Treatment Complexity | Moderate; filters and biological treatment | High; requires advanced biological and chemical treatment |
| Health Risk | Lower risk; fewer pathogens | Higher risk; pathogen-rich and hazardous |
| Reuse Applications | Irrigation, toilet flushing, landscaping | Limited direct reuse, often discharged or further treated |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces freshwater demand and wastewater discharge | Essential for sanitation and pollution control |
| Cost | Lower operational and maintenance costs | Higher costs due to complex treatment needs |
Introduction to Greywater and Blackwater
Greywater refers to gently used water from bathroom sinks, showers, and laundry that can be recycled for irrigation and flushing toilets, reducing overall water consumption significantly. Blackwater contains sewage and waste from toilets, requiring advanced treatment processes to ensure safe disposal or reuse. Understanding the distinct sources and treatment requirements of greywater and blackwater is essential for implementing effective water recycling systems.
Key Differences Between Greywater and Blackwater
Greywater originates from sinks, showers, and laundry, containing fewer pathogens and organic waste than blackwater, which comes from toilets and kitchen drains. Greywater recycling involves treatment processes like filtration and disinfection to reuse water for irrigation or toilet flushing, while blackwater processing requires advanced methods such as anaerobic digestion or wastewater treatment plants to remove hazardous contaminants and pathogens. The primary difference lies in contamination levels and treatment complexity, with greywater offering more cost-effective recycling options compared to the intensive treatment blackwater demands.
Overview of Greywater Recycling Technologies
Greywater recycling technologies primarily involve treatment systems that capture wastewater from baths, sinks, and laundry for non-potable reuse, significantly reducing freshwater consumption. Key methods include membrane bioreactors, constructed wetlands, and filtration combined with disinfection processes such as UV or chlorination to remove contaminants and pathogens. Innovations in greywater recycling also emphasize energy efficiency and scalability for residential and commercial applications, supporting sustainable water management practices.
Blackwater Processing Methods and Innovations
Blackwater processing methods have advanced with the development of anaerobic digestion, membrane bioreactors, and nutrient recovery systems, enabling efficient treatment and resource extraction from sewage containing human waste. Innovations include microbial fuel cells that generate energy from organic matter and advanced oxidation processes that enhance contaminant breakdown. These technologies improve sustainability by reducing environmental pollution and producing valuable byproducts such as biogas and fertilizer.
Environmental Impact of Greywater Recycling
Greywater recycling significantly reduces freshwater consumption by reusing water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation or toilet flushing, lowering the demand on municipal water supplies. This process decreases the volume of wastewater discharged into sewage systems, reducing the burden on treatment plants and minimizing the risk of water pollution in aquatic ecosystems. By conserving water resources and cutting energy use associated with water treatment, greywater recycling plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable water management and mitigating environmental degradation.
Environmental Considerations for Blackwater Treatment
Blackwater processing involves treating sewage containing human waste, which requires advanced biological and chemical methods to remove pathogens and contaminants, preventing soil and water pollution. Proper blackwater treatment reduces the risk of waterborne diseases, protects aquatic ecosystems, and minimizes the emission of greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide during decomposition. Environmental considerations emphasize energy-efficient technologies, safe sludge disposal, and compliance with regulations to ensure sustainable wastewater management.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for Water Reuse
Greywater recycling systems must adhere to specific regulatory standards that focus on pathogen reduction, chemical contaminants, and safe reuse applications, often governed by local or national water authorities such as the EPA in the United States. Blackwater processing involves more stringent compliance requirements due to higher levels of contaminants, necessitating advanced treatment technologies to meet public health regulations before discharge or reuse. Ensuring compliance with these standards is critical for both systems to minimize environmental impact and safeguard human health in water reuse practices.
Economic Comparison: Costs and Savings
Greywater recycling systems generally incur lower installation and operational costs compared to blackwater processing due to simpler treatment requirements and reduced infrastructure needs. Savings from greywater reuse include decreased potable water demand and lower wastewater discharge fees, translating to significant utility cost reductions over time. Blackwater processing, while more expensive upfront, can provide value through advanced nutrient recovery and sludge management, potentially offsetting expenses in industrial or large-scale municipal applications.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Greywater recycling faces implementation challenges such as contamination risks, regulatory barriers, and limited public awareness, requiring advanced filtration systems and robust educational campaigns to ensure safety and acceptance. Blackwater processing involves more complex treatment due to high pathogen loads and nutrient concentrations, necessitating advanced technologies like membrane bioreactors and anaerobic digestion to effectively neutralize contaminants. Integrating decentralized treatment units and incentivizing infrastructure upgrades can address logistical hurdles in both systems, promoting sustainable water reuse and reducing environmental impact.
Future Trends in Water Recycling and Processing
Advancements in greywater recycling technologies emphasize onsite treatment systems that reduce freshwater demand and support sustainable urban water management. Blackwater processing innovations increasingly integrate resource recovery methods such as nutrient extraction and biogas production, promoting circular economy principles. Future trends highlight hybrid systems combining greywater and blackwater treatment to enhance overall efficiency and resilience in water recycling infrastructure.
Related Important Terms
Decentralized Greywater Systems
Decentralized greywater recycling systems treat wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry separately from blackwater, enabling efficient onsite reuse for irrigation and flushing, reducing overall freshwater demand by up to 50%. These systems minimize environmental impact by limiting blackwater generation, lowering treatment costs, and promoting sustainable water management in residential and commercial settings.
Dual Plumbing Retrofit
Dual plumbing retrofit systems enable efficient water management by separating greywater from blackwater, allowing for the recycling of greywater for non-potable uses like irrigation and toilet flushing. This approach reduces potable water demand and minimizes the volume of wastewater requiring blackwater processing, promoting sustainable water conservation in residential and commercial buildings.
Smart Greywater Sensors
Smart greywater sensors enhance greywater recycling by accurately detecting water quality parameters such as pH, turbidity, and organic load, enabling real-time monitoring and efficient reuse in irrigation and non-potable applications. Unlike blackwater processing, which requires advanced treatment for pathogens and contaminants, greywater recycling with smart sensors offers a cost-effective, environmentally sustainable solution to reduce freshwater consumption and wastewater discharge.
Greywater Heat Recovery
Greywater heat recovery systems capture thermal energy from household wastewater, significantly reducing energy consumption for water heating by recycling heat from showers and sinks. Unlike blackwater processing, which treats heavily contaminated wastewater, greywater recycling focuses on reclaiming and purifying lower-risk water streams, making heat recovery more efficient and environmentally sustainable.
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) Filtration
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) filtration enhances greywater recycling by combining biological treatment with membrane filtration, efficiently removing organic matter and pathogens for safe reuse. In blackwater processing, MBR systems provide advanced treatment that significantly reduces contaminants, enabling water recovery while adhering to strict regulatory standards for wastewater discharge.
Onsite Blackwater Digesters
Onsite blackwater digesters efficiently treat sewage by breaking down organic matter through anaerobic digestion, reducing pathogens and producing biogas for energy use. Compared to greywater recycling, which primarily reuses lightly contaminated water from sinks and showers, blackwater processing addresses higher-strength wastewater with complex contaminants, enabling more comprehensive onsite wastewater management.
Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactor (AnMBR)
Greywater recycling utilizing Anaerobic Membrane Bioreactors (AnMBRs) offers efficient organic matter degradation and biogas production, reducing energy consumption compared to conventional blackwater processing. AnMBRs provide high-quality treated water with lower sludge output and enhanced pathogen removal, making them a sustainable choice for decentralizing wastewater management.
Zero-Liquid Discharge (ZLD) Systems
Greywater recycling systems treat and reuse relatively clean wastewater from sinks, showers, and laundry to reduce freshwater consumption, while blackwater processing tackles heavily contaminated sewage requiring advanced treatment technologies. Zero-Liquid Discharge (ZLD) systems integrate multiple treatment stages including membrane filtration, evaporation, and crystallization to eliminate liquid waste entirely, making them critical for sustainable water management in both greywater and blackwater contexts.
Nutrient Recovery from Blackwater
Blackwater processing facilitates higher nutrient recovery, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus, compared to greywater recycling due to the concentrated presence of human waste. Advanced treatment technologies like anaerobic digestion and struvite precipitation in blackwater systems enable efficient extraction and reuse of these nutrients for agricultural fertilizers.
IoT Greywater Monitoring
IoT greywater monitoring systems enhance water conservation by providing real-time data on greywater quality, enabling efficient recycling for non-potable uses and reducing reliance on blackwater processing. Advanced sensors and AI algorithms track contaminants and flow rates, optimizing greywater reuse and minimizing environmental impact compared to traditional blackwater treatment methods.
Greywater Recycling vs Blackwater Processing Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com