An Admin Clerk primarily handles routine office tasks such as data entry, filing, and maintaining records, ensuring smooth daily operations. In contrast, an Automation Specialist focuses on developing and implementing automated systems to streamline workflows and increase efficiency within administrative processes. The shift from manual administration to automation technology highlights the growing importance of technical skills in modern office management.
Table of Comparison
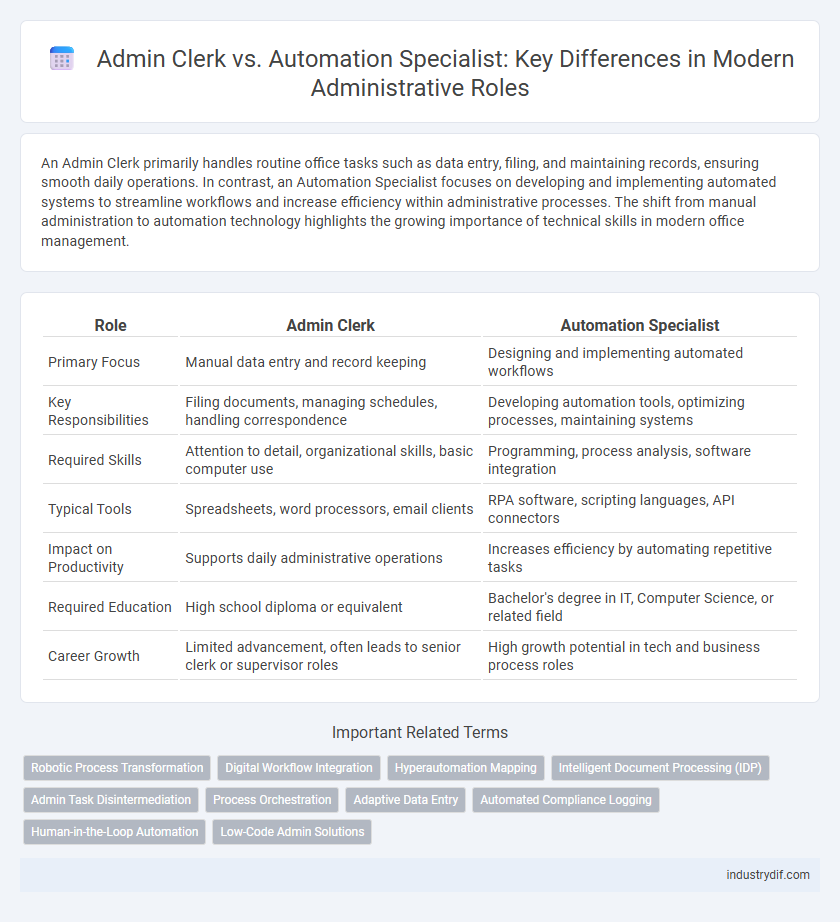
| Role | Admin Clerk | Automation Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Manual data entry and record keeping | Designing and implementing automated workflows |
| Key Responsibilities | Filing documents, managing schedules, handling correspondence | Developing automation tools, optimizing processes, maintaining systems |
| Required Skills | Attention to detail, organizational skills, basic computer use | Programming, process analysis, software integration |
| Typical Tools | Spreadsheets, word processors, email clients | RPA software, scripting languages, API connectors |
| Impact on Productivity | Supports daily administrative operations | Increases efficiency by automating repetitive tasks |
| Required Education | High school diploma or equivalent | Bachelor's degree in IT, Computer Science, or related field |
| Career Growth | Limited advancement, often leads to senior clerk or supervisor roles | High growth potential in tech and business process roles |
Job Role Overview: Admin Clerk vs Automation Specialist
Admin Clerks handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, and record management, ensuring smooth office operations and accurate documentation. Automation Specialists design, implement, and maintain automated systems to optimize workflows and increase efficiency by reducing manual processes. The key distinction lies in the Admin Clerk's focus on traditional administrative duties versus the Automation Specialist's role in leveraging technology to streamline and innovate business functions.
Core Responsibilities and Duties
An Admin Clerk primarily manages clerical tasks such as data entry, filing, scheduling, and maintaining office records to ensure smooth daily operations. An Automation Specialist focuses on designing, developing, and implementing automated systems and workflows to optimize business processes and reduce manual effort. While the Admin Clerk supports administrative efficiency, the Automation Specialist drives technological innovation within administrative functions.
Essential Skills and Competencies
Admin Clerks excel in organizational skills, data entry accuracy, and effective communication, ensuring smooth office operations and record management. Automation Specialists possess strong programming knowledge, process analysis capabilities, and expertise in automation tools to streamline workflows and enhance productivity. Both roles require problem-solving abilities, but Automation Specialists demand advanced technical proficiency to implement and maintain automated systems efficiently.
Required Educational Background
An Admin Clerk typically requires a high school diploma or equivalent, with on-the-job training focused on clerical skills, data entry, and office administration. In contrast, an Automation Specialist generally needs a bachelor's degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field, complemented by expertise in programming, robotics, and automation software. Certification courses in automation platforms or programming languages often enhance the qualifications for Automation Specialist roles.
Tools and Technologies Used
Admin Clerks primarily utilize traditional office software such as Microsoft Office Suite, database management systems, and basic communication tools to manage records and support administrative tasks. Automation Specialists leverage advanced technologies including robotic process automation (RPA) platforms, scripting languages like Python, and AI-driven workflow automation tools to streamline operations and improve efficiency. While Admin Clerks focus on manual data entry and document management, Automation Specialists design and implement systems that reduce repetitive tasks through intelligent automation solutions.
Workflow and Process Differences
An Admin Clerk handles routine tasks such as data entry, document management, and scheduling, relying heavily on manual processes to maintain organizational workflows. In contrast, an Automation Specialist designs and implements automated systems to streamline these workflows, reducing manual intervention and increasing efficiency. The shift from manual administration to automated solutions transforms process management by integrating technology-driven tools that optimize time and resource allocation.
Impact on Organizational Efficiency
Admin Clerks handle routine data entry, document management, and scheduling to maintain smooth daily operations, ensuring accurate record-keeping and timely communication within departments. Automation Specialists design and implement software solutions that streamline repetitive tasks, significantly reducing manual errors and accelerating workflow processes. Integrating automation specialists into administrative functions can exponentially enhance organizational efficiency by minimizing time-consuming tasks and optimizing resource allocation.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
Admin Clerks typically follow a career path rooted in organizational support, advancing to supervisory roles or specialized administrative positions by honing skills in record keeping, scheduling, and office management. Automation Specialists pursue a trajectory focused on technology and process optimization, progressing to roles such as automation engineer or IT manager by developing expertise in software, scripting, and system integration. The Automation Specialist pathway generally offers faster advancement opportunities and higher earning potential due to the increasing demand for automation in businesses.
Salary and Job Market Trends
Admin Clerks typically earn between $30,000 and $45,000 annually, reflecting steady demand in traditional office environments. Automation Specialists command higher salaries, ranging from $70,000 to $100,000, driven by rapid growth in technology integration across industries. The job market trend favors Automation Specialists due to increasing automation needs, while demand for Admin Clerks remains stable but with limited growth.
Future Outlook: Human Roles vs Automation
The future outlook for administrative roles suggests a gradual shift where Automation Specialists increasingly handle repetitive and data-intensive tasks, enhancing efficiency through AI and robotic process automation. Admin Clerks will continue to play a crucial role in managing complex interpersonal communications, decision-making, and exceptions that require human judgment. Organizations are likely to blend human roles with automation, emphasizing collaboration to optimize administrative workflows and maintain adaptability in dynamic business environments.
Related Important Terms
Robotic Process Transformation
Admin Clerks handle routine data entry and document management, while Automation Specialists design and implement Robotic Process Automation (RPA) systems to streamline administrative workflows and reduce manual tasks. Robotic Process Transformation increases operational efficiency by automating repetitive functions traditionally performed by Admin Clerks, enabling organizations to optimize resource allocation and improve accuracy.
Digital Workflow Integration
Admin Clerks traditionally manage manual documentation and data entry tasks, while Automation Specialists design and implement digital workflow integrations using tools like RPA, BPM software, and AI to streamline processes and reduce human error. Automated solutions enhance operational efficiency by enabling real-time data synchronization, improving accuracy, and supporting seamless communication across digital platforms within administrative functions.
Hyperautomation Mapping
Admin Clerks handle routine data entry and document management, while Automation Specialists design and implement hyperautomation mapping to streamline complex workflows using AI and RPA technologies. Hyperautomation mapping enables Automation Specialists to identify inefficiencies and integrate intelligent tools for enhanced operational efficiency.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
An Admin Clerk primarily handles manual data entry and basic document management, while an Automation Specialist leverages Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technologies to automate the extraction, classification, and validation of data from complex documents. IDP enhances operational efficiency by reducing errors, accelerating workflows, and enabling seamless integration with enterprise systems, transforming traditional administrative tasks into streamlined digital processes.
Admin Task Disintermediation
Admin Clerks typically manage routine data entry, document processing, and scheduling while Automation Specialists design and implement software solutions to streamline these administrative tasks by reducing manual intervention. Task disintermediation in administration significantly lowers human error and increases efficiency by automating repetitive workflows, ultimately transforming traditional clerical roles.
Process Orchestration
An Admin Clerk primarily manages routine documentation and supports basic workflow tasks, whereas an Automation Specialist designs and implements process orchestration systems to streamline complex business operations. Process orchestration leverages advanced automation tools like BPM (Business Process Management) software to integrate cross-functional tasks, significantly enhancing efficiency beyond manual administrative workflows.
Adaptive Data Entry
Admin Clerks primarily handle routine adaptive data entry tasks through manual input and verification, ensuring accuracy in varied data formats. Automation Specialists develop and implement adaptive data entry systems using machine learning and robotic process automation to optimize efficiency and reduce human error.
Automated Compliance Logging
Admin Clerks typically manage manual entry and tracking of compliance records, often leading to slower processes and higher error rates. Automation Specialists implement automated compliance logging systems that enhance accuracy, reduce administrative overhead, and enable real-time regulatory reporting.
Human-in-the-Loop Automation
Admin Clerks manage routine office tasks and data entry while Automation Specialists design and oversee automated workflows that integrate Human-in-the-Loop processes to enhance accuracy and decision-making. Human-in-the-Loop automation enables real-time human intervention in automated systems, optimizing efficiency and reducing errors in administrative operations.
Low-Code Admin Solutions
Admin Clerks manage routine office tasks and data entry, ensuring organizational efficiency through manual processes. Automation Specialists leverage low-code platforms to design and implement automated workflows, significantly reducing repetitive tasks and enhancing productivity in administrative operations.
Admin Clerk vs Automation Specialist Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com