Clerical staff handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, ensuring smooth daily operations. Automation integration specialists design and implement automated systems to streamline these tasks, improving accuracy and efficiency. Combining human oversight with automation technology enhances productivity and reduces operational errors in administrative environments.
Table of Comparison
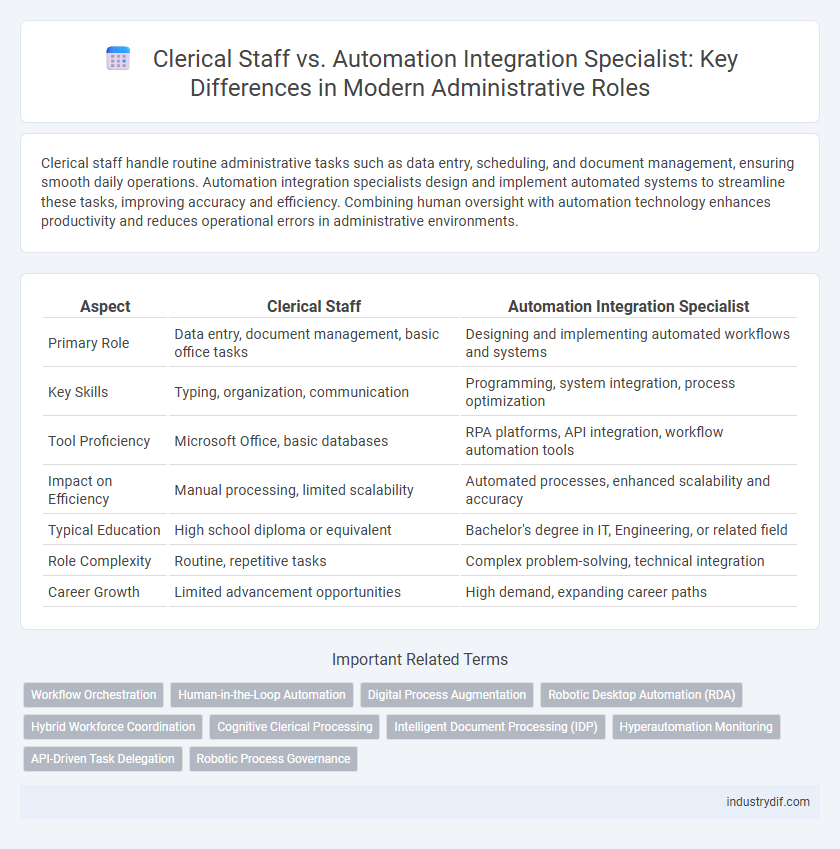
| Aspect | Clerical Staff | Automation Integration Specialist |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Data entry, document management, basic office tasks | Designing and implementing automated workflows and systems |
| Key Skills | Typing, organization, communication | Programming, system integration, process optimization |
| Tool Proficiency | Microsoft Office, basic databases | RPA platforms, API integration, workflow automation tools |
| Impact on Efficiency | Manual processing, limited scalability | Automated processes, enhanced scalability and accuracy |
| Typical Education | High school diploma or equivalent | Bachelor's degree in IT, Engineering, or related field |
| Role Complexity | Routine, repetitive tasks | Complex problem-solving, technical integration |
| Career Growth | Limited advancement opportunities | High demand, expanding career paths |
Defining Clerical Staff Roles in Modern Administration
Clerical staff in modern administration perform essential tasks such as data entry, file management, and communication coordination that ensure smooth office operations. Their roles demand strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and proficiency with office software to support various departments effectively. As administrative environments evolve, clerical staff increasingly collaborate with automation integration specialists to enhance workflow efficiency and reduce manual workloads.
What is an Automation Integration Specialist?
An Automation Integration Specialist designs and implements automated systems to streamline business processes, reducing manual tasks typically performed by clerical staff. They analyze existing workflows, develop integration solutions using software tools, and ensure seamless communication between disparate applications to increase operational efficiency. Mastery in technologies like robotic process automation (RPA), API integration, and workflow management platforms defines their expertise in transforming administrative functions.
Key Responsibilities: Clerical Staff vs Automation Integration Specialist
Clerical staff primarily manage routine administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, scheduling, and handling correspondence to ensure smooth office operations. Automation Integration Specialists focus on designing, implementing, and maintaining automated systems that optimize workflows, reduce manual processes, and enhance operational efficiency. Their responsibilities include programming automation tools, troubleshooting integration issues, and collaborating with IT teams to align automation solutions with business needs.
Required Skills and Training Comparison
Clerical staff require strong organizational skills, proficiency in office software like Microsoft Office Suite, and basic communication abilities, typically gained through high school diplomas or entry-level administrative training. Automation Integration Specialists need advanced technical expertise in software development, understanding of automation tools like UiPath or Blue Prism, and skills in systems integration and programming, often supported by degrees in computer science or specialized certifications. Continuous training in emerging technologies is critical for specialists, while clerical staff benefit from ongoing development in office management and customer service techniques.
Efficiency and Productivity: Manual vs Automated Processes
Clerical staff perform essential manual tasks such as data entry, filing, and scheduling, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error, impacting overall efficiency. Automation Integration Specialists implement automated systems that streamline workflows, reduce repetitive tasks, and increase accuracy, resulting in significant productivity gains. The integration of automation technologies transforms traditional administrative processes, enabling faster data processing and improved resource allocation.
Impact on Operational Costs and Budgeting
Clerical staff typically incur higher operational costs due to salaries, benefits, and human resource management, while Automation Integration Specialists focus on reducing long-term expenses by implementing automated systems that streamline workflows and enhance efficiency. Budgeting for clerical roles often requires allocating funds for training and turnover, whereas automation specialists involve upfront investments in technology with potential significant savings on repetitive tasks. The strategic shift from clerical staff to automation integration can optimize budget allocation by minimizing ongoing labor costs and improving process scalability.
Adaptability in Evolving Work Environments
Clerical staff demonstrate strong adaptability by efficiently managing routine administrative tasks and quickly adjusting to new office procedures and software updates. Automation Integration Specialists exhibit advanced adaptability through their expertise in implementing and optimizing automated systems, ensuring seamless integration with existing workflows in dynamic business environments. Both roles require continuous learning and flexibility to maintain productivity and support organizational growth amid rapidly evolving technological landscapes.
Collaboration Between Clerical and Automation Teams
Clerical staff and automation integration specialists collaborate to streamline administrative workflows by combining human accuracy with advanced technology. By leveraging clerical expertise in data management alongside automation specialists' proficiency in software integration, organizations enhance efficiency and reduce errors. This synergy supports seamless transition from manual processes to automated systems, optimizing operational productivity.
Future Trends: Administrative Workforce Transformation
Clerical staff roles are evolving with the rise of automation integration specialists who focus on implementing AI-driven tools to streamline administrative workflows. Future trends indicate a shift toward hybrid teams where human oversight and automated processes coexist, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Organizations investing in automation are re-skilling clerical employees to adapt, driving transformation in the administrative workforce landscape.
Choosing the Right Fit for Your Organization
Selecting between Clerical Staff and Automation Integration Specialists hinges on organizational needs for efficiency and technological advancement. Clerical Staff excel in managing routine administrative tasks and maintaining accurate records, essential for day-to-day operations. Automation Integration Specialists bring expertise in deploying software solutions to streamline workflows, reducing manual labor and increasing productivity through advanced system integration.
Related Important Terms
Workflow Orchestration
Clerical staff manage routine administrative tasks through manual data entry and document processing, ensuring accuracy in workflow orchestration within traditional office environments. Automation Integration Specialists design and implement automated systems that streamline workflow orchestration by integrating software tools, reducing manual intervention and increasing operational efficiency.
Human-in-the-Loop Automation
Clerical staff play a crucial role in Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) automation by managing exceptions and validating AI outputs to ensure accuracy and compliance in administrative workflows. Automation Integration Specialists design and implement HITL systems that blend human judgment with AI efficiency, optimizing process automation while maintaining oversight and quality control.
Digital Process Augmentation
Clerical staff provide essential administrative support through routine tasks such as data entry, filing, and customer communication, ensuring organizational efficiency. Automation Integration Specialists enhance digital process augmentation by designing and implementing automated workflows, increasing productivity and reducing human error.
Robotic Desktop Automation (RDA)
Clerical staff handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, document management, and scheduling, while Automation Integration Specialists focus on designing and implementing Robotic Desktop Automation (RDA) solutions to streamline these processes, enhance accuracy, and reduce operational costs. The shift towards RDA enables organizations to optimize workflow efficiency by automating repetitive clerical functions, freeing human resources for higher-value strategic activities.
Hybrid Workforce Coordination
Clerical Staff play a vital role in managing day-to-day administrative tasks, ensuring smooth communication and document handling within hybrid work environments. Automation Integration Specialists optimize operational efficiency by implementing and managing technology solutions that harmonize remote and on-site workflows in hybrid workforce coordination.
Cognitive Clerical Processing
Clerical staff traditionally handle cognitive clerical processing tasks such as data entry, document verification, and routine information management, relying heavily on manual accuracy and attention to detail. Automation Integration Specialists enhance these processes by designing and implementing automated systems that optimize workflow efficiency, reduce errors, and enable scalable cognitive task handling through AI and machine learning tools.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Clerical staff traditionally manage manual data entry and document handling, but Automation Integration Specialists leverage Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technologies to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and enhance efficiency. Implementing IDP enables organizations to automate extraction, classification, and validation of data from complex documents, transforming administrative operations and reducing reliance on manual clerical tasks.
Hyperautomation Monitoring
Clerical staff traditionally handle routine data entry, document management, and scheduling tasks, but Hyperautomation Monitoring demands expertise in integrating AI-driven tools to streamline and optimize these processes. Automation Integration Specialists leverage advanced software analytics and robotic process automation (RPA) to continuously monitor, improve, and maintain hyperautomation workflows, ensuring maximum operational efficiency and reduced manual intervention.
API-Driven Task Delegation
Clerical staff primarily handle repetitive administrative tasks such as data entry and document management, often requiring manual input and oversight. Automation Integration Specialists leverage API-driven task delegation to streamline workflows, enabling seamless communication between software systems and reducing human error while enhancing operational efficiency.
Robotic Process Governance
Clerical staff primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry and document management, whereas Automation Integration Specialists focus on implementing and overseeing robotic process governance to ensure efficient, compliant automation workflows. Effective robotic process governance involves monitoring, managing, and optimizing automated systems to maintain accuracy, security, and regulatory adherence within administrative operations.
Clerical Staff vs Automation Integration Specialist Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com