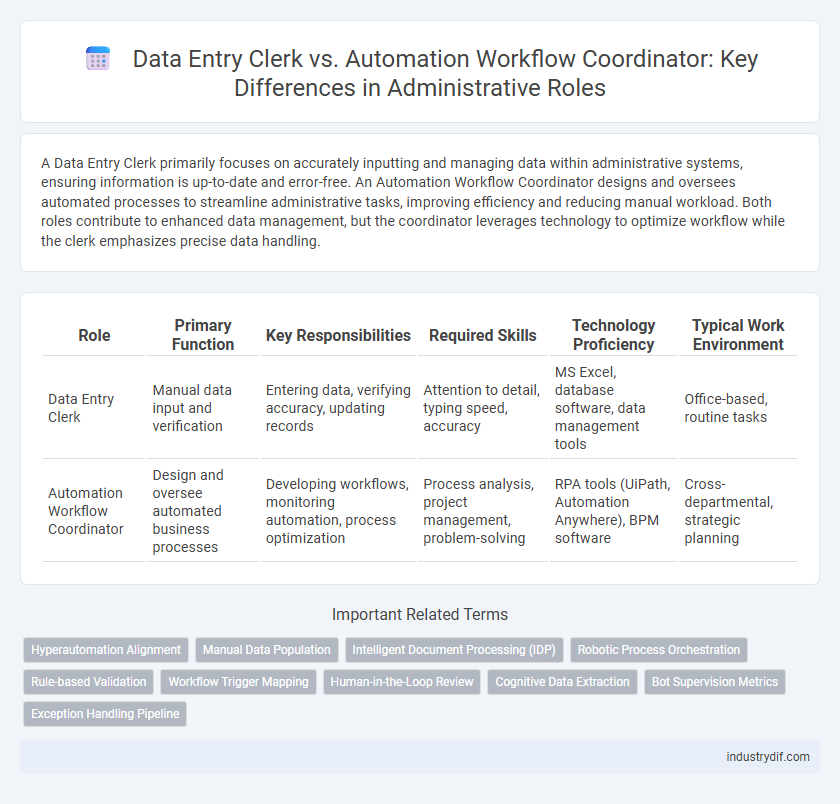
A Data Entry Clerk primarily focuses on accurately inputting and managing data within administrative systems, ensuring information is up-to-date and error-free. An Automation Workflow Coordinator designs and oversees automated processes to streamline administrative tasks, improving efficiency and reducing manual workload. Both roles contribute to enhanced data management, but the coordinator leverages technology to optimize workflow while the clerk emphasizes precise data handling.
Table of Comparison
| Role | Primary Function | Key Responsibilities | Required Skills | Technology Proficiency | Typical Work Environment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Entry Clerk | Manual data input and verification | Entering data, verifying accuracy, updating records | Attention to detail, typing speed, accuracy | MS Excel, database software, data management tools | Office-based, routine tasks |
| Automation Workflow Coordinator | Design and oversee automated business processes | Developing workflows, monitoring automation, process optimization | Process analysis, project management, problem-solving | RPA tools (UiPath, Automation Anywhere), BPM software | Cross-departmental, strategic planning |
Role Overview: Data Entry Clerk vs Automation Workflow Coordinator
A Data Entry Clerk primarily focuses on accurately inputting and updating information into computer systems, ensuring data integrity and consistency. In contrast, an Automation Workflow Coordinator designs, monitors, and manages automated processes to streamline administrative tasks and improve operational efficiency. While the Data Entry Clerk handles manual data processing, the Automation Workflow Coordinator leverages technology to reduce repetitive tasks and enhance workflow productivity.
Key Responsibilities in Administrative Operations
Data Entry Clerks are responsible for accurately inputting, updating, and maintaining data within administrative systems to ensure information integrity. Automation Workflow Coordinators design, implement, and monitor automated processes to streamline administrative tasks and enhance operational efficiency. Both roles are crucial for maintaining data accuracy and optimizing workflow in administrative operations, with the former focusing on manual data handling and the latter on process automation.
Required Technical Skills and Competencies
Data Entry Clerks require proficiency in data management software, strong typing skills, and accuracy in handling large volumes of information. Automation Workflow Coordinators must have expertise in workflow automation tools, programming languages such as Python or SQL, and skills in process optimization and system integration. Both roles demand attention to detail, but Automation Workflow Coordinators also need advanced problem-solving abilities and knowledge of business process automation frameworks.
Workflow Processes: Manual vs Automated Approaches
Data Entry Clerks primarily manage workflow processes through manual data input, often relying on repetitive tasks to ensure accuracy and completeness. Automation Workflow Coordinators design and maintain automated systems that streamline complex workflows, reducing errors and increasing efficiency by integrating software tools and robotic process automation (RPA). Manual approaches depend heavily on human intervention, while automated workflows leverage technology to optimize process speed and consistency.
Accuracy and Error Reduction: Comparative Analysis
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on manual input accuracy by verifying information against source documents, ensuring minimal discrepancies during data transcription. Automation Workflow Coordinators implement and monitor automated systems designed to reduce human errors by streamlining repetitive data handling tasks and validating data through programmed checks. Comparative analysis indicates that while Data Entry Clerks rely on individual precision, Automation Workflow Coordinators enhance overall accuracy through technology-driven error reduction and process optimization.
Impact on Productivity and Efficiency
Data Entry Clerks perform manual input tasks that ensure data accuracy but can be time-consuming and prone to human error, limiting overall productivity. Automation Workflow Coordinators design and manage automated processes that streamline repetitive tasks, significantly increasing efficiency and allowing staff to focus on higher-value activities. Implementing automation workflows reduces processing time by up to 70%, enhancing organizational productivity and minimizing operational costs.
Adaptability to Technological Advancements
Data Entry Clerks primarily rely on manual input methods, which limits their adaptability to rapidly evolving software and automation tools in administrative workflows. Automation Workflow Coordinators possess advanced skills in configuring and optimizing automated processes using technologies like RPA (Robotic Process Automation) and AI-driven platforms, enabling seamless integration with new systems. Their proficiency in adapting to cutting-edge technologies enhances operational efficiency and supports continuous process improvement in dynamic business environments.
Career Pathways and Opportunities
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on manual input and verification of information, offering foundational skills valuable for transitioning into roles involving data management and office administration. Automation Workflow Coordinators oversee automated processes, requiring expertise in software tools and process optimization, which opens pathways to advanced positions like workflow analysts or IT project managers. Career progression from data entry to automation roles reflects growing demand for technical proficiency and strategic process management in administrative careers.
Training and Certification Requirements
Data Entry Clerks typically require basic computer skills and on-the-job training, often supplemented by certifications such as Microsoft Office Specialist (MOS) to enhance proficiency. Automation Workflow Coordinators need advanced knowledge of process automation tools like UiPath, Blue Prism, or Automation Anywhere, with certifications such as Certified RPA Developer or Business Process Automation Specialist proving essential. Employers prioritize candidates with formal training in workflow design, scripting languages, and project management to ensure efficient automation implementation.
Future Trends in Administrative Workflows
Data Entry Clerks are increasingly supplemented by Automation Workflow Coordinators who design and manage intelligent systems to streamline data processing, reducing manual input errors and boosting efficiency. Emerging technologies like AI-driven robotic process automation (RPA) are transforming administrative workflows by enabling real-time data validation and adaptive task management. Future trends emphasize upskilling in automation tools and analytics, positioning coordinators as key drivers in digital transformation across administrative functions.
Related Important Terms
Hyperautomation Alignment
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input of information, whereas Automation Workflow Coordinators design and oversee hyperautomation processes, integrating AI and RPA tools to streamline administrative tasks. Emphasizing hyperautomation alignment, Workflow Coordinators enable scalable efficiency improvements by reducing human error and accelerating data processing cycles.
Manual Data Population
Data Entry Clerks specialize in manual data population, ensuring accurate and timely input of information into databases, which is essential for maintaining data integrity. Automation Workflow Coordinators focus on designing and overseeing automated processes that reduce manual entry, improving efficiency while minimizing human error in administrative tasks.
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Data Entry Clerks manually input and verify information, often facing limitations in handling large volumes and complex documents, whereas Automation Workflow Coordinators leverage Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technology to streamline data extraction, classification, and validation, significantly enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency. Implementing IDP enables organizations to reduce human error, accelerate processing times, and optimize administrative workflows by automating repetitive data handling tasks.
Robotic Process Orchestration
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input tasks, while Automation Workflow Coordinators design and manage Robotic Process Orchestration systems to streamline and automate repetitive administrative processes. Leveraging RPA technology, Automation Workflow Coordinators enhance operational efficiency and accuracy far beyond traditional data entry roles.
Rule-based Validation
Data Entry Clerks manually input and verify data, relying on basic rule-based validation to minimize errors, whereas Automation Workflow Coordinators design and manage automated systems that apply advanced rule-based validation to streamline data accuracy and consistency. Automation enhances efficiency by reducing human error and ensuring compliance with complex validation rules across administrative processes.
Workflow Trigger Mapping
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle manual input of information, whereas Automation Workflow Coordinators design and manage workflow trigger mapping to automate data processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Automation Workflow Coordinators utilize trigger mapping to link specific events with automated actions, streamlining administrative tasks and optimizing operational workflows.
Human-in-the-Loop Review
Data Entry Clerks manually input, verify, and correct data to ensure accuracy, playing a critical role in maintaining data integrity through human oversight. Automation Workflow Coordinators design and oversee automated systems that incorporate human-in-the-loop review processes, ensuring that exceptions and complex cases receive expert intervention for optimal workflow efficiency.
Cognitive Data Extraction
A Data Entry Clerk primarily performs manual input of information into databases, while an Automation Workflow Coordinator leverages cognitive data extraction technologies to streamline data processing and reduce errors. Utilizing AI-driven tools, the Automation Workflow Coordinator enhances data accuracy and accelerates organizational efficiency by automating repetitive administrative tasks.
Bot Supervision Metrics
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on manual input accuracy and speed, while Automation Workflow Coordinators monitor bot supervision metrics such as error rates, task completion times, and exception handling efficiency. Effective bot supervision ensures seamless automation performance, reducing downtime and improving data processing reliability within administrative workflows.
Exception Handling Pipeline
Data Entry Clerks manually input and verify data, often encountering and resolving exceptions on a case-by-case basis, while Automation Workflow Coordinators design and manage exception handling pipelines that automatically detect, route, and remediate data discrepancies to ensure seamless process continuity. Implementing automated exception handling pipelines reduces human error, accelerates resolution times, and enhances overall data integrity within administrative workflows.
Data Entry Clerk vs Automation Workflow Coordinator Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com