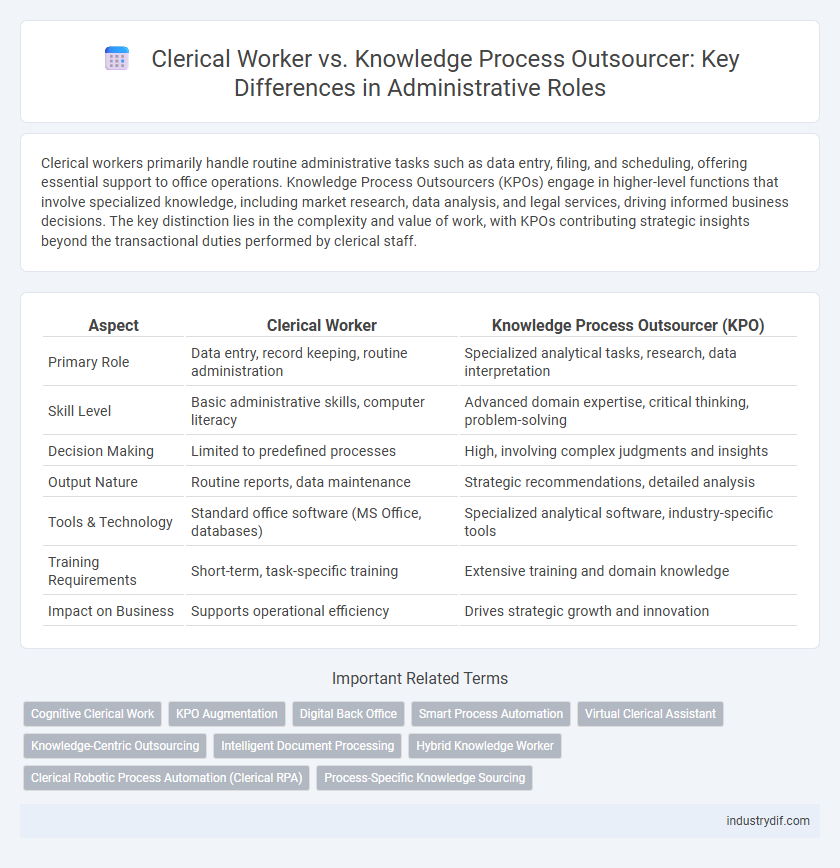
Clerical workers primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, and scheduling, offering essential support to office operations. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) engage in higher-level functions that involve specialized knowledge, including market research, data analysis, and legal services, driving informed business decisions. The key distinction lies in the complexity and value of work, with KPOs contributing strategic insights beyond the transactional duties performed by clerical staff.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clerical Worker | Knowledge Process Outsourcer (KPO) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Data entry, record keeping, routine administration | Specialized analytical tasks, research, data interpretation |
| Skill Level | Basic administrative skills, computer literacy | Advanced domain expertise, critical thinking, problem-solving |
| Decision Making | Limited to predefined processes | High, involving complex judgments and insights |
| Output Nature | Routine reports, data maintenance | Strategic recommendations, detailed analysis |
| Tools & Technology | Standard office software (MS Office, databases) | Specialized analytical software, industry-specific tools |
| Training Requirements | Short-term, task-specific training | Extensive training and domain knowledge |
| Impact on Business | Supports operational efficiency | Drives strategic growth and innovation |
Defining Clerical Workers in the Administrative Sector
Clerical workers in the administrative sector perform routine office tasks including data entry, filing, and managing correspondence to ensure smooth daily operations. Their role typically involves handling physical or digital records, scheduling appointments, and supporting communication between departments. This contrasts with knowledge process outsourcers who engage in more analytical and specialized tasks such as data analysis and decision support within business processes.
What is Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO)?
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) involves delegating high-level, knowledge-intensive tasks to external service providers, focusing on expertise in areas such as data analysis, research, and specialized consulting. Unlike clerical work that handles routine administrative tasks, KPO requires advanced analytical skills, domain-specific knowledge, and decision-making capabilities. Organizations leverage KPO to gain access to specialized intellectual resources, enhance operational efficiency, and improve business outcomes through strategic support activities.
Key Roles and Responsibilities: Clerical Workers vs KPO Professionals
Clerical workers primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, scheduling, and basic correspondence, ensuring smooth office operations and document management. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPO) professionals engage in specialized activities requiring analytical skills, critical thinking, and domain expertise, including data analysis, research, financial modeling, and business intelligence. The key distinction lies in the complexity and value of tasks, with clerical workers focusing on operational support and KPO professionals driving strategic decision-making through advanced knowledge work.
Skill Sets: Routine Tasks vs Specialized Expertise
Clerical workers primarily handle routine tasks such as data entry, filing, and basic record management that require attention to detail and organizational skills. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) demand specialized expertise in areas like data analysis, market research, and legal services, leveraging advanced analytical and critical thinking abilities. The distinction in skill sets highlights the transition from repetitive clerical functions to value-driven, knowledge-intensive processes.
Workflow Automation: Impact on Clerical and KPO Roles
Workflow automation significantly transforms clerical worker roles by reducing repetitive tasks such as data entry, allowing a shift toward more analytical and supervisory responsibilities. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) benefit from automation through enhanced data processing accuracy and faster decision-making, enabling greater focus on complex problem-solving and strategic analysis. This shift in workflow dynamics fosters increased efficiency and value creation within both clerical and KPO environments.
Cost Efficiency and Productivity Considerations
Clerical workers typically handle routine administrative tasks with lower skill requirements, resulting in relatively lower labor costs but limited scalability and productivity gains. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) provide specialized, high-value services such as data analysis and research, which enhance productivity through advanced expertise but often involve higher initial costs. Evaluating cost efficiency involves balancing the predictable expenses of clerical roles against the potential long-term returns from increased accuracy, faster turnaround, and value-added insights delivered by KPOs.
Training and Educational Requirements
Clerical workers typically require a high school diploma with basic training in office software, data entry, and administrative procedures, emphasizing organizational skills and attention to detail. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) demand higher educational qualifications, often a bachelor's degree or specialized certification in fields such as finance, engineering, or research, alongside advanced analytical and domain-specific training. Training for KPOs focuses heavily on critical thinking, data analysis, and subject matter expertise, differentiating it from the routine administrative skill set required for clerical roles.
Job Outlook: Trends in Administrative Employment
Clerical worker roles are expected to decline due to automation and digital record-keeping, with employment projected to decrease by 7% over the next decade. Knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) positions, however, are growing rapidly as companies seek specialized expertise in data analysis, legal services, and financial research. This shift highlights an increasing demand for advanced cognitive skills and domain-specific knowledge within the administrative employment sector.
Benefits and Challenges of KPO in Administration
Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) in administration offer advanced expertise and analytical capabilities that surpass traditional clerical duties, enhancing strategic decision-making and process efficiency. Challenges include the need for highly skilled personnel, increased costs, and the complexity of managing knowledge-intensive tasks remotely. Benefits such as improved innovation, data-driven insights, and scalability make KPOs a valuable asset for organizations seeking to optimize administrative functions.
Choosing the Right Model: When to Use Clerical Workers or KPO
Clerical workers are ideal for routine administrative tasks such as data entry, scheduling, and document management, offering cost-effective solutions for high-volume, repetitive work. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) provide specialized expertise in areas like research, analytics, and complex problem-solving, suitable for projects requiring strategic insight and decision-making. Organizations should choose clerical workers for standardized, operational efficiency and KPOs when advanced knowledge, analytical skills, and industry-specific expertise are critical for business outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Cognitive Clerical Work
Cognitive clerical work in knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) involves higher-level analytical tasks such as data interpretation and decision-making, contrasting with traditional clerical work that focuses primarily on routine administrative duties like data entry and record maintenance. KPO professionals leverage advanced cognitive skills and domain expertise to enhance organizational efficiency, while clerical workers typically handle standardized processes within administrative support.
KPO Augmentation
Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) provide specialized expertise and strategic analysis beyond routine clerical tasks, enhancing decision-making through advanced data interpretation and research capabilities. KPO augmentation streamlines complex workflows by integrating domain-specific knowledge, thus increasing organizational efficiency and reducing time spent on administrative processes.
Digital Back Office
Clerical workers in the digital back office typically handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, document management, and scheduling, ensuring organizational efficiency through standardized processes. Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) perform higher-level functions like data analysis, research, and decision support, leveraging specialized expertise and advanced technologies to drive strategic business outcomes.
Smart Process Automation
Clerical workers primarily handle routine administrative tasks such as data entry, filing, and scheduling, whereas Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) focus on specialized, information-intensive processes requiring analytical skills and domain expertise. Smart Process Automation (SPA) enhances KPO efficiency by integrating artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics to automate complex workflows, thereby reducing manual errors and accelerating decision-making cycles.
Virtual Clerical Assistant
A Virtual Clerical Assistant streamlines administrative tasks such as scheduling, data entry, and email management, enhancing efficiency compared to traditional clerical workers. In contrast to Knowledge Process Outsourcers who handle specialized, value-driven tasks, virtual clerical assistants focus on routine office functions with remote accessibility and scalability.
Knowledge-Centric Outsourcing
Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO) involves outsourcing specialized tasks that require advanced analytical skills and subject matter expertise, unlike traditional clerical work which focuses on routine administrative duties such as data entry and record keeping. KPO enhances business efficiency by leveraging knowledge-centric outsourcing to deliver high-value services like market research, data analysis, and financial consultancy, enabling companies to access expert insights without expanding in-house teams.
Intelligent Document Processing
Clerical workers handle routine data entry and document management, whereas Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) leverage Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) technologies to automate complex data extraction, classification, and validation tasks. IDP enhances KPO efficiency by using artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to streamline administrative workflows and reduce manual errors.
Hybrid Knowledge Worker
Hybrid knowledge workers combine the routine administrative tasks of clerical workers with the analytical and decision-making responsibilities typical of knowledge process outsourcers, enhancing operational efficiency and strategic output. This integrated role leverages advanced digital tools and domain expertise to optimize workflow automation and data-driven insights in administrative functions.
Clerical Robotic Process Automation (Clerical RPA)
Clerical Robotic Process Automation (Clerical RPA) streamlines routine administrative tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and document management, significantly reducing manual errors and operational costs compared to traditional clerical work. By automating repetitive workflows, Clerical RPA enhances efficiency, enabling businesses to reallocate human resources towards higher-value knowledge process outsourcing (KPO) activities that require analytical and decision-making skills.
Process-Specific Knowledge Sourcing
Clerical workers handle routine, well-defined administrative tasks, whereas Knowledge Process Outsourcers (KPOs) specialize in sourcing and analyzing complex, process-specific knowledge to enhance decision-making and strategic initiatives. KPOs leverage advanced expertise and domain-specific insights to drive innovation and efficiency beyond traditional data entry and record-keeping functions.
Clerical Worker vs Knowledge Process Outsourcer Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com