Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting and updating information into databases, ensuring that records are complete and correctly formatted. Data Integrity Analysts concentrate on validating data quality and consistency across systems, identifying discrepancies, and implementing protocols to maintain data accuracy. Both roles are crucial for maintaining reliable administrative records but differ in scope, with clerks handling the initial data input and analysts overseeing the integrity of data over time.
Table of Comparison
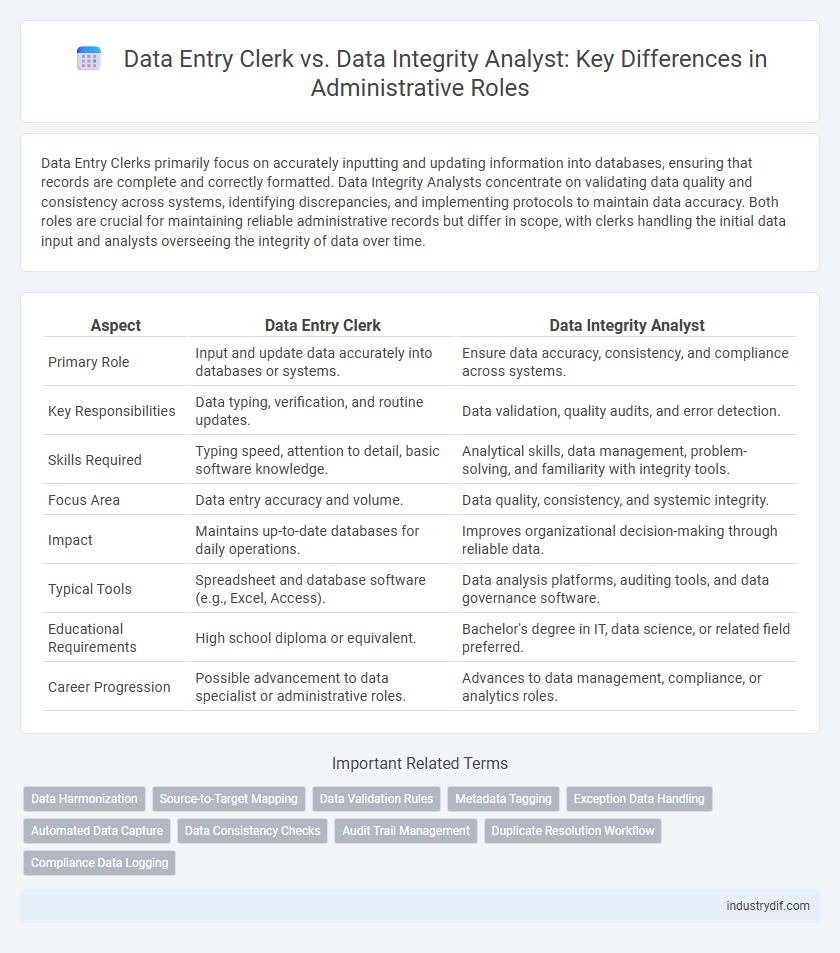
| Aspect | Data Entry Clerk | Data Integrity Analyst |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Role | Input and update data accurately into databases or systems. | Ensure data accuracy, consistency, and compliance across systems. |
| Key Responsibilities | Data typing, verification, and routine updates. | Data validation, quality audits, and error detection. |
| Skills Required | Typing speed, attention to detail, basic software knowledge. | Analytical skills, data management, problem-solving, and familiarity with integrity tools. |
| Focus Area | Data entry accuracy and volume. | Data quality, consistency, and systemic integrity. |
| Impact | Maintains up-to-date databases for daily operations. | Improves organizational decision-making through reliable data. |
| Typical Tools | Spreadsheet and database software (e.g., Excel, Access). | Data analysis platforms, auditing tools, and data governance software. |
| Educational Requirements | High school diploma or equivalent. | Bachelor's degree in IT, data science, or related field preferred. |
| Career Progression | Possible advancement to data specialist or administrative roles. | Advances to data management, compliance, or analytics roles. |
Role Overview: Data Entry Clerk vs Data Integrity Analyst
A Data Entry Clerk is responsible for inputting, updating, and maintaining accurate information in databases, ensuring data is organized and accessible. In contrast, a Data Integrity Analyst focuses on validating, auditing, and analyzing data quality to detect inconsistencies and prevent errors across systems. While both roles prioritize data accuracy, the Analyst role requires advanced skills in data management tools and methodologies to uphold organizational data integrity.
Key Responsibilities and Tasks
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting, updating, and maintaining data within various databases and systems, ensuring data accuracy and timely processing. Data Integrity Analysts are responsible for monitoring, auditing, and validating data quality, implementing data validation protocols, and identifying discrepancies to ensure compliance with organizational standards. Both roles demand attention to detail, but Data Integrity Analysts require a deeper understanding of data governance and quality assurance processes.
Required Skills and Qualifications
Data Entry Clerks require strong typing skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in data management software like Microsoft Excel and database systems. Data Integrity Analysts need advanced analytical skills, expertise in data validation techniques, and knowledge of data governance frameworks to ensure accuracy and consistency across complex datasets. Both roles demand a strong understanding of data security protocols and the ability to identify and resolve discrepancies efficiently.
Essential Tools and Software Used
Data Entry Clerks primarily utilize spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel and database systems such as Oracle or SAP for efficient data input and management. Data Integrity Analysts rely on advanced data governance tools like Informatica and data quality platforms including Talend to ensure accuracy and compliance across datasets. Both roles increasingly incorporate automation software like Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to streamline workflows and minimize errors.
Data Accuracy and Quality Assurance
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting information into databases, ensuring the initial capture of data is error-free and consistent. Data Integrity Analysts specialize in monitoring and validating data quality to maintain accuracy over time, identifying discrepancies or anomalies. Both roles are essential for robust quality assurance processes, with Clerks ensuring precise data entry and Analysts safeguarding data integrity across systems.
Career Paths and Advancement Opportunities
Data Entry Clerks primarily handle routine input tasks with limited advancement opportunities, often progressing to supervisory roles or specialized clerical positions. Data Integrity Analysts possess advanced skills in data management and analysis, enabling career growth into roles such as data quality manager, business analyst, or IT project coordinator. Emphasizing analytical expertise and process improvement expands advancement opportunities in the data integrity field compared to entry-level data entry positions.
Typical Challenges and Problem-Solving
Data Entry Clerks often face challenges such as managing high volumes of repetitive input tasks prone to human error, requiring meticulous attention to detail and rapid typing skills to maintain accuracy. Data Integrity Analysts encounter complex problems involving data validation, anomaly detection, and system integration issues, necessitating advanced analytical tools and cross-department collaboration to ensure data accuracy and consistency. Both roles demand problem-solving strategies that optimize workflow efficiency and uphold organizational data standards through continuous monitoring and corrective action.
Industry Demand and Job Market Trends
Data entry clerks face a declining demand due to automation and advanced software reducing manual input needs, while data integrity analysts are seeing increased employment opportunities as organizations prioritize data accuracy and compliance across industries like healthcare and finance. The job market trends indicate a shift towards roles requiring analytical skills and proficiency in data governance tools, reflecting broader digital transformation efforts. Employers seek candidates adept at ensuring data quality and regulatory compliance, highlighting the growing importance of data integrity analysts over entry-level data clerks.
Salary Expectations and Compensation
Data Entry Clerks typically earn an average salary ranging from $28,000 to $40,000 annually, reflecting the entry-level nature of the role focused on accurate data input and maintenance. Data Integrity Analysts command higher compensation, with salaries averaging $55,000 to $75,000 per year, due to their responsibility for ensuring data accuracy, consistency, and compliance across systems. The salary gap underscores the advanced analytical skills and critical oversight required for Data Integrity Analysts compared to the routine data entry tasks performed by clerks.
How to Choose the Right Role for You
Choosing between a Data Entry Clerk and a Data Integrity Analyst depends on your skills and career goals; Data Entry Clerks focus on accurate and efficient input of information, ideal for those with strong attention to detail and typing proficiency. Data Integrity Analysts require analytical skills to audit, validate, and maintain data accuracy across systems, suited for individuals interested in data quality control and reporting. Assessing your technical abilities, interest in data analysis, and long-term professional aspirations will help determine the role best aligned with your strengths and objectives.
Related Important Terms
Data Harmonization
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting and updating data into systems, ensuring initial data consistency, while Data Integrity Analysts specialize in data harmonization by validating, cross-referencing, and standardizing data across multiple sources to maintain accuracy and reliability. Effective data harmonization requires analysts to implement protocols and leverage software tools that align disparate datasets, enhancing organizational decision-making and compliance reporting.
Source-to-Target Mapping
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting data from source documents into target systems, ensuring that information is recorded correctly but with limited involvement in data transformation processes. In contrast, Data Integrity Analysts specialize in source-to-target mapping by validating data consistency, identifying discrepancies between source and target datasets, and implementing controls to maintain data accuracy throughout the ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) pipeline.
Data Validation Rules
Data Entry Clerks primarily follow predefined data validation rules to ensure accurate input and minimize errors during the initial data capture process. Data Integrity Analysts develop and refine these validation rules, conducting regular audits to maintain data consistency and support compliance across systems.
Metadata Tagging
Data Entry Clerks specialize in accurately inputting and organizing metadata tags to ensure consistent categorization across databases, enhancing data retrieval efficiency. Data Integrity Analysts focus on validating and auditing these metadata tags to maintain data quality, accuracy, and compliance with organizational standards.
Exception Data Handling
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on accurately inputting and verifying routine data, while Data Integrity Analysts specialize in identifying, investigating, and resolving exception data to maintain database accuracy and compliance. Exception Data Handling involves detecting irregularities or discrepancies in datasets that require analytical skills and decision-making beyond standard data entry tasks.
Automated Data Capture
A Data Entry Clerk primarily focuses on manual input and verification of data, whereas a Data Integrity Analyst leverages automated data capture technologies such as optical character recognition (OCR) and intelligent document processing (IDP) to enhance data accuracy and streamline validation processes. Implementing automated data capture reduces human error and accelerates data processing, enabling analysts to focus on maintaining data quality and compliance within administrative systems.
Data Consistency Checks
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on inputting accurate information into databases, while Data Integrity Analysts conduct comprehensive data consistency checks to identify discrepancies and maintain data quality across systems. Their role involves validating data accuracy, implementing error detection protocols, and ensuring compliance with organizational standards for reliable data management.
Audit Trail Management
A Data Entry Clerk primarily ensures accurate input and verification of data, maintaining consistency for an effective audit trail. In contrast, a Data Integrity Analyst specializes in analyzing and monitoring audit trail data to detect discrepancies, enforce compliance, and strengthen data governance protocols.
Duplicate Resolution Workflow
Data Entry Clerks primarily focus on inputting and verifying accurate data to minimize duplicates at the source, while Data Integrity Analysts oversee the Duplicate Resolution Workflow by identifying, investigating, and resolving data redundancies to maintain database accuracy. Effective collaboration between these roles ensures seamless duplicate detection, removal, and prevention processes within administrative data management systems.
Compliance Data Logging
A Data Entry Clerk primarily handles accurate and timely input of compliance data into management systems, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements. In contrast, a Data Integrity Analyst monitors and verifies the consistency, accuracy, and security of compliance data, implementing controls to prevent data breaches and maintain audit readiness.
Data Entry Clerk vs Data Integrity Analyst Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com