File clerks traditionally handle physical documents, organizing, storing, and retrieving paper records to ensure easy access and proper filing. Digital records managers focus on electronic data management, employing software tools to maintain, secure, and archive digital files while ensuring compliance with data governance policies. Both roles are critical in administrative settings but differ significantly in their approach to managing information assets.
Table of Comparison
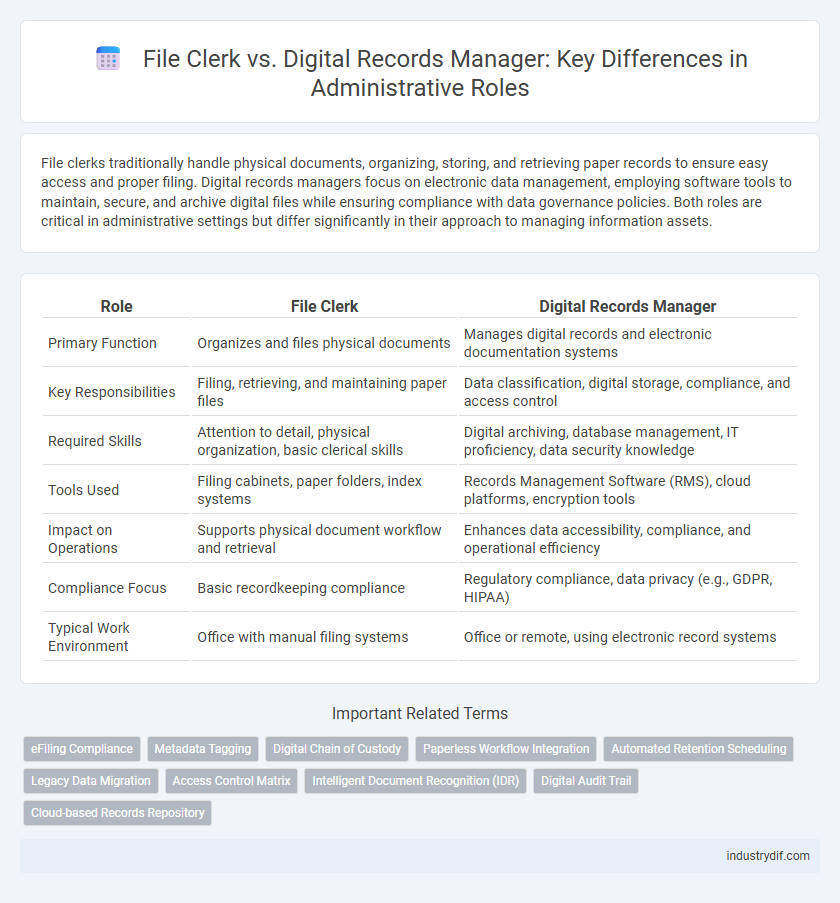
| Role | File Clerk | Digital Records Manager |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Organizes and files physical documents | Manages digital records and electronic documentation systems |
| Key Responsibilities | Filing, retrieving, and maintaining paper files | Data classification, digital storage, compliance, and access control |
| Required Skills | Attention to detail, physical organization, basic clerical skills | Digital archiving, database management, IT proficiency, data security knowledge |
| Tools Used | Filing cabinets, paper folders, index systems | Records Management Software (RMS), cloud platforms, encryption tools |
| Impact on Operations | Supports physical document workflow and retrieval | Enhances data accessibility, compliance, and operational efficiency |
| Compliance Focus | Basic recordkeeping compliance | Regulatory compliance, data privacy (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) |
| Typical Work Environment | Office with manual filing systems | Office or remote, using electronic record systems |
Overview: File Clerk vs Digital Records Manager
A File Clerk primarily handles the physical organization, sorting, and retrieval of paper documents within an office environment, ensuring accurate filing and easy access. In contrast, a Digital Records Manager oversees the management, storage, and security of electronic records, implementing digital systems and compliance protocols to maintain data integrity. Both roles are essential for efficient records management, but the Digital Records Manager requires expertise in digital archiving technologies and regulatory standards related to information governance.
Key Responsibilities and Duties
File Clerks primarily focus on organizing, sorting, and maintaining physical documents to ensure easy retrieval and proper storage. Digital Records Managers oversee electronic records management systems, including data classification, secure access, and compliance with digital archiving standards. Both roles require meticulous attention to detail, but Digital Records Managers also manage data integrity, backup protocols, and digital lifecycle policies.
Required Skills and Qualifications
File Clerks require strong organizational skills, attention to detail, and proficiency in physical document handling, filing systems, and basic office software. Digital Records Managers need advanced knowledge of electronic records management systems, data privacy regulations, and information governance, along with expertise in digital archiving and metadata standards. Both roles demand effective communication abilities and a commitment to maintaining accuracy and confidentiality in handling sensitive information.
Tools and Technologies Utilized
A File Clerk primarily utilizes physical filing systems, barcode scanners, and basic office software such as Microsoft Office Suite to organize, store, and retrieve paper documents efficiently. In contrast, a Digital Records Manager leverages advanced electronic records management systems (ERMS), cloud storage solutions, and data encryption tools to oversee digital archives, ensuring security, compliance, and seamless access to electronic records. Both roles require adapting to evolving technologies, but the Digital Records Manager depends heavily on automation, metadata tagging, and electronic workflow software to optimize records lifecycle management.
Workflow and Process Differences
File Clerks primarily handle physical documents, organizing, filing, and retrieving paper records within a structured filing system to maintain office workflow continuity. Digital Records Managers oversee electronic document management systems, ensuring the secure storage, indexing, and retrieval of digital files while implementing data governance policies and compliance regulations. Workflow differences include manual, paper-based processes for File Clerks versus automated, metadata-driven processes for Digital Records Managers enhancing efficiency and information accessibility.
Data Security and Compliance
File clerks primarily handle physical documents, maintaining organized paper records but with limited capacity to enforce advanced data security protocols or ensure regulatory compliance. Digital records managers implement robust access controls, encryption, and audit trails to protect electronic information, ensuring adherence to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX. Organizations prioritizing data security and compliance benefit significantly from digital records management systems that provide secure, searchable, and compliant record-keeping solutions.
Efficiency and Productivity Comparison
File clerks primarily handle physical document organization, which can slow workflow due to manual retrieval and limited accessibility, while digital records managers utilize advanced software systems enabling rapid data access and streamlined document management. Digital records management reduces errors and supports automated indexing, leading to higher accuracy and faster processing times compared to traditional filing methods. This shift enhances overall organizational efficiency and productivity by minimizing time spent on record handling and improving information retrieval speed.
Career Path and Advancement Opportunities
File clerks typically start with basic document organization responsibilities, offering limited advancement mostly within entry-level administrative roles. Digital records managers engage with advanced information management systems, providing career growth opportunities in data governance, compliance, and IT management. The transition from file clerk to digital records manager often requires upskilling in digital tools, information security, and records management certifications.
Challenges and Solutions in Record Management
File clerks face challenges in managing physical documents due to space limitations, misfiling risks, and time-consuming retrieval processes. Digital records managers mitigate these issues by implementing electronic document management systems (EDMS) that enable efficient indexing, secure storage, and rapid access to digital files. These solutions enhance data accuracy, ensure compliance with regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA, and streamline workflow automation in administrative environments.
Future Trends in Administrative Records Management
File Clerks traditionally manage paper-based records, but the rise of digital transformation shifts focus toward Digital Records Managers who utilize cloud storage, AI-driven indexing, and automated retrieval systems. Emerging trends emphasize data security, compliance with evolving regulations like GDPR, and integration of blockchain for tamper-proof recordkeeping. Future administrative records management relies heavily on leveraging advanced technologies to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility across organizational workflows.
Related Important Terms
eFiling Compliance
File Clerks primarily handle physical document organization and manual filing processes, which may limit efficiency and accuracy in meeting eFiling compliance standards. Digital Records Managers specialize in electronic recordkeeping systems, ensuring regulatory adherence and streamlined workflow through automated eFiling compliance protocols.
Metadata Tagging
File Clerks primarily handle physical document organization and basic metadata tagging to facilitate manual retrieval, often relying on standardized labeling systems. Digital Records Managers utilize advanced metadata tagging techniques, including automated classification and semantic indexing, to enhance digital asset management and ensure compliance with information governance policies.
Digital Chain of Custody
A Digital Records Manager ensures the integrity and security of electronic documents by implementing a digital chain of custody, which tracks every access and modification to maintain an auditable history. Unlike a File Clerk who handles physical paperwork, the Digital Records Manager leverages advanced software to automate record classification, retention schedules, and compliance with regulatory standards.
Paperless Workflow Integration
A Digital Records Manager streamlines paperless workflow integration by utilizing electronic document management systems, enabling efficient storage, retrieval, and compliance with data governance policies. In contrast, a File Clerk primarily handles physical documents, limiting their ability to support seamless digital transformation and automation within administrative processes.
Automated Retention Scheduling
File Clerks traditionally manage physical documents with manual tracking and paper-based retention schedules, leading to potential inefficiencies and compliance risks. Digital Records Managers utilize automated retention scheduling software that enforces policies based on metadata and legal requirements, enhancing accuracy, reducing human error, and streamlining records lifecycle management.
Legacy Data Migration
Legacy data migration requires meticulous handling by a File Clerk focused on physical document organization and basic data entry, while a Digital Records Manager leverages advanced digital tools and metadata standards to ensure seamless integration and long-term accessibility in electronic records systems. Effective migration reduces data loss risks, optimizes retrieval efficiency, and supports regulatory compliance within evolving administrative frameworks.
Access Control Matrix
An Access Control Matrix is essential in distinguishing the roles of a File Clerk and a Digital Records Manager by defining and enforcing permissions for document access, modification, and distribution. While a File Clerk primarily manages physical file handling with limited access controls, a Digital Records Manager utilizes complex access control matrices to ensure secure, role-based access to electronic records, enhancing compliance and data integrity.
Intelligent Document Recognition (IDR)
File Clerks primarily handle physical documents with manual sorting and filing tasks, whereas Digital Records Managers leverage Intelligent Document Recognition (IDR) technology to automate the extraction, classification, and indexing of digital documents, significantly improving accuracy and efficiency. IDR integration supports compliance and enhances data retrieval speed by minimizing human error in record management workflows.
Digital Audit Trail
A Digital Records Manager ensures a comprehensive digital audit trail by systematically capturing, organizing, and securing electronic documents and metadata, enabling efficient tracking of file access and modifications. In contrast, a File Clerk primarily handles physical documents with limited capability to maintain detailed audit trails, making digital record management essential for compliance and accountability in modern administrative operations.
Cloud-based Records Repository
File Clerks primarily manage physical documents and basic digital files, often relying on local storage systems, whereas Digital Records Managers oversee cloud-based records repositories that enable scalable, secure, and centralized access to organizational data. Utilizing cloud technology, Digital Records Managers enhance compliance, streamline retrieval processes, and support collaborative workflows across multiple locations.
File Clerk vs Digital Records Manager Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com