Farm management relies on traditional methods such as crop rotation, soil testing, and resource allocation to optimize productivity and sustainability. Digital twin agriculture leverages real-time data, simulations, and predictive analytics to create virtual replicas of farms, enhancing decision-making and efficiency. Integrating digital twin technology with farm management transforms agricultural practices by enabling precise monitoring and proactive interventions.
Table of Comparison
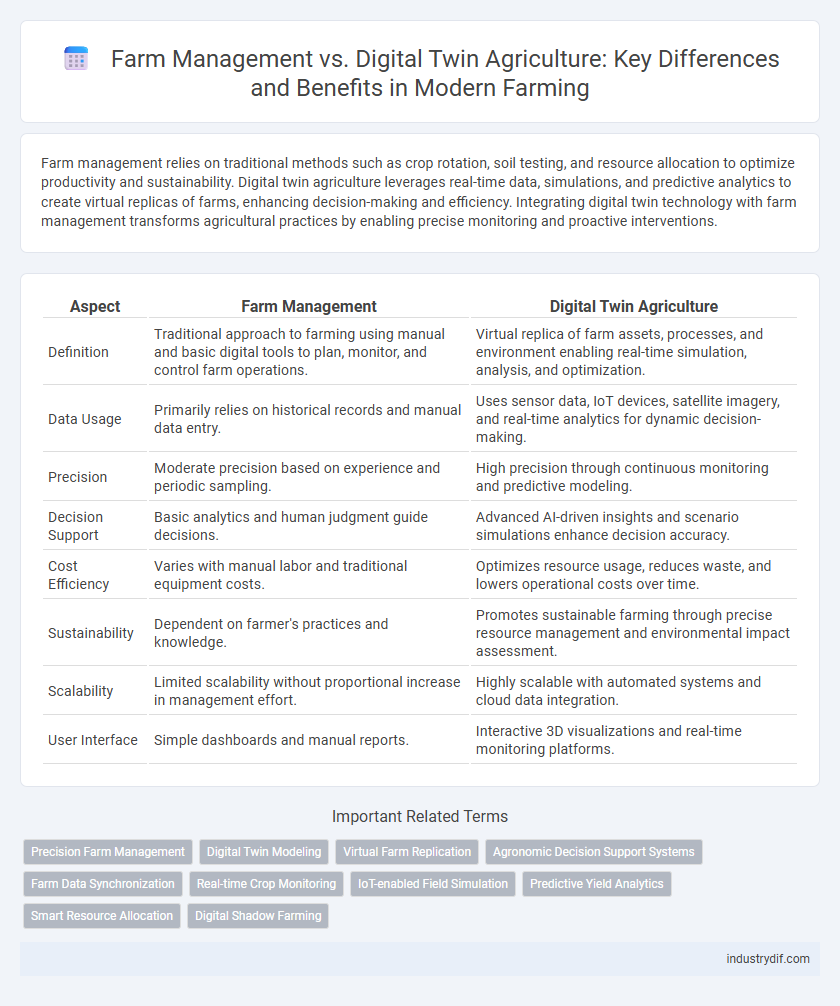
| Aspect | Farm Management | Digital Twin Agriculture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional approach to farming using manual and basic digital tools to plan, monitor, and control farm operations. | Virtual replica of farm assets, processes, and environment enabling real-time simulation, analysis, and optimization. |
| Data Usage | Primarily relies on historical records and manual data entry. | Uses sensor data, IoT devices, satellite imagery, and real-time analytics for dynamic decision-making. |
| Precision | Moderate precision based on experience and periodic sampling. | High precision through continuous monitoring and predictive modeling. |
| Decision Support | Basic analytics and human judgment guide decisions. | Advanced AI-driven insights and scenario simulations enhance decision accuracy. |
| Cost Efficiency | Varies with manual labor and traditional equipment costs. | Optimizes resource usage, reduces waste, and lowers operational costs over time. |
| Sustainability | Dependent on farmer's practices and knowledge. | Promotes sustainable farming through precise resource management and environmental impact assessment. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability without proportional increase in management effort. | Highly scalable with automated systems and cloud data integration. |
| User Interface | Simple dashboards and manual reports. | Interactive 3D visualizations and real-time monitoring platforms. |
Introduction to Farm Management and Digital Twin Agriculture
Farm management involves planning, monitoring, and analyzing all activities related to crop production and livestock to maximize yield and optimize resource use. Digital twin agriculture creates virtual replicas of physical farming environments using sensors and IoT to simulate, predict, and enhance farm operations in real-time. Integrating digital twin technology with traditional farm management offers precise data-driven decisions, improving efficiency and sustainability in modern agriculture.
Core Principles of Traditional Farm Management
Traditional farm management emphasizes crop rotation, soil fertility maintenance, and efficient resource allocation to optimize yields. It relies heavily on experiential knowledge and manual monitoring of field conditions, pest populations, and weather patterns. These core principles prioritize sustainability and risk management through adaptive decision-making grounded in real-time observation and historical data.
Understanding Digital Twin Technology in Agriculture
Farm management relies on traditional data collection and experience to optimize crop yields, whereas digital twin agriculture uses real-time, sensor-driven data to create virtual models of physical farms. Digital twin technology enables precise simulation of environmental conditions, soil health, and crop growth, allowing farmers to predict outcomes and make data-driven decisions. Integrating IoT devices, AI analytics, and geospatial information enhances resource efficiency and reduces risks in modern agricultural practices.
Key Differences Between Farm Management and Digital Twin Approaches
Farm management relies on traditional practices and manual decision-making processes for crop production, resource allocation, and labor scheduling, whereas digital twin agriculture employs real-time data simulation and virtual modeling to optimize farm operations and predict outcomes. Digital twin technology integrates IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and AI analytics to provide precise monitoring of soil conditions, plant health, and environmental factors, unlike farm management's broader, experience-based methods. The key difference lies in digital twin's ability to create dynamic, data-driven representations of the farm environment, enabling proactive interventions and enhanced sustainability compared to conventional farm management techniques.
Benefits of Digital Twin Solutions in Modern Farming
Digital twin technology revolutionizes farm management by providing real-time data simulation and predictive analytics, enabling precise crop monitoring and resource optimization. This innovation reduces operational risks, enhances yield forecasting, and supports sustainable practices by modeling soil health and weather patterns. Integrating digital twins into agriculture streamlines decision-making, maximizes efficiency, and drives higher profitability through data-driven insights.
Challenges of Implementing Digital Twin Systems on Farms
Implementing digital twin systems on farms faces significant challenges such as high initial costs, lack of technical expertise, and data integration complexities. Many farms struggle with limited connectivity and insufficient infrastructure to support real-time data collection and analysis. Ensuring data accuracy and securing sensitive farm data also pose critical hurdles in adopting digital twin technology for effective farm management.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Digital Twins vs Traditional Methods
Digital twin agriculture leverages real-time sensor data and advanced analytics to provide precise, predictive insights, enabling optimized resource allocation and crop management. Traditional farm management relies heavily on historical data and farmer experience, often leading to less accurate and slower decision-making processes. The integration of digital twins transforms data-driven decision-making by offering dynamic simulations and scenario planning that enhance yield, sustainability, and operational efficiency.
Impact on Yield Optimization and Resource Efficiency
Farm management integrates traditional practices with modern techniques to optimize crop yields and resource use, relying on real-time data for informed decision-making. Digital twin agriculture creates virtual replicas of farmland, enabling precise simulation and analysis of variable factors that influence plant growth and resource allocation. The combination of digital twins with farm management significantly enhances yield optimization and resource efficiency by enabling predictive insights and targeted interventions.
Real-Life Case Studies: Farm Management vs Digital Twin Adoption
Real-life case studies in agriculture reveal that traditional farm management relies heavily on manual data collection and experience-based decisions, often leading to inefficiencies in resource use and crop yield predictions. Digital twin technology provides a virtual replica of farms, enabling real-time monitoring, precise simulations of crop growth, and optimized resource allocation, as demonstrated in pilot projects across North America and Europe where yield improvements of up to 20% were recorded. These case studies highlight the transformative impact of digital twins in enhancing decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency compared to conventional farm management approaches.
Future Trends: Integrating Digital Twins with Farm Management Practices
Farm management is evolving by integrating digital twin technology, enabling real-time simulation and predictive analysis of crop growth, soil health, and resource usage. Digital twins create detailed virtual replicas of farms that optimize decision-making, enhance yield forecasts, and improve sustainability through data-driven insights. Future trends highlight increased adoption of AI-powered digital twins to streamline precision agriculture and automate management practices for higher efficiency and resilience.
Related Important Terms
Precision Farm Management
Precision Farm Management leverages digital twin agriculture to create virtual replicas of physical farm environments, enabling real-time monitoring and data-driven decision-making for enhanced crop yield and resource efficiency. By integrating IoT sensors, satellite imagery, and AI analytics, digital twins facilitate precise irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, optimizing farm operations and sustainability.
Digital Twin Modeling
Digital Twin Modeling in agriculture creates a virtual replica of farm operations, integrating real-time data from sensors and machinery to optimize resource allocation, crop monitoring, and yield predictions. This advanced simulation technique enhances decision-making accuracy beyond traditional farm management by enabling predictive analytics and scenario testing for sustainable farming practices.
Virtual Farm Replication
Farm management integrates traditional agricultural practices with real-time data analysis to optimize crop yields and resource use, whereas digital twin agriculture creates a virtual farm replication using IoT sensors and AI to simulate and predict crop growth and environmental impacts. Virtual farm replication enables precise decision-making by modeling various scenarios for irrigation, pest control, and harvesting, significantly enhancing productivity and sustainability.
Agronomic Decision Support Systems
Farm management integrates traditional techniques with Agronomic Decision Support Systems (ADSS) to optimize crop yield and resource use through real-time data and predictive analytics. Digital twin agriculture enhances this process by creating virtual replicas of farm environments, enabling precise simulation and analysis for improved decision-making in areas like pest control, irrigation, and soil health.
Farm Data Synchronization
Farm management relies on traditional data collection methods, which often result in delayed or fragmented information, whereas digital twin agriculture enables real-time farm data synchronization through IoT sensors and cloud platforms, improving decision-making accuracy. This synchronized digital replication of farm operations optimizes resource allocation, crop monitoring, and yield prediction, driving higher agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Real-time Crop Monitoring
Farm management integrates traditional crop monitoring techniques with periodic field inspections, relying heavily on historical data and manual observations to make decisions. Digital twin agriculture revolutionizes real-time crop monitoring by using IoT sensors, GIS mapping, and AI analytics to create dynamic virtual models that enable instant adaptation to changing environmental conditions and precise resource allocation.
IoT-enabled Field Simulation
Farm management leverages IoT-enabled field simulation through digital twin agriculture to create precise, real-time models of crop conditions and soil health, optimizing resource allocation and crop yields. Digital twins integrate sensor data and environmental variables to simulate field scenarios, enhancing decision-making accuracy and reducing operational risks in modern agricultural practices.
Predictive Yield Analytics
Farm management leverages traditional data collection and manual analysis to optimize crop production, while digital twin agriculture employs real-time sensor data and advanced simulation models to enhance predictive yield analytics. This technological integration allows for precise forecasting of crop performance, enabling proactive interventions that improve resource efficiency and maximize harvest outcomes.
Smart Resource Allocation
Farm management integrates crop cycles, labor, and equipment scheduling to maximize productivity, while digital twin agriculture leverages real-time data simulations to optimize smart resource allocation such as water, fertilizers, and energy. Digital twins enhance decision-making by predicting resource needs and minimizing waste, leading to increased efficiency and sustainable farming practices.
Digital Shadow Farming
Digital Shadow Farming integrates real-time data streams from sensors, drones, and IoT devices to create a dynamic, virtual representation of farm operations, enhancing precision and decision-making beyond traditional farm management. This approach enables continuous monitoring and predictive analytics, optimizing resource use and crop yields by mirroring actual field conditions in a comprehensive digital shadow.
Farm management vs Digital twin agriculture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com