Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots through a network of tubes, minimizing water waste and enhancing soil moisture control. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air, misting them with nutrient-rich water for rapid growth and higher oxygen access. Comparing both, drip irrigation is cost-effective and suitable for various crops, while aeroponics optimizes growth rates and resource efficiency in controlled environments.
Table of Comparison
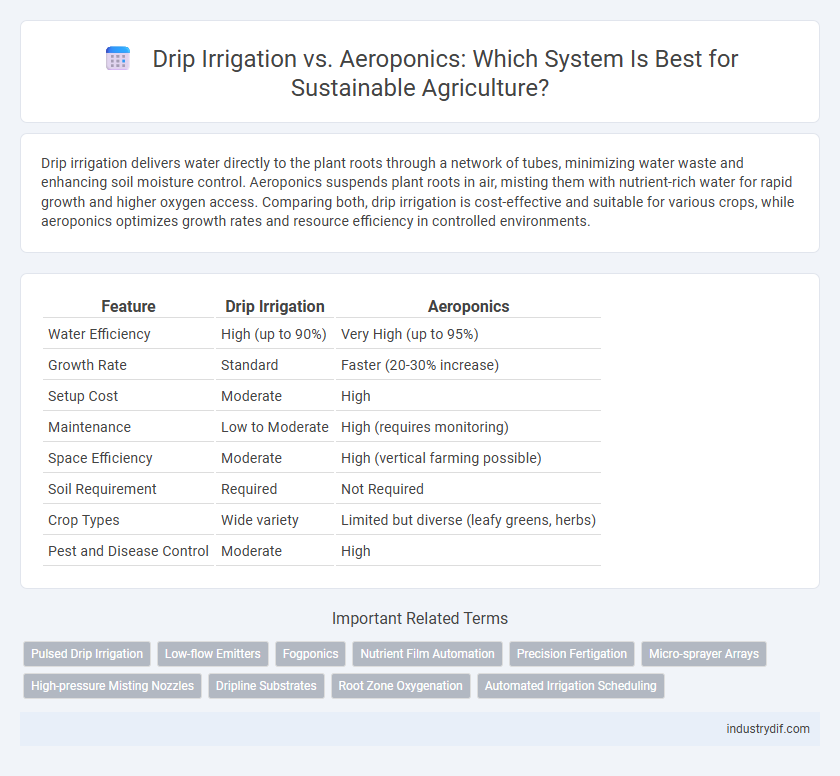
| Feature | Drip Irrigation | Aeroponics |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (up to 90%) | Very High (up to 95%) |
| Growth Rate | Standard | Faster (20-30% increase) |
| Setup Cost | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance | Low to Moderate | High (requires monitoring) |
| Space Efficiency | Moderate | High (vertical farming possible) |
| Soil Requirement | Required | Not Required |
| Crop Types | Wide variety | Limited but diverse (leafy greens, herbs) |
| Pest and Disease Control | Moderate | High |
Introduction to Drip Irrigation and Aeroponics
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters, optimizing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and intermittently sprays them with nutrient-rich mist, promoting faster growth and higher oxygen availability. Both technologies offer innovative solutions for water conservation and enhanced crop yields in modern agriculture.
Core Principles and Technologies
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots through a network of valves, pipes, and emitters, optimizing water efficiency and minimizing evaporation. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in the air and mist them with nutrient-rich water, enhancing oxygen access and accelerating growth. Both systems utilize precision technology but differ significantly in water delivery methods and root environment control.
Water Efficiency Comparison
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff, achieving water use efficiency of up to 90%. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in air and mist them with nutrient-rich water, utilizing 80-95% less water than traditional soil methods due to minimal water waste and precise delivery. Both methods significantly improve water efficiency, but aeroponics offers superior conservation by recycling mist and reducing water consumption in controlled environments.
Nutrient Delivery Methods
Drip irrigation delivers nutrients directly to the soil at the root zone through a controlled, slow-release system, optimizing water and fertilizer efficiency and reducing runoff. Aeroponics suspends plant roots in the air and mists them with a nutrient-rich solution, enabling precise nutrient absorption and oxygen exposure that enhances growth rates and resource use. Both nutrient delivery methods maximize crop yields by targeting nutrient availability, but aeroponics offers superior control over nutrient composition and delivery frequency, vital for high-value or sensitive plants.
Cost Analysis and Investment
Drip irrigation systems typically require a lower initial investment ranging from $500 to $1,500 per acre, making them more accessible for small to medium-scale farms, while aeroponics setups can cost between $10,000 and $30,000 per unit due to advanced technology and automation needs. Operating costs for drip irrigation are moderate, involving regular maintenance and occasional replacement of emitters, whereas aeroponics demands higher energy consumption and constant system monitoring, translating to increased ongoing expenses. The return on investment for drip irrigation is generally quicker, driven by water efficiency and crop yield improvement, but aeroponics offers potentially higher long-term profitability through faster growth cycles and reduced pesticide use.
Scalability and Infrastructure Needs
Drip irrigation systems require moderate infrastructure investments, including pipelines and emitters, making them highly scalable for large-scale agricultural operations. Aeroponics demands advanced technology, such as misting systems and climate control, resulting in higher initial costs and complex infrastructure that can limit scalability. Scalability in aeroponics is better suited for controlled environments like vertical farms, whereas drip irrigation adapts efficiently to extensive outdoor fields.
Crop Suitability and Yield Potential
Drip irrigation excels in water-efficient delivery for a wide range of soil-grown crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucurbits, supporting high yield potential through precise moisture control. Aeroponics suits leafy greens, herbs, and small root vegetables by providing nutrient-rich mist directly to roots, enabling faster growth rates and potentially higher yields in controlled environments. Crop suitability depends on factors like root structure and growth stage, with drip irrigation favored for soil-dependent crops and aeroponics ideal for hydroponic systems aiming for maximum yield intensity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Drip irrigation conserves water by delivering it directly to plant roots, reducing runoff and evaporation, which enhances soil moisture retention and lowers water waste in agriculture. Aeroponics uses up to 90% less water than conventional methods, recycling nutrient-rich mist in a controlled environment, minimizing resource usage and eliminating soil degradation. Both systems support sustainable farming by optimizing water efficiency, but aeroponics offers greater environmental benefits through reduced land use and lower chemical runoff.
Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Drip irrigation systems require regular maintenance to prevent clogging of emitters and ensure uniform water distribution, often demanding periodic filtration and flushing. Aeroponics involves complex root chamber management, requiring precise control of misting cycles and nutrient solution quality to avoid root diseases and system malfunctions. While drip irrigation is relatively straightforward to operate, aeroponics demands higher technical expertise and continuous monitoring to maintain optimal plant growth conditions.
Future Trends in Precision Agriculture
Drip irrigation and aeroponics represent cutting-edge solutions in precision agriculture, with drip irrigation optimizing water efficiency by delivering nutrients directly to plant roots, significantly reducing water waste. Aeroponics, a soil-free cultivation method, utilizes misted nutrient solutions, allowing for faster plant growth and higher yields in controlled environments, ideal for urban agriculture. Future trends indicate a convergence of these technologies with IoT sensors and AI-driven systems, enabling real-time monitoring and adaptive water management to maximize crop productivity and sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Pulsed Drip Irrigation
Pulsed drip irrigation enhances water efficiency by delivering precise, intermittent pulses of water directly to plant roots, reducing runoff and evaporation compared to continuous drip systems. This method optimizes moisture levels, promoting healthier crop growth and higher yields while conserving water, making it more sustainable than aeroponics, which relies on misting roots without soil.
Low-flow Emitters
Low-flow emitters in drip irrigation deliver precise water quantities directly to plant roots, minimizing wastage and enhancing water-use efficiency in agriculture. Compared to aeroponics, which suspends roots in air and mist nutrients, drip irrigation with low-flow emitters provides consistent moisture essential for soil-grown crops, optimizing nutrient uptake and crop yields.
Fogponics
Fogponics, an advanced form of aeroponics, delivers micron-sized nutrient-rich water droplets directly to plant roots, enhancing oxygen availability and nutrient absorption compared to traditional drip irrigation systems that rely on periodic water delivery. This method reduces water usage by up to 90% while promoting faster plant growth and higher yields, making it a highly efficient technique in precision agriculture.
Nutrient Film Automation
Drip irrigation delivers a controlled flow of nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots, optimizing water efficiency and nutrient uptake, while Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) used in aeroponics continuously circulates a thin film of nutrient solution, enhancing oxygen availability and root nutrient absorption. Automation in these systems allows precise regulation of nutrient delivery rates and timing, improving crop yield and resource management in controlled environment agriculture.
Precision Fertigation
Drip irrigation delivers water and nutrients directly to the root zone with high precision, minimizing waste and ensuring consistent nutrient availability for optimal plant growth. Aeroponics enhances precision fertigation by suspending roots in a nutrient-rich mist, enabling fine-tuned control over nutrient delivery and promoting faster uptake and improved crop yields.
Micro-sprayer Arrays
Micro-sprayer arrays in drip irrigation systems deliver precise water distribution directly to plant roots, enhancing water efficiency and crop yield compared to aeroponics, which relies on misting nutrient-rich solutions in a soil-free environment. The micro-sprayers' ability to target specific plant zones minimizes water waste and nutrient runoff, making them highly suitable for sustainable agriculture in arid regions.
High-pressure Misting Nozzles
High-pressure misting nozzles in aeroponics deliver nutrient-rich water directly to plant roots in the form of fine droplets, enhancing oxygen availability and promoting faster growth compared to drip irrigation. This technology reduces water usage by up to 90% and minimizes nutrient runoff, making it a sustainable alternative for precision agriculture.
Dripline Substrates
Dripline substrates in drip irrigation systems provide efficient water delivery directly to plant roots, minimizing water waste and optimizing nutrient absorption compared to aeroponics, which relies on misting roots in air. These substrates enhance soil moisture retention and promote consistent root-zone hydration, crucial for high-yield crop production in varying soil conditions.
Root Zone Oxygenation
Drip irrigation supplies water directly to the root zone, helping maintain consistent soil moisture but often limiting oxygen availability due to saturated conditions. Aeroponics delivers nutrient-rich mist to roots suspended in air, maximizing oxygen exposure and promoting faster root growth and nutrient uptake efficiency.
Automated Irrigation Scheduling
Automated irrigation scheduling in drip irrigation systems delivers precise water application directly to plant roots, maximizing water efficiency and crop yield while minimizing waste. In contrast, aeroponics utilizes mist-based nutrient delivery controlled by automated schedules that optimize oxygen and nutrient uptake, promoting faster plant growth with minimal water usage.
Drip Irrigation vs Aeroponics Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com