Green manure improves soil fertility by enriching organic matter and enhancing nutrient cycling through the natural decomposition of cover crops. Plant biostimulants stimulate plant growth and resilience by activating physiological processes and improving nutrient uptake without supplying nutrients directly. Both practices complement sustainable agriculture by promoting soil health and crop productivity through different mechanisms.
Table of Comparison
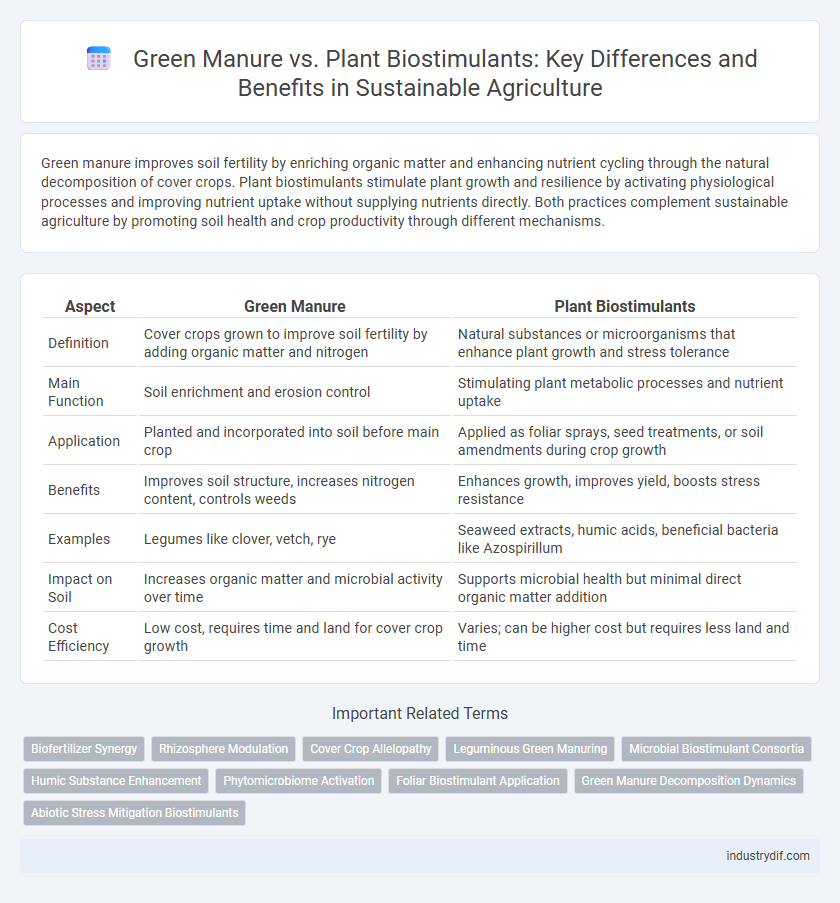
| Aspect | Green Manure | Plant Biostimulants |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cover crops grown to improve soil fertility by adding organic matter and nitrogen | Natural substances or microorganisms that enhance plant growth and stress tolerance |
| Main Function | Soil enrichment and erosion control | Stimulating plant metabolic processes and nutrient uptake |
| Application | Planted and incorporated into soil before main crop | Applied as foliar sprays, seed treatments, or soil amendments during crop growth |
| Benefits | Improves soil structure, increases nitrogen content, controls weeds | Enhances growth, improves yield, boosts stress resistance |
| Examples | Legumes like clover, vetch, rye | Seaweed extracts, humic acids, beneficial bacteria like Azospirillum |
| Impact on Soil | Increases organic matter and microbial activity over time | Supports microbial health but minimal direct organic matter addition |
| Cost Efficiency | Low cost, requires time and land for cover crop growth | Varies; can be higher cost but requires less land and time |
Introduction to Green Manure and Plant Biostimulants
Green manure involves growing specific crops, such as legumes or cover crops, that are plowed back into the soil to enhance organic matter and nutrient content, primarily nitrogen. Plant biostimulants consist of natural or synthetic substances, including seaweed extracts and humic acids, designed to improve plant growth, stress tolerance, and nutrient uptake without directly providing nutrients. Both green manure and plant biostimulants serve as sustainable agricultural practices that promote soil health and crop productivity through different biological mechanisms.
Defining Green Manure in Modern Agriculture
Green manure refers to specific cover crops grown primarily to improve soil fertility and structure by adding organic matter and fixing nitrogen through symbiotic bacteria. These crops, such as legumes, are incorporated into the soil before planting main crops, enhancing nutrient availability and promoting sustainable farming practices. In modern agriculture, green manure serves as a natural soil amendment, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and improving crop yields.
Understanding Plant Biostimulants: Key Components
Plant biostimulants contain key components such as humic acids, seaweed extracts, beneficial microorganisms, and amino acids that enhance nutrient uptake, stress tolerance, and soil health. Unlike green manure, which primarily improves soil organic matter through cover cropping, biostimulants directly stimulate plant physiological processes and microbial activity. These bioactive substances optimize crop growth, improve nutrient efficiency, and increase resilience against environmental stressors in sustainable agriculture systems.
Soil Health Benefits: Green Manure vs Plant Biostimulants
Green manure enhances soil health by increasing organic matter, improving soil structure, and promoting microbial activity through the decomposition of cover crops. Plant biostimulants stimulate plant growth and nutrient uptake while enhancing microbial populations and enzymatic activities, leading to improved soil fertility and resilience. Both approaches contribute to sustainable agriculture by boosting soil biology, but green manure primarily adds biomass while biostimulants optimize soil microbial functions.
Mechanisms of Action: Biological Processes Compared
Green manure enhances soil fertility primarily through nitrogen fixation, organic matter addition, and stimulation of beneficial microbial activity, which improves soil structure and nutrient cycling. Plant biostimulants operate by activating plant metabolic pathways, enhancing stress tolerance, nutrient uptake, and hormonal balance through bioactive compounds like humic acids, seaweed extracts, and beneficial microbes. Both methods promote sustainable agriculture by leveraging biological processes but differ in their mechanisms; green manure acts mostly through soil ecosystem enrichment, while biostimulants directly influence plant physiology and growth regulation.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Green manure is typically applied by incorporating cover crops such as legumes or grasses into the soil before planting, enhancing soil fertility through natural nitrogen fixation and organic matter addition. Plant biostimulants are applied via foliar sprays, seed treatments, or soil drenches, stimulating plant growth and stress resistance through bioactive compounds like humic acids, seaweed extracts, or beneficial microbes. Best practices emphasize timing green manure incorporation just before the main crop planting and using biostimulants tailored to crop species and growth stages for maximum nutrient uptake and yield improvement.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Green manure enhances soil fertility by increasing organic matter and nutrient availability, leading to improved crop yield and quality through better root development and nutrient absorption. Plant biostimulants stimulate plant physiological processes, resulting in increased crop resilience, nutrient efficiency, and higher yields with enhanced fruit and grain quality. Combining green manure with plant biostimulants synergistically optimizes soil health and crop productivity, maximizing agricultural output sustainably.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Green manure improves soil fertility and organic matter content by decomposing cover crops, reducing chemical fertilizer reliance and enhancing carbon sequestration. Plant biostimulants promote plant growth and stress resilience through natural extracts and microbes, minimizing environmental pollution from agrochemical use and improving water efficiency. Both methods contribute to environmental sustainability, but green manure emphasizes soil health restoration while biostimulants target plant productivity and resource use optimization.
Economic Analysis: Cost-Effectiveness in Farm Management
Green manure offers a cost-effective soil fertility strategy by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers, lowering input expenses for farmers. Plant biostimulants, while often more expensive upfront, can enhance crop yields and stress tolerance, potentially increasing overall profitability through improved productivity. Economic analysis shows that integrating green manure with targeted use of biostimulants can optimize farm management by balancing input costs with yield gains for sustainable financial returns.
Future Trends in Sustainable Crop Production
Green manure incorporates organic matter directly into soil, enhancing nutrient cycling and soil structure, while plant biostimulants activate natural processes to improve crop resilience and yield. Future trends in sustainable crop production emphasize integrating these methods to reduce synthetic inputs and promote ecosystem health. Advances in biotechnology and precision agriculture are expected to optimize the application timing and dosage of biostimulants alongside green manure practices for maximum environmental and economic benefits.
Related Important Terms
Biofertilizer Synergy
Green manure enriches soil organic matter and microbial diversity, enhancing nutrient availability and structure, while plant biostimulants stimulate plant growth and stress resilience through biochemical pathways. Combining green manure with biofertilizers creates synergistic effects, improving nutrient uptake efficiency and crop yield by optimizing soil microbial activity and plant physiological processes.
Rhizosphere Modulation
Green manure improves soil fertility and structure by increasing organic matter and microbial activity in the rhizosphere, enhancing nutrient availability and root growth. Plant biostimulants modulate the rhizosphere biome by stimulating beneficial microbial populations and promoting stress resilience, which optimizes nutrient uptake and plant health.
Cover Crop Allelopathy
Cover crop allelopathy releases bioactive compounds that suppress weed growth and enhance soil health, serving as a natural green manure strategy. Plant biostimulants complement this by stimulating plant growth and stress resilience through microbial inoculants and organic extracts, optimizing crop productivity without synthetic inputs.
Leguminous Green Manuring
Leguminous green manuring enriches soil nitrogen through biological nitrogen fixation, enhancing soil fertility naturally without synthetic inputs. Plant biostimulants stimulate plant growth and stress resilience via bioactive compounds but do not directly contribute nitrogen fixation, making leguminous green manure more effective for sustainable nitrogen management.
Microbial Biostimulant Consortia
Microbial biostimulant consortia enhance soil fertility and crop growth by promoting nutrient cycling and suppressing pathogens more effectively than traditional green manure, which primarily adds organic matter. These consortia, composed of synergistic beneficial microbes such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria, mycorrhizal fungi, and phosphate-solubilizing bacteria, optimize plant nutrient uptake and stress resilience, leading to improved agricultural productivity and sustainability.
Humic Substance Enhancement
Green manure improves soil fertility by increasing organic matter and humic substances through crop residues, enhancing nutrient retention and microbial activity. Plant biostimulants, particularly humic substances, directly stimulate soil microbial communities and nutrient uptake efficiency, promoting plant growth and resilience without the need for extensive biomass incorporation.
Phytomicrobiome Activation
Green manure enhances soil fertility by incorporating nitrogen-rich plants that stimulate beneficial microbial activity in the phytomicrobiome, promoting nutrient cycling and improving soil structure. Plant biostimulants activate specific microbial communities within the phytomicrobiome, boosting plant resilience and growth through targeted enhancement of root exudates and microbial symbiosis.
Foliar Biostimulant Application
Foliar biostimulant application enhances crop growth by improving nutrient uptake, stress tolerance, and photosynthetic efficiency, offering a rapid and targeted benefit compared to green manure, which enriches soil organic matter and microbial activity over time. While green manure contributes primarily to long-term soil fertility, foliar biostimulants provide immediate physiological stimulation, leading to increased yield and improved plant resilience in various agricultural systems.
Green Manure Decomposition Dynamics
Green manure decomposition dynamics significantly enhance soil fertility by accelerating nutrient release through microbial activity, improving soil structure and organic matter content. Unlike plant biostimulants, green manure serves as both a nutrient source and a substrate for beneficial soil microbes, promoting sustainable crop production through natural nutrient cycling.
Abiotic Stress Mitigation Biostimulants
Abiotic stress mitigation biostimulants enhance plant resilience to drought, salinity, and temperature extremes by stimulating root growth and improving nutrient uptake more rapidly than traditional green manure methods. While green manure enriches soil organic matter and nutrient content over time, biostimulants provide targeted metabolic support that accelerates stress tolerance and crop productivity under adverse environmental conditions.
Green Manure vs Plant Biostimulants Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com