Irrigation methods vary significantly in water efficiency and crop yield impact. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation techniques. This targeted watering system enhances plant growth, reduces water usage, and promotes sustainable agriculture.
Table of Comparison
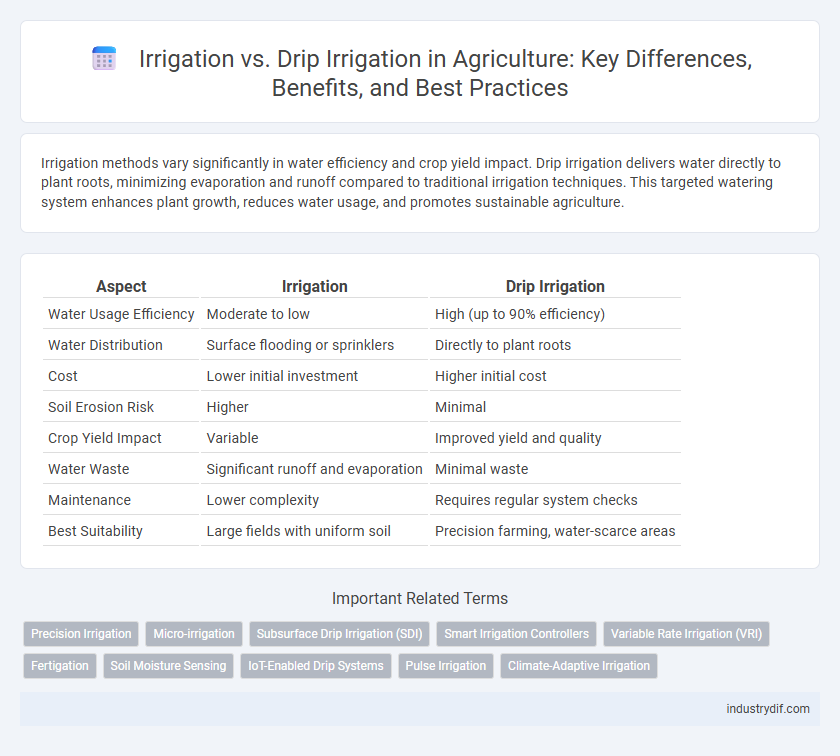
| Aspect | Irrigation | Drip Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage Efficiency | Moderate to low | High (up to 90% efficiency) |
| Water Distribution | Surface flooding or sprinklers | Directly to plant roots |
| Cost | Lower initial investment | Higher initial cost |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Higher | Minimal |
| Crop Yield Impact | Variable | Improved yield and quality |
| Water Waste | Significant runoff and evaporation | Minimal waste |
| Maintenance | Lower complexity | Requires regular system checks |
| Best Suitability | Large fields with uniform soil | Precision farming, water-scarce areas |
Overview of Irrigation Methods
Irrigation methods vary widely, including surface irrigation, sprinkler irrigation, and drip irrigation, each with distinct water application techniques. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, and emitters, maximizing efficiency and minimizing water waste. This method is especially effective in arid regions and for high-value crops, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional surface irrigation.
What is Traditional Irrigation?
Traditional irrigation involves distributing water over the soil surface through methods such as flooding, furrow, or basin irrigation, often resulting in significant water loss due to evaporation and runoff. This method typically requires large amounts of water and can lead to soil erosion and nutrient depletion in agricultural fields. In contrast to drip irrigation, traditional irrigation is less efficient and may negatively impact water conservation efforts in farming practices.
Introduction to Drip Irrigation
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient watering technique that delivers water directly to the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. This method reduces water wastage and soil erosion compared to traditional irrigation systems, making it ideal for arid regions and water-scarce environments. Studies show drip irrigation can increase crop yields by 20-50% while using 30-60% less water, optimizing agricultural productivity.
Key Differences: Irrigation vs Drip Irrigation
Irrigation broadly refers to the application of water to soil or land to assist in the growth of crops, often using methods like flood or sprinkler systems that cover large areas. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters, maximizing water efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff. Key differences include water usage, with drip irrigation reducing consumption by up to 50-70%, and improved crop yield due to precise water delivery compared to conventional irrigation methods.
Water Efficiency Comparative Analysis
Drip irrigation offers superior water efficiency compared to traditional irrigation methods by delivering water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff losses. Studies show that drip irrigation can reduce water usage by up to 50-70% while maintaining or improving crop yields. This targeted water application enhances soil moisture retention and reduces weed growth, making it a sustainable choice for water-scarce agricultural regions.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, significantly improving crop yield by enhancing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation losses compared to traditional irrigation methods. This targeted water application promotes healthier plant growth, resulting in higher quality produce with better nutrient content and reduced disease incidence. Studies show farmers using drip irrigation can increase crop yields by up to 40% while improving fruit size, taste, and shelf life, optimizing both quantity and quality of agricultural output.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Irrigation systems generally require extensive installation involving pipes, pumps, and channels, often leading to higher water loss and soil erosion. Drip irrigation involves precise placement of emitters near the plant roots, requiring careful installation but resulting in more efficient water use and reduced weed growth. Maintenance for drip systems is focused on checking for emitter clogging and ensuring uniform water distribution, whereas traditional irrigation systems demand regular cleaning of canals and pumps to prevent blockages and mechanical failures.
Cost Analysis: Upfront and Long-Term
Drip irrigation systems typically involve a higher upfront cost due to specialized equipment like emitters and tubing, but they offer significant water savings and reduced labor expenses over time, leading to lower operational costs. Traditional irrigation methods, such as flood or sprinkler systems, require less initial investment but often result in higher water usage, increased energy consumption, and greater maintenance expenses. Long-term cost analysis favors drip irrigation in regions with water scarcity and high labor costs, as efficient water delivery enhances crop yield and sustainability.
Suitability for Different Crops and Terrains
Irrigation methods vary in suitability depending on crop type and terrain; conventional irrigation suits large, flat fields with water-intensive crops like rice and wheat, while drip irrigation is ideal for water-sensitive crops such as tomatoes, grapes, and vegetables, promoting water efficiency in uneven or sloped terrains. Drip systems deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which benefits sandy or rocky soils prone to erosion. Understanding soil texture, crop water requirements, and topography ensures optimal irrigation strategy selection for maximizing yield and conserving water resources.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Drip irrigation uses water more efficiently than traditional irrigation by delivering moisture directly to plant roots, reducing water runoff and evaporation. This method significantly cuts water waste, promoting sustainable agriculture by conserving freshwater resources and lowering energy consumption for pumping. Compared to conventional irrigation, drip systems minimize soil erosion and nutrient leaching, supporting long-term soil health and environmental protection.
Related Important Terms
Precision Irrigation
Precision irrigation enhances water use efficiency by delivering water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. Drip irrigation exemplifies precision irrigation by providing controlled, localized water application that optimizes crop yield and conserves water resources.
Micro-irrigation
Micro-irrigation, particularly drip irrigation, offers precise water delivery directly to plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. This technique enhances water use efficiency by up to 90%, promotes healthier crop growth, and minimizes soil erosion, making it a sustainable choice for modern agriculture.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to plant root zones through buried emitters, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. This targeted approach enhances water use efficiency, improves crop yield, and minimizes soil erosion and nutrient leaching in agricultural operations.
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers optimize water usage by automatically adjusting irrigation schedules based on soil moisture, weather forecasts, and crop water requirements compared to traditional irrigation systems. Integrating drip irrigation with smart controllers enhances efficiency by delivering precise water amounts directly to plant roots, reducing waste and improving crop yield.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) enhances traditional irrigation methods by applying precise water volumes tailored to specific field zones, significantly improving water efficiency compared to conventional drip irrigation. This technology integrates soil moisture data and crop requirements, optimizing resource use while boosting crop yield and reducing environmental impact.
Fertigation
Fertigation efficiency significantly increases with drip irrigation compared to traditional irrigation methods, as it delivers water and nutrients directly to the plant root zone, reducing waste and enhancing nutrient uptake by up to 30%. This targeted delivery system optimizes fertilizer use, minimizes leaching, and improves crop yield and quality in various agricultural settings.
Soil Moisture Sensing
Soil moisture sensing technology enhances drip irrigation by delivering precise water amounts directly to plant roots, reducing water waste and improving crop yield efficiency compared to traditional irrigation methods. This targeted approach maintains optimal soil moisture levels, promoting healthier plant growth and conserving valuable water resources in agricultural systems.
IoT-Enabled Drip Systems
IoT-enabled drip irrigation systems optimize water usage by delivering precise amounts directly to crop roots, reducing water waste by up to 40% compared to traditional irrigation methods. These smart systems leverage sensors and real-time data analytics to monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health, enhancing yield and resource efficiency in modern agriculture.
Pulse Irrigation
Pulse irrigation delivers water in controlled, intermittent bursts, enhancing moisture absorption and reducing runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. This technique is particularly effective for drip irrigation systems, maximizing water efficiency and promoting healthy pulse crop growth by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels.
Climate-Adaptive Irrigation
Climate-adaptive irrigation enhances water efficiency by precisely delivering moisture to crops, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional irrigation methods. Drip irrigation systems optimize water use in arid and drought-prone regions by targeting plant roots directly, improving crop yields while conserving vital water resources.
Irrigation vs Drip irrigation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com