Collage art combines various materials and images to create a layered, tactile composition that emphasizes texture and physicality. Data-driven art transforms numbers and algorithms into visual representations, focusing on patterns, statistics, and information flow. Both forms challenge traditional aesthetics, but collage prioritizes sensory experience while data-driven art centers on conceptual interpretation.
Table of Comparison
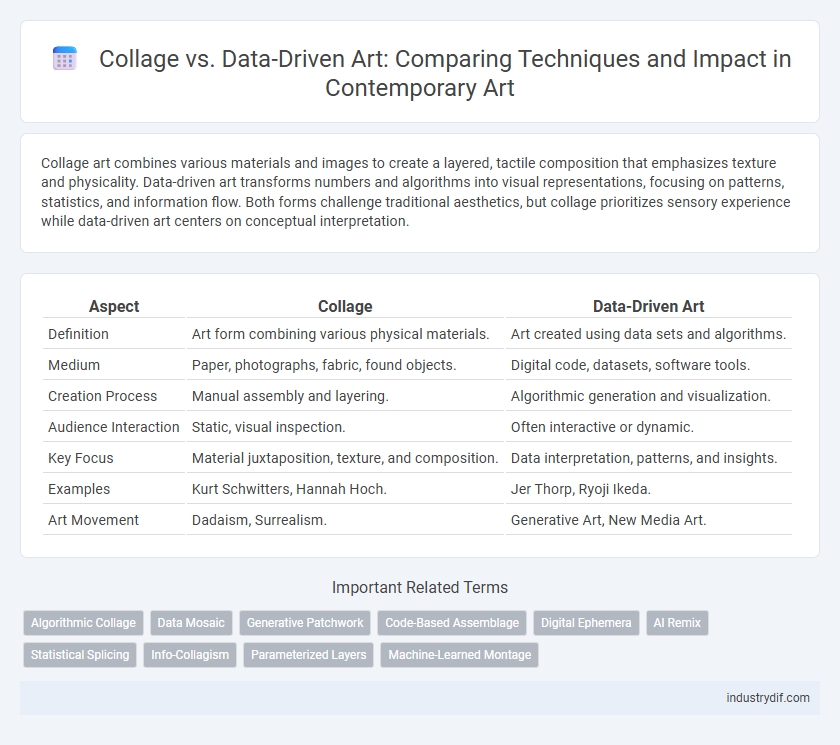
| Aspect | Collage | Data-Driven Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Art form combining various physical materials. | Art created using data sets and algorithms. |
| Medium | Paper, photographs, fabric, found objects. | Digital code, datasets, software tools. |
| Creation Process | Manual assembly and layering. | Algorithmic generation and visualization. |
| Audience Interaction | Static, visual inspection. | Often interactive or dynamic. |
| Key Focus | Material juxtaposition, texture, and composition. | Data interpretation, patterns, and insights. |
| Examples | Kurt Schwitters, Hannah Hoch. | Jer Thorp, Ryoji Ikeda. |
| Art Movement | Dadaism, Surrealism. | Generative Art, New Media Art. |
Defining Collage in Contemporary Art
Collage in contemporary art involves assembling diverse materials such as paper, fabric, photographs, and found objects onto a single surface to create a unified composition that challenges traditional narratives. This technique emphasizes texture, layering, and juxtaposition to evoke complex meanings and visual dialogues, distinguishing it from purely data-driven art which relies on algorithmic or quantitative inputs. Collage remains a tactile and intuitive practice that foregrounds materiality and sensory experience in a digital age.
Exploring Data-Driven Art: A Modern Approach
Data-driven art integrates algorithms and large datasets to create dynamic visual narratives that evolve based on real-time information, distinguishing it from traditional collage, which relies on static, hand-assembled materials. This modern approach leverages machine learning and interactive technologies to push creative boundaries, enabling artists to visualize complex patterns and trends embedded within data. The fusion of art and data analytics fosters innovative expressions that resonate with contemporary digital culture and audience engagement.
Historical Evolution of Collage Techniques
Collage techniques have evolved significantly since their inception in the early 20th century, beginning with Cubist artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque who incorporated fragmented paper and materials to challenge traditional representation. Over time, collage expanded to include diverse media such as photographs, fabric, and digital elements, reflecting cultural and technological shifts. In contrast, data-driven art emerged more recently, utilizing algorithms, big data, and interactive technology to create dynamic compositions that respond to real-time information, marking a departure from the tactile and material focus of traditional collage.
The Rise of Data Visualization in Artistic Expression
The rise of data visualization in artistic expression transforms traditional collage by integrating vast datasets into visual narratives that reveal patterns and insights beyond aesthetic appeal. Data-driven art leverages algorithms and interactive platforms to create dynamic compositions reflecting societal trends, contrasting with the tactile, fragmented nature of collage. This fusion of technology and creativity redefines how audiences engage with art, emphasizing analytical interpretation alongside emotional response.
Materials and Mediums: Traditional vs Digital
Collage traditionally employs physical materials such as paper, fabric, and found objects, creating tactile, layered compositions that emphasize texture and materiality. Data-driven art leverages digital mediums, utilizing algorithms, code, and interactive interfaces to generate dynamic visualizations and immersive experiences. The contrast between tangible materials in collage and intangible digital processes in data-driven art highlights distinct approaches to creativity and audience engagement within contemporary art practices.
Conceptual Frameworks: Narrative in Collage vs Data Art
Collage relies on juxtaposing disparate visual elements to create a layered narrative that invites subjective interpretation and emotional resonance. Data-driven art constructs narratives through algorithmic processing and visualization of quantitative information, emphasizing patterns and inherent meanings within datasets. The conceptual framework of collage centers on fragmented storytelling and symbolic reassembly, while data art prioritizes empirical insight and dynamic representation of reality.
Technological Tools Shaping Data-Driven Art
Technological tools such as machine learning algorithms, generative adversarial networks (GANs), and data visualization software have revolutionized data-driven art by enabling artists to manipulate vast datasets into captivating visual narratives. Unlike traditional collage, which relies on physical materials and manual assembly, data-driven art harnesses programming languages like Python and platforms like Processing to algorithmically generate complex, dynamic compositions. These advancements foster interactive experiences and real-time data integration, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression beyond conventional mediums.
Aesthetic Outcomes: Analog Texture vs Algorithmic Patterns
Collage embraces analog texture by layering tangible materials like paper, fabric, and photographs, creating a multidimensional aesthetic that evokes tactile richness and organic randomness. Data-driven art relies on algorithmic patterns generated through computational processes, producing precise, often complex visual structures that reveal underlying data relationships and mathematical beauty. The contrasting aesthetic outcomes highlight a tension between human touch and machine logic, manifesting in textural warmth versus digital abstraction.
The Role of Audience Interpretation
Collage art invites audience interpretation through its layered visuals and fragmented narratives, allowing viewers to derive personal meanings from diverse materials and textures. Data-driven art challenges traditional perception by transforming complex datasets into dynamic visual forms that engage viewers in decoding patterns and insights. Audience interaction in both mediums is critical, as subjective interpretation shapes the experiential and conceptual impact of the artwork.
Future Trends in Collage and Data-Driven Art
Future trends in collage art emphasize integration with augmented reality and digital interfaces, allowing artists to create immersive, multidimensional experiences that blend physical and virtual elements. Data-driven art is evolving through advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning, enabling dynamic, interactive works that respond to real-time data inputs and audience engagement. The convergence of these approaches is expected to produce hybrid artworks that combine tactile collage techniques with algorithmic data visualization, reshaping contemporary art landscapes.
Related Important Terms
Algorithmic Collage
Algorithmic collage merges traditional collage techniques with computational algorithms to create dynamic, data-infused visual compositions that reveal complex patterns and unexpected juxtapositions. This method leverages generative algorithms and large datasets to automate layering, blending, and transformation, distinguishing it from purely manual or static data-driven art forms.
Data Mosaic
Data mosaic in data-driven art transforms vast datasets into intricate visual compositions, revealing patterns and insights through algorithmic aggregation. Unlike traditional collage which combines physical fragments, data mosaics use digital information as modular elements, creating dynamic artworks that evolve with real-time data inputs.
Generative Patchwork
Generative Patchwork merges traditional collage techniques with algorithmic processes, creating dynamic compositions that evolve through data-driven inputs. This approach leverages AI-generated patterns and textures, transforming static imagery into interactive, continuously reassembled artworks.
Code-Based Assemblage
Code-based assemblage in data-driven art employs algorithmic processes to integrate diverse data elements, creating dynamic and interactive visual compositions that contrast with the tactile layering of traditional collage. This approach leverages programming languages and real-time data manipulation to generate evolving artworks that reflect digital culture and information flows.
Digital Ephemera
Collage art recontextualizes physical and digital fragments to create layered visual narratives, while data-driven art transforms vast digital ephemera into dynamic, algorithmic expressions reflecting contemporary information flows. Emphasizing digital ephemera highlights how transient online data becomes raw material for both tactile and computational artworks, bridging analog and digital realms in the artistic process.
AI Remix
AI Remix in art merges traditional collage techniques with data-driven algorithms, enabling artists to transform and recontextualize visual elements through machine learning models. This fusion expands creative boundaries by generating hybrid artworks that balance human intuition and computational remixing, highlighting the evolving role of artificial intelligence in contemporary visual culture.
Statistical Splicing
Statistical splicing in data-driven art involves algorithmically combining datasets to generate visual narratives, contrasting with the tactile layering and manual assembly characteristic of traditional collage techniques. This method enables artists to explore complex patterns and correlations within data, transforming raw information into dynamic, interpretable compositions that challenge conventional aesthetics.
Info-Collagism
Info-collagism merges traditional collage techniques with data-driven inputs, creating layered visuals that represent complex information patterns. This art form leverages algorithms and real-world datasets to construct compositions, emphasizing the synthesis of aesthetic fragmentation and data visualization.
Parameterized Layers
Parameterized layers in data-driven art enable dynamic manipulation of visual elements using algorithms and real-time data inputs, creating adaptive and evolving compositions. In contrast, traditional collage relies on fixed physical layers assembled manually, limiting variability but offering tactile richness and deliberate texture contrasts.
Machine-Learned Montage
Machine-learned montage leverages advanced algorithms to synthesize diverse visual elements, creating data-driven art that transcends traditional collage methods through dynamic image fusion and pattern recognition. This technique enables artists to generate complex, evolving compositions that reflect algorithmic decision-making and vast datasets, pushing the boundaries of contemporary digital artistry.
Collage vs Data-Driven Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com