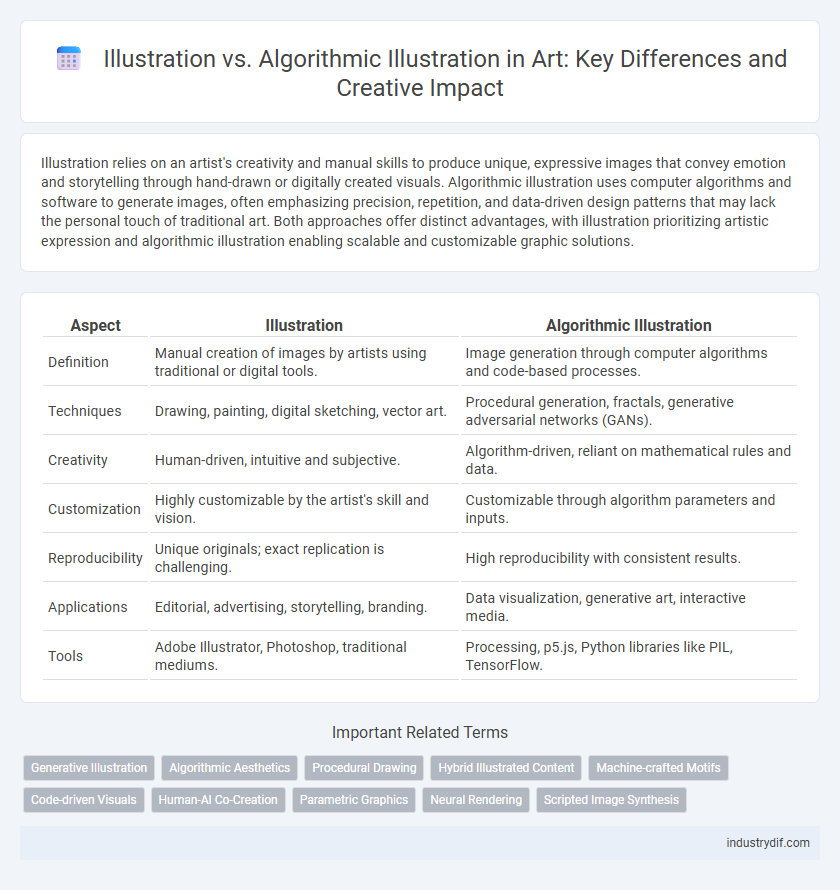
Illustration relies on an artist's creativity and manual skills to produce unique, expressive images that convey emotion and storytelling through hand-drawn or digitally created visuals. Algorithmic illustration uses computer algorithms and software to generate images, often emphasizing precision, repetition, and data-driven design patterns that may lack the personal touch of traditional art. Both approaches offer distinct advantages, with illustration prioritizing artistic expression and algorithmic illustration enabling scalable and customizable graphic solutions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Illustration | Algorithmic Illustration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual creation of images by artists using traditional or digital tools. | Image generation through computer algorithms and code-based processes. |
| Techniques | Drawing, painting, digital sketching, vector art. | Procedural generation, fractals, generative adversarial networks (GANs). |
| Creativity | Human-driven, intuitive and subjective. | Algorithm-driven, reliant on mathematical rules and data. |
| Customization | Highly customizable by the artist's skill and vision. | Customizable through algorithm parameters and inputs. |
| Reproducibility | Unique originals; exact replication is challenging. | High reproducibility with consistent results. |
| Applications | Editorial, advertising, storytelling, branding. | Data visualization, generative art, interactive media. |
| Tools | Adobe Illustrator, Photoshop, traditional mediums. | Processing, p5.js, Python libraries like PIL, TensorFlow. |
Defining Traditional Illustration
Traditional illustration involves creating images by hand using techniques such as drawing, painting, or printmaking to convey ideas visually. It emphasizes the artist's skill, creativity, and personal style to produce unique and expressive artwork. Unlike algorithmic illustration, traditional illustration relies on manual processes and tactile materials rather than digital computation or code.
Understanding Algorithmic Illustration
Algorithmic illustration leverages computational algorithms to generate visual art, enabling complex patterns and dynamic designs that traditional illustration methods may struggle to produce. Understanding algorithmic illustration involves grasping coding languages like Processing or Python to manipulate shapes, colors, and forms programmatically. This approach expands creative possibilities by combining artistic expression with mathematical precision and automation.
Historical Evolution of Illustration Techniques
Traditional illustration evolved through manual techniques such as hand drawing, painting, and printmaking, rooted deeply in artistic craftsmanship from ancient cave paintings to Renaissance masterpieces. Algorithmic illustration emerged in the late 20th century with advances in computer science, utilizing mathematical algorithms and software to generate complex, precise images and patterns. This shift revolutionized the field by enabling scalable, reproducible artwork that blends creativity with computational power, marking a significant milestone in the history of visual arts.
Key Tools and Technologies Used
Illustration relies heavily on traditional tools such as pencils, inks, and digital tablets like Wacom or iPad Pro combined with software like Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator for creating visually compelling art. Algorithmic illustration, on the other hand, uses programming languages such as Python and JavaScript along with frameworks like Processing and p5.js to generate art through code and mathematical algorithms. Key technologies in algorithmic illustration also include machine learning models and generative adversarial networks (GANs) that enable complex, dynamic designs beyond manual drawing capabilities.
Artistic Intent: Human Touch vs Machine Logic
Artistic intent in traditional illustration centers on the human touch, where the artist's emotions, intuition, and creativity shape every stroke, creating unique, expressive visuals. Algorithmic illustration relies on machine logic, using coded rules and data to generate images that prioritize precision and reproducibility over emotional nuance. This contrast highlights the organic imperfection and personal narrative of human art versus the systematic, scalable output of algorithm-driven creations.
Workflow and Creative Process Comparison
Illustration relies on manual techniques such as sketching, inking, and coloring, emphasizing artistic intuition and hands-on creativity throughout the workflow. Algorithmic illustration incorporates computational methods and generative algorithms, enabling iterative refinement and exploration of complex visual patterns driven by code. The creative process in traditional illustration centers on individual expression, while algorithmic workflows blend artistic direction with procedural automation to produce dynamic and scalable visual outcomes.
Visual Styles and Aesthetic Outcomes
Illustration emphasizes handcrafted visual styles, blending traditional techniques with digital tools to create unique, expressive aesthetics defined by artist intuition. Algorithmic illustration leverages computational processes and generative algorithms to produce intricate, often repetitive patterns, achieving precision and complex visual structures unattainable by hand. The aesthetic outcomes of traditional illustration tend to evoke emotional resonance and organic variability, while algorithmic methods offer innovative, data-driven visuals with scalable complexity and novel textures.
Practical Applications in the Arts Industry
Illustration involves manual techniques like drawing and painting to create visually expressive artworks, while algorithmic illustration uses computer algorithms to generate images based on data patterns and rules. Practical applications in the arts industry include traditional book illustration and editorial design alongside generative art, procedural texture creation, and dynamic visualizations for media and advertising. Algorithmic illustration enhances efficiency and enables complex designs that are difficult to achieve by hand, expanding creative possibilities for artists and designers.
Limitations and Ethical Considerations
Illustration relies on an artist's creativity, intuition, and manual skill, which allows for nuanced expression but limits scalability and consistency. Algorithmic illustration automates image generation through code, enabling rapid production and pattern recognition but often lacks emotional depth and originality. Ethical considerations include issues of authorship, potential biases in algorithm training data, and the impact on livelihoods of traditional illustrators.
The Future of Illustration in a Digital Age
Illustration in the digital age is rapidly evolving with algorithmic illustration leading innovation by leveraging artificial intelligence and generative design to create complex, adaptive visuals. Traditional illustrators increasingly integrate algorithmic tools to enhance creativity and efficiency, transforming artistic workflows. The future of illustration will blend human intuition with machine-driven processes, resulting in highly personalized and dynamic artworks.
Related Important Terms
Generative Illustration
Generative illustration leverages algorithmic processes and machine learning to create dynamic, unique artwork, contrasting traditional hand-drawn illustration that relies solely on manual creativity and craftsmanship. By integrating computational algorithms, generative illustration enables scalable, adaptive visual designs that evolve in real time, enhancing the scope and complexity of artistic expression in digital art.
Algorithmic Aesthetics
Algorithmic aesthetics in illustration leverages computational algorithms to generate complex visual patterns and forms that traditional hand-drawn methods cannot easily achieve. This approach integrates mathematical models, procedural generation, and artificial intelligence to produce dynamic, scalable artworks that emphasize structure, symmetry, and emergent design elements.
Procedural Drawing
Procedural drawing in illustration uses algorithmic processes to generate images based on defined rules and parameters, enabling complex patterns and textures that traditional hand-drawn methods might struggle to replicate. This algorithmic illustration allows for scalable, editable, and reproducible art, enhancing creative efficiency while maintaining high visual complexity.
Hybrid Illustrated Content
Hybrid illustrated content merges traditional hand-drawn techniques with algorithmic illustration, enhancing creativity through computational precision and artistic expression. This fusion enables illustrators to produce dynamic visuals that adapt algorithmically while retaining the unique aesthetic qualities of manual illustration.
Machine-crafted Motifs
Machine-crafted motifs in algorithmic illustration leverage complex algorithms and artificial intelligence to generate intricate, unique patterns that transcend traditional hand-drawn techniques. These data-driven designs enable scalable creativity and precision, transforming the artistic process by combining computational power with aesthetic innovation.
Code-driven Visuals
Code-driven visuals in algorithmic illustration leverage programming languages such as Python, Processing, and JavaScript to generate dynamic, data-driven artwork that evolves based on input parameters, contrasting with traditional illustration's manual creation techniques. This method enables complex patterns, generative art, and real-time visual manipulation, pushing the boundaries of creativity through algorithmic precision and automation.
Human-AI Co-Creation
Human-AI co-creation in illustration merges traditional artistic intuition with algorithmic precision, enabling artists to generate complex visuals beyond manual capabilities. This collaboration enhances creative expression by combining human imagination with AI-driven pattern recognition, resulting in innovative and richly detailed artworks.
Parametric Graphics
Parametric graphics in illustration utilize mathematical algorithms to create dynamic, scalable visuals that adapt to variable inputs, contrasting with traditional hand-drawn illustration's fixed, static forms. Algorithmic illustration leverages generative design principles, enabling complex pattern creation and precision unattainable through conventional artistic techniques.
Neural Rendering
Neural rendering leverages deep learning algorithms to generate hyper-realistic illustrations by interpreting and synthesizing visual data, contrasting traditional illustration techniques that rely on manual skill and creativity. Algorithmic illustration employs mathematical models and code to create art, but neural rendering enhances this process by using neural networks to produce complex textures, lighting effects, and intricate details that mimic natural artistic styles.
Scripted Image Synthesis
Scripted Image Synthesis merges traditional illustration techniques with algorithmic processes, enabling artists to generate complex visuals through coded instructions that evolve with variable inputs. Unlike manual illustration, this method leverages computational algorithms to automate pattern creation, enhancing precision and fostering innovative artistic expressions in digital art.
Illustration vs Algorithmic Illustration Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com