Illustration showcases an artist's unique skill and personal touch, creating original and expressive pet artworks that capture character and emotion. AI art generates images through algorithms, offering rapid and diverse visual options but often lacks the nuanced creativity found in hand-drawn pieces. Choosing between illustration and AI art depends on whether you prioritize artistic individuality or innovative technology in your pet art.
Table of Comparison
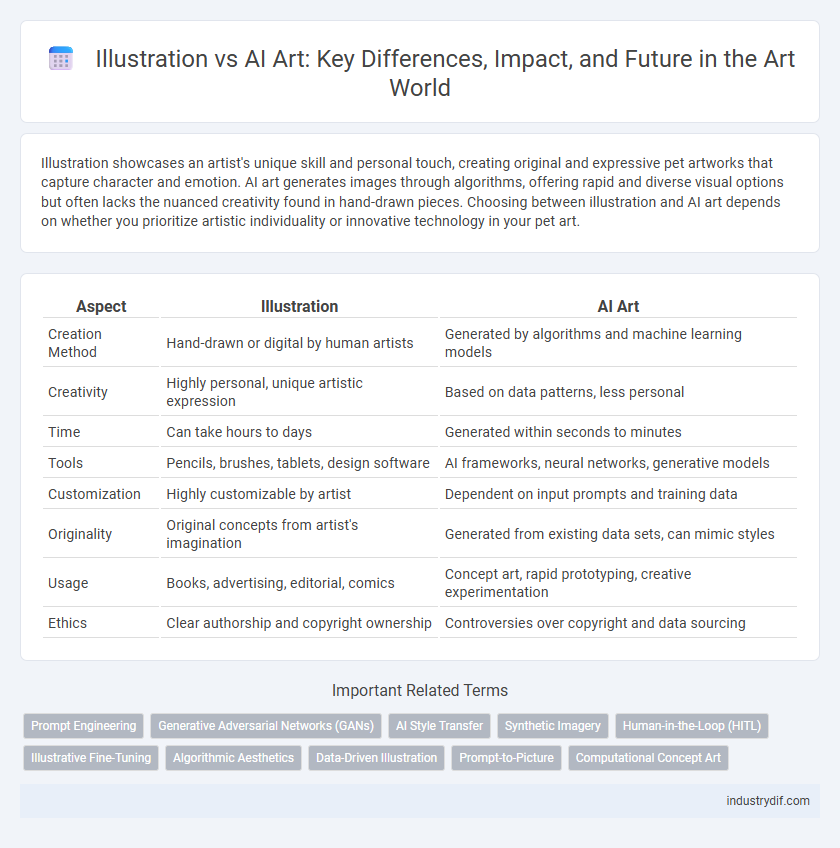
| Aspect | Illustration | AI Art |
|---|---|---|
| Creation Method | Hand-drawn or digital by human artists | Generated by algorithms and machine learning models |
| Creativity | Highly personal, unique artistic expression | Based on data patterns, less personal |
| Time | Can take hours to days | Generated within seconds to minutes |
| Tools | Pencils, brushes, tablets, design software | AI frameworks, neural networks, generative models |
| Customization | Highly customizable by artist | Dependent on input prompts and training data |
| Originality | Original concepts from artist's imagination | Generated from existing data sets, can mimic styles |
| Usage | Books, advertising, editorial, comics | Concept art, rapid prototyping, creative experimentation |
| Ethics | Clear authorship and copyright ownership | Controversies over copyright and data sourcing |
Overview: Illustration vs AI Art
Illustration involves traditional or digital techniques where artists manually create images to convey specific ideas, emotions, or narratives, emphasizing human creativity and skill. AI art leverages machine learning algorithms to generate visuals based on data inputs and patterns, often resulting in novel and evolving styles without direct human craftsmanship. The distinction lies in illustration's intentional artistic expression by humans versus AI art's algorithm-driven image synthesis.
Historical Evolution of Illustration
Illustration originated as a manual craft during the Renaissance, with artists like Albrecht Durer advancing woodcuts and engravings to tell stories visually in books and prints. The 20th century saw the rise of commercial illustration in magazines and advertising, evolving with technological advances such as digital tablets and software like Adobe Illustrator. AI art now challenges traditional illustration by generating complex images through neural networks and algorithms, pushing the boundaries of creativity and authorship in visual storytelling.
Emergence and Rise of AI Art
The rise of AI art marks a transformative shift in creative expression, blending algorithmic precision with artistic vision to generate novel visual experiences. Unlike traditional illustration, which relies on human skill and intuition, AI art harnesses deep learning models trained on vast datasets to produce intricate, often unexpected compositions. This emergence challenges conventional boundaries, fostering new dialogues around creativity, authorship, and the future of art in the digital age.
Techniques Used in Traditional Illustration
Traditional illustration relies on techniques such as hand-drawing, painting with watercolors or acrylics, and using tools like pencils, ink pens, and brushes to create detailed, textured images. Artists emphasize manual skill, layering, shading, and precise line work to express creativity and depth. These techniques provide a tactile richness and personal touch that differentiates traditional illustration from AI-generated art.
Core Algorithms Behind AI-generated Art
AI-generated art relies heavily on generative adversarial networks (GANs) and diffusion models, which use neural networks to create images based on vast datasets of existing artwork. These core algorithms analyze patterns, textures, and styles to produce novel illustrations that mimic human creativity while maintaining unique features. Unlike traditional illustration that depends on manual skill and intuition, AI art employs algorithmic processes to iterate and optimize visuals through training data and computational power.
Creative Process: Human vs Machine
The creative process in illustration relies on human intuition, emotion, and experiential knowledge, allowing artists to infuse their work with personal storytelling and unique stylistic choices. AI art generates images based on algorithms and vast datasets, producing visually complex results but lacking intrinsic emotional depth or intentionality. While illustration embodies individual creativity and expressive nuances, AI art emphasizes pattern recognition and computational efficiency in visual creation.
Artistic Authenticity and Originality Comparison
Illustration embodies artistic authenticity through handcrafted techniques showcasing an artist's unique style and emotional depth, often rooted in years of skill development. AI art utilizes algorithms to generate images, raising questions about originality since the output is based on data patterns rather than personal creative intent. The fundamental distinction lies in human authorship versus machine-assisted creation, challenging traditional notions of what constitutes genuine artistic expression.
Commercial Use in Creative Industries
Illustration in commercial use remains valued for its unique human touch and interpretive creativity, essential in branding, advertising, and product design. AI art, increasingly adopted for its efficiency and scalability, offers rapid generation of diverse visuals, though often raises questions about originality and copyright in creative industries. Balancing traditional illustration with AI-generated content enables businesses to leverage innovation while maintaining artistic integrity in competitive markets.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Illustration and AI art involve distinct legal challenges, with traditional illustration typically protected by clear copyrights held by human creators, whereas AI-generated art faces ambiguity in authorship and ownership rights under current intellectual property laws. Ethical considerations arise from AI art's potential to replicate styles without consent, raising concerns about originality, attribution, and the impact on illustrators' livelihoods. Regulatory frameworks continue to evolve to address these issues, balancing innovation with respect for artistic integrity and creators' rights.
Future Trends in Illustration and AI Art
The future of illustration is increasingly intertwined with AI art, as generative algorithms enable artists to explore complex visual styles and create highly detailed compositions efficiently. Advances in neural networks and machine learning models are driving innovation in both traditional hand-drawn techniques and digitally generated imagery, expanding the creative toolkit available to illustrators. This convergence suggests a hybrid approach where human creativity and AI-powered tools collaborate to push the boundaries of visual storytelling and artistic expression.
Related Important Terms
Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering plays a crucial role in AI art by transforming conceptual ideas into detailed textual inputs that guide algorithmic generation, bridging the gap between human creativity and machine output. Unlike traditional illustration, which relies on manual skill and direct artistic intervention, prompt engineering requires a strategic combination of language and context to produce nuanced, diverse, and customizable visual art through AI platforms.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) revolutionize AI art by enabling machines to create complex, original images through the interaction of two neural networks, challenging traditional illustration techniques that rely on human creativity and manual skill. While illustration embodies deliberate artistic expression and craftsmanship, GAN-based AI art explores vast possibilities in pattern generation and style fusion, often producing unexpected visual outcomes beyond conventional boundaries.
AI Style Transfer
AI style transfer transforms traditional illustrations by applying neural network algorithms to replicate famous art styles, enhancing creativity through digital synthesis. This technology enables artists to merge handcrafted details with AI-generated aesthetics, expanding the boundaries of visual expression in contemporary art.
Synthetic Imagery
Synthetic imagery in illustration leverages AI algorithms to create complex visuals by blending data patterns and artistic styles, enhancing efficiency and expanding creative possibilities. Traditional illustration emphasizes manual skill and personal expression, while AI-generated art transforms the creative process through automation and novel generative techniques.
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) integrates human creativity and decision-making into AI-generated art, ensuring that illustrations maintain emotional depth and artistic intent while benefiting from machine efficiency. This collaborative process enhances originality and quality by allowing artists to guide AI algorithms, blending traditional skills with cutting-edge technology in the art creation workflow.
Illustrative Fine-Tuning
Illustrative fine-tuning enhances AI art by refining neural networks with vast datasets of traditional illustrations, enabling the generation of artworks that closely mimic human craftsmanship and style diversity. This technique bridges the gap between classical illustration techniques and algorithmic creativity, elevating AI-generated art's authenticity and emotional resonance.
Algorithmic Aesthetics
Illustration relies on human creativity and manual skill to convey narrative and emotion, whereas AI art uses algorithmic aesthetics to generate images by analyzing vast datasets and pattern recognition. The algorithmic approach enables AI art to explore novel visual combinations and styles beyond traditional boundaries, reshaping the definition of artistic authorship.
Data-Driven Illustration
Data-driven illustration leverages algorithms and vast datasets to generate precise, customizable visuals that reflect current trends and user preferences, contrasting traditional illustration which relies on human creativity and manual skill. AI art utilizes machine learning models trained on massive image databases to produce unique compositions, enhancing efficiency and innovation in the artistic process.
Prompt-to-Picture
Illustration involves hand-crafted techniques by artists translating ideas into visuals, whereas AI Art relies on prompt-to-picture algorithms interpreting textual input to generate images instantly. The prompt-to-picture process optimizes creativity through machine learning models like GANs and diffusion, offering rapid, diverse, and customizable art outputs.
Computational Concept Art
Illustration traditionally relies on artist-driven techniques and manual skill, while AI art leverages algorithms and machine learning to generate visuals autonomously, emphasizing computational concept art as a fusion of human creativity and artificial intelligence. Computational concept art utilizes neural networks and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to create dynamic, data-driven imagery that challenges conventional artistic boundaries.
Illustration vs AI Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com