Landscape art captures the natural beauty of outdoor scenes through traditional mediums like painting and photography, emphasizing texture, color, and light to evoke emotion. Virtual landscape art uses digital technology to create immersive, interactive environments that blend realism with imaginative elements. The contrast highlights the tactile charm of physical art versus the dynamic, customizable experience of virtual worlds.
Table of Comparison
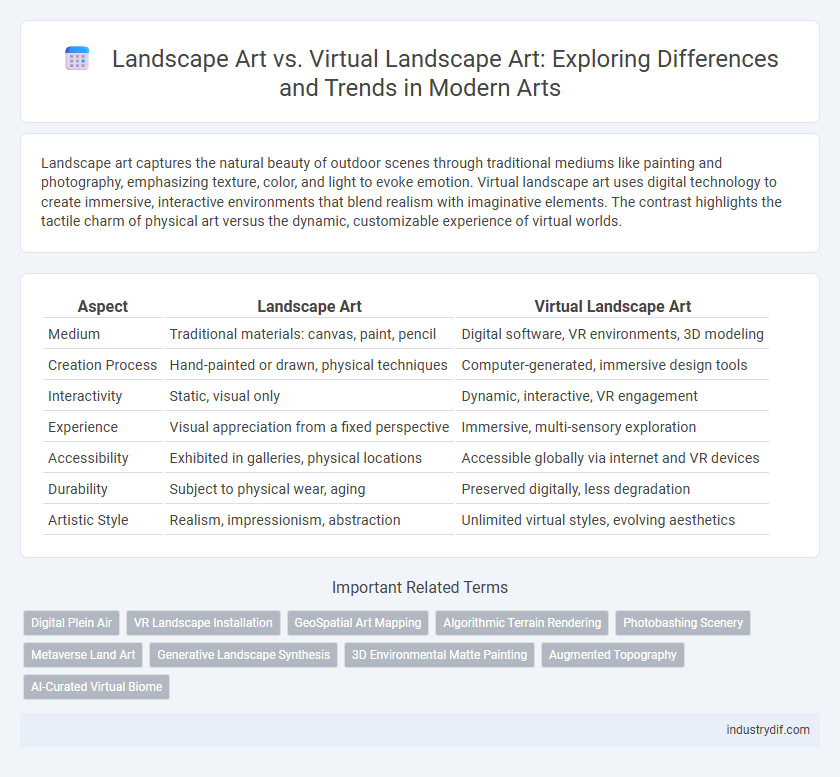
| Aspect | Landscape Art | Virtual Landscape Art |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Traditional materials: canvas, paint, pencil | Digital software, VR environments, 3D modeling |
| Creation Process | Hand-painted or drawn, physical techniques | Computer-generated, immersive design tools |
| Interactivity | Static, visual only | Dynamic, interactive, VR engagement |
| Experience | Visual appreciation from a fixed perspective | Immersive, multi-sensory exploration |
| Accessibility | Exhibited in galleries, physical locations | Accessible globally via internet and VR devices |
| Durability | Subject to physical wear, aging | Preserved digitally, less degradation |
| Artistic Style | Realism, impressionism, abstraction | Unlimited virtual styles, evolving aesthetics |
Defining Traditional Landscape Art
Traditional landscape art captures natural scenery through mediums such as oil paints, watercolors, and charcoal, emphasizing realistic representation and tangible texture. Artists often focus on elements like mountains, rivers, forests, and skies, using perspective and light to evoke atmosphere and depth. This form prioritizes direct observation and manual skill to convey the beauty and emotional impact of real-world environments.
Understanding Virtual Landscape Art
Virtual landscape art redefines traditional landscape art by incorporating digital technologies such as 3D modeling, augmented reality, and virtual reality to create immersive environments that transcend physical limitations. This form of art allows artists to manipulate natural elements dynamically, enabling interactive experiences where viewers can explore and engage with the digital landscape in real-time. Advances in software like Unreal Engine and Unity have expanded the possibilities for virtual landscapes, blending artistic creativity with cutting-edge technology to revolutionize how nature and space are represented.
Historical Evolution of Landscape Art
Landscape art originated during the Renaissance, emphasizing natural scenery through oil painting techniques that captured light and perspective, evolving through Romanticism's emotive depictions of nature. Virtual landscape art emerged with digital technology advancements in the late 20th century, utilizing 3D modeling and computer-generated imagery to create immersive, interactive environments. This evolution reflects a shift from traditional observation to digital innovation, expanding the boundaries of how landscapes are represented and experienced.
Digital Tools in Virtual Landscape Creation
Digital tools such as 3D modeling software, augmented reality (AR), and virtual reality (VR) platforms have revolutionized virtual landscape art by enabling artists to create immersive and interactive environments. Unlike traditional landscape art, which relies on physical mediums like paint and canvas, virtual landscape art utilizes algorithms, digital textures, and real-time rendering to generate dynamic and highly customizable scenes. These technologies allow for unprecedented experimentation with scale, lighting, and perspective, expanding the creative possibilities beyond the constraints of physical landscapes.
Aesthetic Principles in Traditional vs Virtual Landscapes
Traditional landscape art emphasizes natural textures, organic lighting, and atmospheric perspective to evoke realism and emotional depth, relying on tactile brushstrokes and natural color palettes. Virtual landscape art prioritizes immersive interactivity, dynamic lighting effects, and algorithmic generation, creating adjustable environments that challenge conventional spatial perceptions. Both forms engage with principles of composition and balance, yet virtual landscapes expand aesthetic possibilities through digital manipulation and user experience integration.
Techniques and Mediums: Paint vs Pixels
Landscape art traditionally employs mediums such as oil, watercolor, and acrylic paints, utilizing brushstrokes and texture to capture natural scenes with depth and tactile quality. Virtual landscape art relies on digital tools, including software like Adobe Photoshop or 3D modeling programs, enabling artists to manipulate pixels for hyper-realistic or fantastical environments. The transition from paint to pixels allows for dynamic editing, layering, and effects that are impossible with traditional techniques, expanding the creative possibilities for landscape representation.
Viewer Experience: Gallery vs Digital Platforms
Landscape art in galleries offers tactile engagement and immersive spatial context, allowing viewers to appreciate texture, scale, and lighting nuances in a physical environment. Virtual landscape art on digital platforms provides interactive features such as zoom, rotation, and augmented reality, enhancing accessibility and personalization of the viewing experience. The contrast lies in tangible sensory immersion versus dynamic, customizable digital interaction, shaping distinct emotional and cognitive responses.
Preservation and Longevity of Artworks
Traditional landscape art uses physical materials like canvas and paint, which require proper care to prevent deterioration from environmental factors such as light, humidity, and temperature. Virtual landscape art is preserved digitally, offering resilience against physical wear and enabling infinite replication and storage without quality loss. However, digital preservation depends heavily on technological advances and data migration to secure longevity.
Commercial Value and Collectibility
Landscape art holds enduring commercial value due to its historical significance and tactile appeal, attracting traditional collectors who prioritize physical ownership and provenance. Virtual landscape art, leveraging blockchain technology and NFTs, offers unique digital scarcity and provenance, appealing to a growing market of tech-savvy collectors seeking innovation and instantaneous global transactions. The collectibility of virtual landscapes is rapidly increasing as digital platforms expand, though traditional landscape art maintains stable value grounded in established auction markets and galleries.
The Future of Landscape Art in the Digital Age
The future of landscape art in the digital age is shaped by the integration of traditional techniques with virtual reality and augmented reality technologies, allowing artists to create immersive and interactive environments. Virtual landscape art expands the boundaries of spatial perception and artistic expression by enabling dynamic, multi-sensory experiences that adapt to viewer interaction. Advancements in AI-driven generative design and high-resolution 3D modeling further enhance the complexity and realism of digital landscapes, positioning virtual art as a transformative medium in contemporary landscape art.
Related Important Terms
Digital Plein Air
Digital plein air transforms traditional landscape art by using portable devices and software to capture real-time environmental elements with precision and immediacy. Unlike classic plein air painting, virtual landscape art allows artists to manipulate lighting, texture, and atmospheric effects digitally, creating immersive scenes that blend natural observation with innovative technology.
VR Landscape Installation
VR landscape installations transform traditional landscape art by immersing viewers in interactive, three-dimensional environments that blend natural aesthetics with digital technology. These virtual experiences expand creative possibilities, allowing artists to manipulate spatial perception and sensory engagement beyond conventional canvas presentations.
GeoSpatial Art Mapping
Landscape art captures natural environments through traditional media, emphasizing geographic features and spatial relationships, while virtual landscape art leverages geospatial art mapping technology to create immersive, interactive representations of terrains and environments. Geospatial art mapping integrates GIS data, enabling dynamic visualization of landscapes that blend artistic expression with precise spatial analytics for enhanced environmental awareness and cultural interpretation.
Algorithmic Terrain Rendering
Algorithmic terrain rendering in landscape art utilizes mathematical formulas to generate realistic natural environments, enhancing traditional techniques with precise elevation, texture, and vegetation details. Virtual landscape art leverages these algorithms to create immersive, interactive digital terrains that adapt dynamically to user input and environmental changes, expanding the boundaries of artistic expression.
Photobashing Scenery
Photobashing scenery in traditional landscape art involves manual blending of photographic elements to create realistic composites, whereas virtual landscape art leverages advanced digital tools and software to seamlessly integrate high-resolution textures and 3D models for immersive environments. The evolution of photobashing enables artists to achieve hyper-realistic landscapes with enhanced lighting, perspective, and atmospheric effects, revolutionizing concept art and virtual scenery creation.
Metaverse Land Art
Metaverse Land Art redefines traditional landscape art by integrating immersive virtual environments, enabling artists to create dynamic, interactive terrains within digital ecosystems. This fusion leverages blockchain technology and augmented reality to offer users a participatory experience in evolving digital landscapes, expanding the boundaries of artistic expression beyond physical limitations.
Generative Landscape Synthesis
Generative landscape synthesis leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to create intricate virtual landscapes that mimic natural terrains with unprecedented detail and variation. This technology enables artists to transcend traditional landscape art by producing dynamic, immersive environments that evolve in real-time, expanding possibilities for creative expression and experiential engagement.
3D Environmental Matte Painting
3D Environmental Matte Painting integrates digital techniques with traditional landscape art principles, creating immersive, photorealistic environments used in films and video games. Unlike traditional landscape art, it leverages software like Maya and Photoshop to construct dynamic, layered scenes that enhance storytelling through depth and perspective.
Augmented Topography
Augmented topography in landscape art integrates digital overlays onto physical terrains, enhancing spatial perception and interaction beyond traditional representation. Virtual landscape art employs augmented topography to create immersive, dynamic environments that blend real-world geographic data with augmented reality, transforming viewer engagement in contemporary art exhibitions.
AI-Curated Virtual Biome
AI-curated virtual biomes transform traditional landscape art by creating immersive, interactive environments that evolve through machine learning algorithms, enabling dynamic and personalized artistic experiences. This fusion of digital technology and natural aesthetics redefines the boundaries of landscape art, offering innovative possibilities for environmental storytelling and ecological simulation.
Landscape Art vs Virtual Landscape Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com