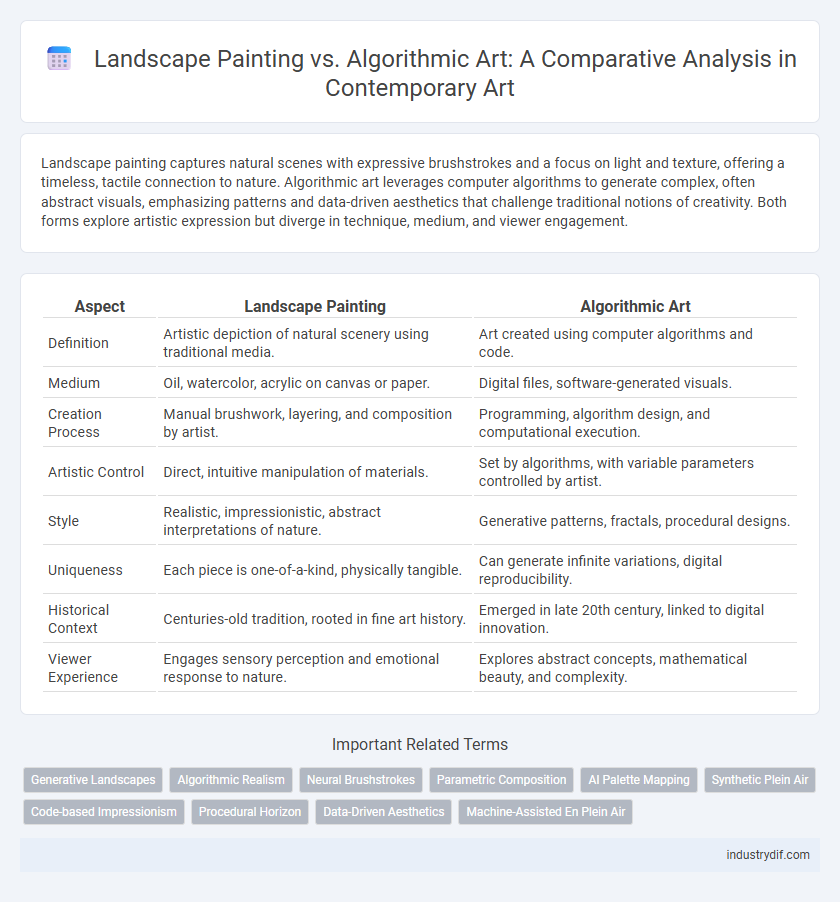
Landscape painting captures natural scenes with expressive brushstrokes and a focus on light and texture, offering a timeless, tactile connection to nature. Algorithmic art leverages computer algorithms to generate complex, often abstract visuals, emphasizing patterns and data-driven aesthetics that challenge traditional notions of creativity. Both forms explore artistic expression but diverge in technique, medium, and viewer engagement.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Landscape Painting | Algorithmic Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artistic depiction of natural scenery using traditional media. | Art created using computer algorithms and code. |
| Medium | Oil, watercolor, acrylic on canvas or paper. | Digital files, software-generated visuals. |
| Creation Process | Manual brushwork, layering, and composition by artist. | Programming, algorithm design, and computational execution. |
| Artistic Control | Direct, intuitive manipulation of materials. | Set by algorithms, with variable parameters controlled by artist. |
| Style | Realistic, impressionistic, abstract interpretations of nature. | Generative patterns, fractals, procedural designs. |
| Uniqueness | Each piece is one-of-a-kind, physically tangible. | Can generate infinite variations, digital reproducibility. |
| Historical Context | Centuries-old tradition, rooted in fine art history. | Emerged in late 20th century, linked to digital innovation. |
| Viewer Experience | Engages sensory perception and emotional response to nature. | Explores abstract concepts, mathematical beauty, and complexity. |
Definition and Evolution of Landscape Painting
Landscape painting, a traditional art form depicting natural scenery, has evolved significantly since the Renaissance, shifting from idealized views to more realistic and expressive representations. This genre highlights elements such as mountains, forests, rivers, and skies, capturing the interplay of light and atmosphere to evoke emotion and narrative. Over centuries, advancements in techniques and cultural perspectives have expanded the depth and diversity of landscape painting, contrasting with the digital and generative nature of algorithmic art.
Understanding Algorithmic Art: Concepts and Techniques
Algorithmic art employs computational algorithms and mathematical models to generate visual compositions, contrasting traditional landscape painting that relies on manual brushwork and observational skills. Techniques such as fractal generation, procedural modeling, and generative adversarial networks (GANs) enable artists to create complex, dynamic images that evolve through code rather than direct handcraft. Understanding algorithmic art involves grasping programming languages like Python or Processing and concepts like randomness, recursion, and data visualization to produce innovative aesthetics beyond conventional landscapes.
Historical Perspectives: Tradition vs Innovation
Landscape painting, rooted in centuries-old traditions, emphasizes natural beauty, atmospheric effects, and emotional depth through meticulous brushwork and compositional techniques developed since the Renaissance. In contrast, algorithmic art harnesses computer-generated processes and mathematical algorithms to create dynamic, often abstract visuals that challenge conventional aesthetics and expand the boundaries of creativity. This juxtaposition reflects a broader historical tension between preserving classical artistic values and embracing technological innovation in the evolution of visual art.
Tools and Mediums: Brushes vs Code
Landscape painting relies on traditional tools such as brushes, canvases, and pigments to create detailed, tactile compositions that emphasize texture and color blending. Algorithmic art utilizes software, coding languages like Python or JavaScript, and digital platforms, enabling dynamic and generative visuals driven by mathematical formulas and data inputs. The contrast between these mediums highlights the physicality and craftsmanship of painting versus the precision and adaptability of computational creation.
Artistic Intent: Expressionism in Landscape vs Computational Creativity
Landscape painting embodies artistic intent through expressionism, emphasizing the artist's emotional response to natural environments and capturing subjective moods and atmospheres. Algorithmic art leverages computational creativity, using algorithms and code to generate original patterns and visuals that reflect a fusion of human direction and machine autonomy. Both approaches prioritize creative expression but diverge in how intentionality is realized, with landscape painting rooted in traditional emotional depth and algorithmic art exploring innovative procedural aesthetics.
Visual Aesthetics: Human Touch vs Digital Precision
Landscape painting showcases the rich textures and subtle color variations achieved through human brushstrokes, emphasizing emotional depth and organic imperfections. Algorithmic art leverages digital precision to create intricate patterns and symmetry that are difficult to replicate by hand, offering a unique blend of complexity and innovation. The contrast between the tactile warmth of traditional landscapes and the calculated finesse of algorithmic creations highlights evolving visual aesthetics in contemporary art.
Notable Artists and Milestones in Both Genres
Notable artists in landscape painting include J.M.W. Turner and Claude Monet, pioneers who captured natural light and atmospheric effects, while algorithmic art features innovators like Vera Molnar and Manfred Mohr, known for integrating computer-generated algorithms into visual compositions. Milestones in landscape painting involve the development of plein air techniques in the 19th century, transforming realism and Impressionism, whereas algorithmic art reached significant advances in the late 20th century with the advent of digital technology and generative processes. Both genres marked pivotal shifts in artistic expression, reflecting evolving relationships between technology, nature, and human creativity.
Audience Reception: Interpretation and Emotional Impact
Landscape painting evokes a direct emotional response through natural imagery, allowing audiences to connect with familiar scenes and traditional aesthetics. Algorithmic art, generated by computational processes, challenges viewers to interpret abstract patterns and underlying codes, often eliciting curiosity and intellectual engagement. Both forms impact audience reception differently, with landscape painting fostering nostalgia and calm, while algorithmic art stimulates analytical thought and contemporary discourse.
The Role of Technology in Contemporary Art
Technology redefines contemporary art by merging traditional landscape painting with algorithmic art, enabling intricate visual complexity and dynamic interactivity. Advanced software and AI algorithms generate unique patterns and transformations beyond manual capabilities, expanding artistic expression and audience engagement. This integration challenges conventional aesthetics and fosters new dialogues between human creativity and digital innovation.
Future Trends: Blending Traditional and Digital Practices
Landscape painting continues to evolve as artists integrate algorithmic art techniques, creating hybrid works that combine classical brushwork with generative digital patterns. Future trends indicate an increasing use of artificial intelligence to enhance texture, color, and composition in landscape art, bridging the gap between handmade and computer-generated aesthetics. This fusion encourages new modes of creativity, expanding artistic expression while preserving the emotional depth and natural inspiration central to traditional landscapes.
Related Important Terms
Generative Landscapes
Generative landscapes in algorithmic art utilize complex neural networks and procedural algorithms to create dynamic, evolving scenes that surpass traditional landscape painting's static compositions. This fusion of art and technology enables infinite variations and intricate details impossible to replicate by hand, expanding the boundaries of visual storytelling in contemporary digital art.
Algorithmic Realism
Algorithmic realism in art leverages complex computational algorithms to generate highly detailed, lifelike landscapes that challenge traditional landscape painting by introducing dynamic, data-driven elements. This fusion of technology and aesthetics creates immersive visuals that evolve based on real-time parameters, pushing the boundaries of realism beyond manual brushwork.
Neural Brushstrokes
Neural brushstrokes in algorithmic art mimic traditional landscape painting techniques by using deep learning algorithms to replicate the texture, depth, and color dynamics of natural scenes. This fusion of artificial intelligence and classical artistry enhances creative expression, transforming digital canvases into visually compelling landscapes that challenge conventional artistic boundaries.
Parametric Composition
Parametric composition in landscape painting emphasizes natural elements arranged through traditional perspectives and brush techniques, highlighting the artist's control over spatial harmony and tonal balance. In contrast, algorithmic art employs computational parameters to generate evolving landscapes, enabling dynamic interpretations and complex patterns unattainable through manual methods.
AI Palette Mapping
Landscape painting captures natural scenery through traditional brushwork and color theory, emphasizing human emotion and interpretation. Algorithmic art, particularly AI palette mapping, generates color schemes via machine learning algorithms to transform images with precise, data-driven aesthetics that challenge conventional artistic boundaries.
Synthetic Plein Air
Synthetic Plein Air combines traditional landscape painting techniques with algorithmic art, creating dynamic digital environments that simulate natural scenes through computational processes. This fusion allows artists to explore complex visual patterns and real-time environmental data, pushing the boundaries of how landscapes are perceived and represented in contemporary art.
Code-based Impressionism
Code-based Impressionism merges traditional landscape painting techniques with algorithmic processes, transforming brushstrokes into dynamic visual data that simulate natural scenes through computational patterns. This fusion redefines artistic expression by employing algorithms to replicate the textured, light-dappled effects characteristic of Impressionism while exploring the intersection of art and technology.
Procedural Horizon
Procedural Horizon in landscape painting emphasizes natural gradients and atmospheric perspective crafted by artists to evoke depth and realism, whereas in algorithmic art, it utilizes computational algorithms to generate mathematically precise horizon lines and evolving visual patterns. This contrast highlights the fusion of traditional artistic techniques with digital innovation, where procedural generation enhances creative possibilities in both mediums.
Data-Driven Aesthetics
Landscape painting captures natural scenery through traditional techniques emphasizing color, light, and texture, while algorithmic art leverages data-driven aesthetics by utilizing mathematical models and computational algorithms to generate complex, often abstract visual compositions. These contrasting methods highlight the evolving role of technology in artistic expression, where landscape painting embodies human perception and emotion, and algorithmic art reflects precision, variability, and the synthesis of data into visual forms.
Machine-Assisted En Plein Air
Machine-assisted en plein air integrates traditional landscape painting techniques with advanced algorithmic art, enabling artists to enhance natural scenes with real-time data processing and computational creativity. This fusion leverages AI algorithms to analyze environmental variables such as light, color, and atmosphere, producing dynamic artworks that reflect both organic observation and digital augmentation.
Landscape Painting vs Algorithmic Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com