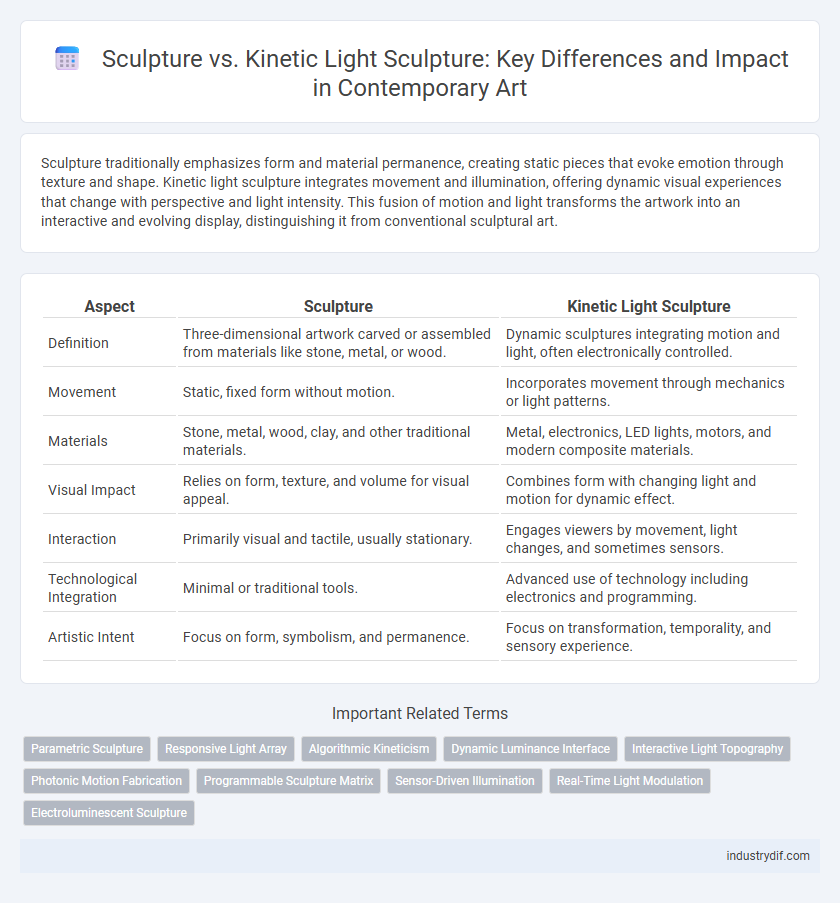
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes form and material permanence, creating static pieces that evoke emotion through texture and shape. Kinetic light sculpture integrates movement and illumination, offering dynamic visual experiences that change with perspective and light intensity. This fusion of motion and light transforms the artwork into an interactive and evolving display, distinguishing it from conventional sculptural art.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sculpture | Kinetic Light Sculpture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional artwork carved or assembled from materials like stone, metal, or wood. | Dynamic sculptures integrating motion and light, often electronically controlled. |
| Movement | Static, fixed form without motion. | Incorporates movement through mechanics or light patterns. |
| Materials | Stone, metal, wood, clay, and other traditional materials. | Metal, electronics, LED lights, motors, and modern composite materials. |
| Visual Impact | Relies on form, texture, and volume for visual appeal. | Combines form with changing light and motion for dynamic effect. |
| Interaction | Primarily visual and tactile, usually stationary. | Engages viewers by movement, light changes, and sometimes sensors. |
| Technological Integration | Minimal or traditional tools. | Advanced use of technology including electronics and programming. |
| Artistic Intent | Focus on form, symbolism, and permanence. | Focus on transformation, temporality, and sensory experience. |
Defining Traditional Sculpture: Forms and Materials
Traditional sculpture encompasses three-dimensional artworks created using materials such as stone, bronze, wood, and clay, emphasizing permanence and tactile form. These sculptures prioritize static shapes and textures, often depicting human figures, animals, or abstract forms with careful attention to proportion and detail. In contrast to kinetic light sculpture, traditional sculptures engage viewers through physical presence rather than movement or illumination.
Introduction to Kinetic Light Sculpture
Kinetic Light Sculpture combines traditional sculptural techniques with moving light elements to create dynamic visual experiences that change over time. This art form integrates mechanical motion and illumination to engage viewers through shifting patterns, shadows, and reflections. Unlike static sculpture, kinetic light sculpture emphasizes interaction between light, movement, and space, redefining the boundaries of contemporary art.
Historical Evolution: From Static to Dynamic Art
Sculpture has evolved from classical static forms carved in marble and bronze to kinetic light sculptures that integrate movement and illumination, transforming traditional art into sensory experiences. Early static sculptures emphasized permanence and form, while kinetic light sculptures, emerging prominently in the 20th century, make use of mechanical motion and light technology to engage viewers dynamically. This historical evolution reflects broader technological advancements and shifting artistic philosophies that prioritize interaction and temporality in contemporary art.
Core Techniques in Conventional Sculpture
Conventional sculpture primarily relies on core techniques such as carving, modeling, casting, and assembling to shape materials like stone, clay, metal, and wood. These methods focus on static forms and tactile textures, emphasizing physical manipulation and structural integrity. Unlike kinetic light sculptures, which incorporate motion and illumination, traditional sculpture centers on creating enduring, tangible artistic objects through time-honored craftsmanship.
Technology’s Role in Kinetic Light Art
Kinetic light sculptures harness advanced technology such as programmable LED systems and microcontrollers to create dynamic visual effects that traditional sculptures lack. These interactive artworks respond to environmental stimuli or audience interaction, blending engineering and artistry to redefine contemporary sculpture. The integration of sensors, motors, and lighting software allows artists to explore motion and light as expressive mediums, pushing the boundaries of static form.
Differences in Audience Experience and Interaction
Traditional sculpture offers a static, tactile experience where viewers engage visually and physically through movement around the piece, emphasizing form and material permanence. Kinetic light sculpture introduces dynamic motion and illumination, creating an immersive interaction that changes perception based on light patterns and viewer position. Audience experience shifts from passive observation to active participation, as light sculptures respond to environmental stimuli and invite emotional and sensory engagement.
Materials and Mediums: Static vs Kinetic Light
Traditional sculpture primarily relies on materials such as stone, metal, clay, and wood, emphasizing static forms that capture solidity and permanence. Kinetic light sculpture integrates dynamic elements like LED lights, motors, and reflective surfaces, using light as both medium and motion to create evolving visual experiences. The interplay of movement and illumination in kinetic light sculptures distinguishes them from conventional static sculptures by adding temporal and sensory dimensions.
Iconic Artists in Both Genres
Auguste Rodin revolutionized traditional sculpture with expressive realism, while Alexander Calder pioneered kinetic light sculptures, integrating motion and illumination to transform static art into dynamic experiences. Jean Tinguely's mechanically-driven creations emphasized playful interaction, contrasting with Anish Kapoor's monumental, reflective sculptures that engage viewers through form and surface. Both genres showcase the evolution of sculptural art, blending physical presence with innovation in movement and light.
Conservation Challenges: Traditional vs Light-Based Works
Traditional sculptures face conservation challenges such as material degradation, environmental exposure, and structural instability, requiring specialized restoration techniques. Kinetic light sculptures introduce complexities involving electronic components, light sources, and moving parts, which demand ongoing maintenance, software updates, and protection from power surges. Preservation of kinetic light sculptures integrates both traditional conservation methods and technological expertise to ensure longevity and functionality.
Future Trends in Sculpture and Kinetic Light Sculpture
Future trends in sculpture emphasize the integration of technology, with kinetic light sculptures gaining prominence due to their dynamic interaction with environments and viewers. Innovations in LED technology, motion sensors, and sustainable materials enable artists to create immersive, responsive artworks that blur the lines between physical form and digital experience. The convergence of sculpture and kinetic light elements is shaping a forward-thinking art landscape that prioritizes interactivity, ecological consciousness, and experiential engagement.
Related Important Terms
Parametric Sculpture
Parametric sculpture leverages digital algorithms to create complex, adaptive forms that transform traditional static sculptures into dynamic, evolving structures. Kinetic light sculptures integrate motion and illumination, enhancing the sensory experience by merging form, movement, and light through programmable, responsive designs.
Responsive Light Array
Traditional sculpture emphasizes static material forms, while kinetic light sculpture integrates motion and illumination through responsive light arrays that dynamically react to environmental stimuli. This interactive technology transforms visual perception, creating immersive art experiences that evolve in real-time based on viewer interaction or ambient changes.
Algorithmic Kineticism
Algorithmic kineticism in kinetic light sculptures integrates precision programming and dynamic light movement to create immersive, interactive art experiences distinct from traditional static sculptures. This fusion of algorithms and motion enhances sensory engagement, transforming spatial perception through responsive, evolving light patterns.
Dynamic Luminance Interface
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes static form and materiality, while kinetic light sculpture integrates movement and illumination to create a dynamic luminance interface that interacts with space and viewer perception. This innovative art form leverages light modulation and mechanical motion to produce evolving visual experiences, enhancing sensory engagement beyond conventional sculptural boundaries.
Interactive Light Topography
Sculpture traditionally involves static forms crafted from materials like stone or metal, while kinetic light sculpture incorporates movement and illumination to create dynamic visual experiences. Interactive light topography enhances this art form by allowing viewers to influence light patterns and shapes through sensory input, blending physical space with digital interactivity for immersive engagement.
Photonic Motion Fabrication
Photonic Motion Fabrication revolutionizes traditional sculpture by integrating dynamic light patterns and motion, creating immersive kinetic light sculptures that interact with their environment. This technique utilizes advanced light manipulation and precise motion control to produce visually captivating artworks that transcend static forms.
Programmable Sculpture Matrix
Programmable Sculpture Matrix revolutionizes traditional sculpture by integrating dynamic light elements and motion control, enabling kinetic light sculptures to transform visual and spatial experiences through interactive programming. This fusion of art and technology enhances viewer engagement, creating evolving aesthetic compositions that respond to environmental stimuli or user input.
Sensor-Driven Illumination
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes static form and materiality, whereas kinetic light sculpture integrates movement with sensor-driven illumination, creating dynamic interactions between light, shadow, and space. Sensor technology enables these sculptures to respond to environmental stimuli or viewer presence, transforming static objects into immersive, adaptive art experiences.
Real-Time Light Modulation
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes static form and materiality, whereas kinetic light sculpture incorporates dynamic elements through real-time light modulation, creating interactive and evolving visual experiences. Real-time light modulation uses sensors and programming to adjust illumination patterns in response to environmental changes or viewer interactions, transforming sculptures into immersive, living artworks.
Electroluminescent Sculpture
Electroluminescent sculptures incorporate electroluminescent materials that emit light when energized, blending traditional sculptural forms with dynamic illumination, creating interactive and visually striking artworks. Unlike static sculptures, electroluminescent kinetic light sculptures leverage electrical currents to produce continuous or programmable light effects, enhancing viewer engagement through movement and light interplay.
Sculpture vs Kinetic Light Sculpture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com