Oil painting remains a classic medium celebrated for its rich textures, vibrant colors, and timeless appeal in depicting artistic subjects. BioArt, by contrast, integrates living organisms and biological processes, pushing boundaries and sparking ethical discussions within the art community. The contrast between the traditional craftsmanship of oil painting and the experimental nature of BioArt highlights evolving definitions of creativity and artistic expression.
Table of Comparison
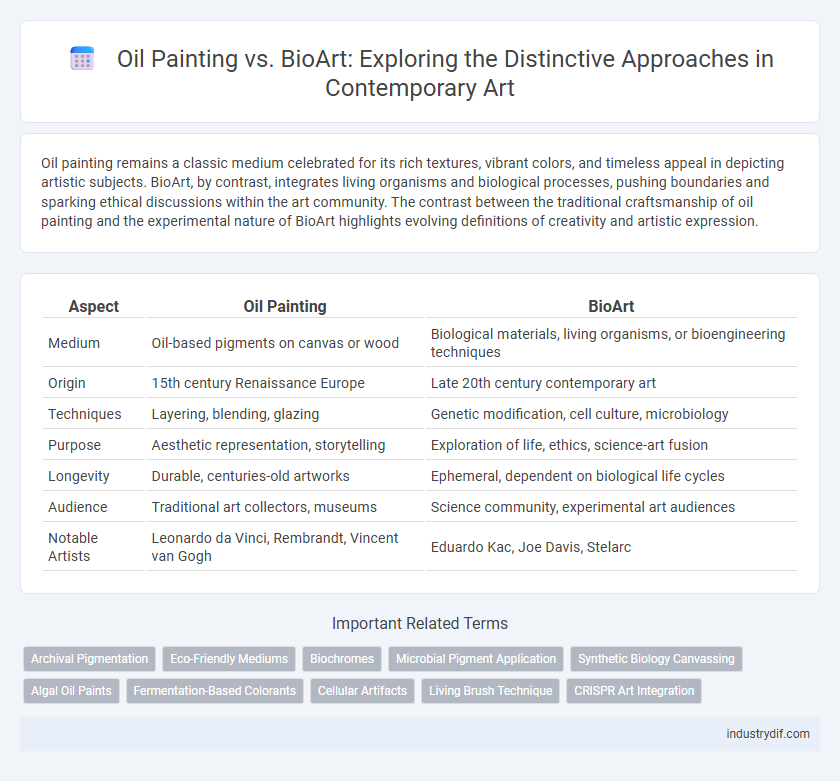
| Aspect | Oil Painting | BioArt |
|---|---|---|
| Medium | Oil-based pigments on canvas or wood | Biological materials, living organisms, or bioengineering techniques |
| Origin | 15th century Renaissance Europe | Late 20th century contemporary art |
| Techniques | Layering, blending, glazing | Genetic modification, cell culture, microbiology |
| Purpose | Aesthetic representation, storytelling | Exploration of life, ethics, science-art fusion |
| Longevity | Durable, centuries-old artworks | Ephemeral, dependent on biological life cycles |
| Audience | Traditional art collectors, museums | Science community, experimental art audiences |
| Notable Artists | Leonardo da Vinci, Rembrandt, Vincent van Gogh | Eduardo Kac, Joe Davis, Stelarc |
Introduction to Oil Painting and BioArt
Oil painting, a traditional medium dating back to the 15th century, involves pigments suspended in drying oils like linseed, enabling rich textures and vibrant colors. BioArt integrates living organisms or biological materials, blending science and art to explore life processes and ethical questions. Both mediums offer unique sensory experiences, with oil painting emphasizing tactile craftsmanship and BioArt provoking conceptual engagement through biological innovation.
Historical Evolution: Oil Painting vs. BioArt
Oil painting, with origins tracing back to the 15th century Renaissance, revolutionized artistic expression through its rich textures and vibrant colors, enabling detailed realism and depth. In contrast, BioArt emerged in the late 20th century, integrating living organisms and biotechnological processes, reflecting contemporary dialogues between art, science, and ethics. This historical evolution highlights a shift from traditional pigment-based mediums to dynamic, living materials, expanding the conceptual boundaries of art.
Materiality and Mediums in Oil Painting and BioArt
Oil painting utilizes traditional mediums such as linseed oil combined with pigments on canvas, emphasizing texture and layering to create depth and vivid color. BioArt integrates living organisms, biological processes, and scientific materials like bacteria, DNA, or tissue cultures as its medium, challenging conventional artistic materiality by blending art with biotechnology. The contrast highlights oil painting's fixed, tangible surfaces versus BioArt's dynamic, ephemeral nature that evolves over time.
Techniques and Methodologies: Traditional vs. Contemporary
Oil painting employs traditional techniques involving layering pigment mixed with oil on canvas, emphasizing brushwork, color blending, and texture development, rooted in centuries-old practices. BioArt integrates contemporary methodologies using living organisms, biotechnology, and scientific processes, creating dynamic, evolving artworks that challenge conventional definitions of art. The contrast highlights oil painting's reliance on manual dexterity and historic materials versus BioArt's fusion of science, technology, and artistic experimentation.
Aesthetic Values and Visual Language
Oil painting conveys rich texture and depth through layered brushstrokes and vibrant pigments, emphasizing traditional aesthetic values rooted in realism and emotional expression. BioArt employs living organisms and biological processes as a medium, challenging conventional visual language by integrating science and art to provoke reflection on life, ethics, and identity. The contrast highlights oil painting's focus on permanence and craftsmanship, while BioArt prioritizes temporality, interactivity, and conceptual engagement in contemporary art discourse.
Conceptual Frameworks in Oil Painting and BioArt
Oil painting relies on traditional conceptual frameworks emphasizing color theory, composition, and representation to evoke emotional and aesthetic responses. BioArt integrates living organisms and biotechnological processes, challenging conventional boundaries by exploring ethical, scientific, and ecological themes. Both mediums engage viewers through distinct ontological questions--Oil Painting reflects human experience and perception, while BioArt interrogates life, biology, and the fusion of art with science.
Interaction with Technology and Science
Oil painting, a traditional medium dating back centuries, emphasizes manual skill and tactile interaction with physical materials such as canvas and pigments. BioArt integrates living organisms and biotechnologies, creating dynamic artworks that evolve through scientific processes and technological interventions, fostering an interactive relationship between art and life sciences. The contrast highlights oil painting's static, material-based expression versus BioArt's fluid, technology-driven experience that actively involves scientific experimentation and ecological concepts.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Oil painting, a traditional art form, often raises sustainability concerns due to the use of toxic pigments and solvents that impact environmental health. BioArt, emerging as a contemporary practice, integrates living materials and biotechnology, promoting eco-friendly methods and ethical reflection on life sciences. Evaluating these art forms involves examining their ecological footprints and contributions to ethical discourse in sustainability.
Viewer Engagement and Experiential Impact
Oil painting captivates viewers through rich textures and vivid color palettes, fostering deep emotional connections via traditional craftsmanship and storytelling. BioArt, integrating living organisms and scientific processes, challenges audience perceptions by creating immersive, dynamic experiences that blur boundaries between art and biology. Both mediums redefine viewer engagement by eliciting sensory and intellectual responses, yet BioArt pushes experiential impact further through interactive, evolving installations.
Comparative Analysis: Future Trends in Oil Painting and BioArt
Oil painting continues to evolve with innovations in synthetic pigments and digital integration, preserving traditional techniques while enhancing durability and color vibrancy. BioArt leverages biotechnology and living organisms as media, pushing boundaries in sustainability and interactive art experiences, positioning it as a forefront of eco-conscious creativity. Future trends suggest a convergence where oil painting may incorporate bio-based materials, merging classic artistry with biological innovation to create hybrid art forms.
Related Important Terms
Archival Pigmentation
Archival pigmentation in oil painting ensures vibrant, long-lasting colors due to durable mineral-based pigments suspended in linseed oil, maintaining the artwork's integrity over centuries. In contrast, BioArt employs living organisms and organic materials, where pigmentation is inherently ephemeral, challenging traditional archival methods and prompting innovative preservation techniques.
Eco-Friendly Mediums
Oil painting traditionally involves synthetic chemicals and solvents with high environmental impact, while BioArt utilizes living organisms and biodegradable materials to create eco-friendly artworks. Artists adopting BioArt increasingly emphasize sustainability by reducing toxic waste and promoting ecological awareness through innovative, organic mediums.
Biochromes
BioArt utilizes living organisms to create dynamic biochromes that evolve over time, offering a unique interplay of biology and pigment beyond the static nature of traditional oil painting. These biochromes introduce a living palette that challenges conventional artistry by incorporating genetic expression and cellular processes as integral components of the visual experience.
Microbial Pigment Application
Oil painting employs traditional pigment binded with oil mediums, creating rich textures and vibrant colors that age over centuries, whereas BioArt integrates microbial pigments derived from bacteria and fungi, offering dynamic, living color palettes that evolve over time. The application of microbial pigments in BioArt challenges conventional aesthetics by introducing temporal variability and ecological awareness, contrasting with the permanence and materiality of oil paints.
Synthetic Biology Canvassing
Oil painting, a traditional medium renowned for its rich textures and vibrant colors, contrasts sharply with BioArt, which employs synthetic biology techniques to manipulate living organisms as dynamic canvases, creating evolving, interactive artworks. Synthetic biology canvassing in BioArt enables artists to engineer genetic materials and cellular behaviors, transforming biological systems into innovative, living masterpieces that challenge conventional artistic boundaries.
Algal Oil Paints
Algal oil paints represent an innovative fusion of traditional oil painting techniques and sustainable materials, derived from microalgae oils that offer rich pigmentation and faster drying times compared to conventional petroleum-based oils. This bioart medium not only reduces environmental impact but also introduces unique textures and vibrant colors, expanding creative possibilities for contemporary artists exploring eco-friendly alternatives.
Fermentation-Based Colorants
Fermentation-based colorants in oil painting offer rich, natural pigments that enhance texture and depth, contrasting with BioArt's experimental use of living organisms to produce dynamic, evolving hues. This sustainable approach in both mediums highlights a shift towards ecological awareness and innovative biological processes in contemporary artistic expression.
Cellular Artifacts
Oil painting, a classical medium revered for its rich textures and vibrant colors, contrasts significantly with BioArt, which employs living cells as dynamic, evolving artifacts to challenge traditional perceptions of life and creativity. Cellular artifacts in BioArt integrate biotechnology and artistic expression, offering a unique medium where cells become both the subject and material, pushing boundaries far beyond the static nature of oil painting pigments.
Living Brush Technique
Oil painting, characterized by its rich texture and vibrant color blending, contrasts sharply with BioArt's Living Brush Technique, which utilizes living organisms as dynamic, evolving pigments to create organic, interactive artworks. This innovative method merges biological processes with traditional artistry, pushing the boundaries of contemporary art by incorporating life itself into the creative process.
CRISPR Art Integration
Oil painting, a traditional art form using pigment and oil medium, contrasts sharply with BioArt where living organisms, often manipulated through CRISPR technology, become the medium, enabling artists to explore genetic editing as a creative tool. CRISPR art integration opens new paradigms in contemporary art by merging science and aesthetics, allowing for dynamic, evolving artworks that question the boundaries of life, identity, and ethics.
Oil Painting vs BioArt Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com