Painting captures the essence of traditional artistry through brushstrokes and texture, emphasizing color harmony and composition. Glitch art transforms digital errors and distortions into intentional aesthetics, creating unique visual narratives rooted in technology. Both forms challenge perceptions, with painting rooted in classical techniques and glitch art embracing modern digital disruption.
Table of Comparison
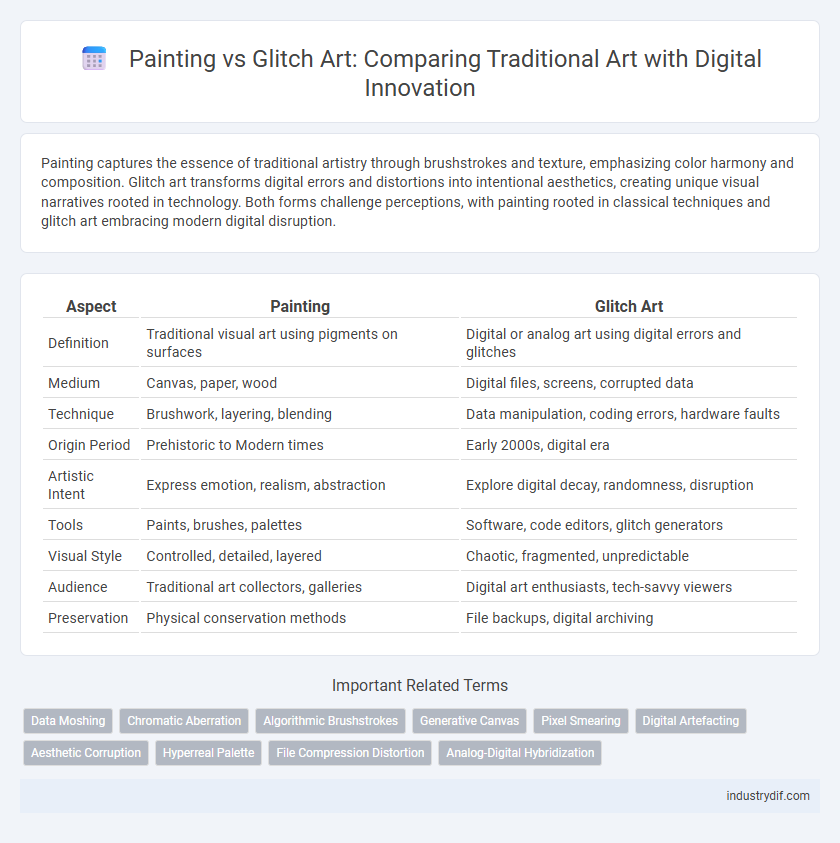
| Aspect | Painting | Glitch Art |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional visual art using pigments on surfaces | Digital or analog art using digital errors and glitches |
| Medium | Canvas, paper, wood | Digital files, screens, corrupted data |
| Technique | Brushwork, layering, blending | Data manipulation, coding errors, hardware faults |
| Origin Period | Prehistoric to Modern times | Early 2000s, digital era |
| Artistic Intent | Express emotion, realism, abstraction | Explore digital decay, randomness, disruption |
| Tools | Paints, brushes, palettes | Software, code editors, glitch generators |
| Visual Style | Controlled, detailed, layered | Chaotic, fragmented, unpredictable |
| Audience | Traditional art collectors, galleries | Digital art enthusiasts, tech-savvy viewers |
| Preservation | Physical conservation methods | File backups, digital archiving |
Understanding Traditional Painting Techniques
Traditional painting techniques involve mastery of materials like oil, acrylic, and watercolor, emphasizing brushwork, layering, and color theory to create depth and texture. Artists utilize methods such as glazing, impasto, and chiaroscuro to achieve realistic lighting and dimensionality. Understanding these foundational skills contrasts with Glitch Art's digital manipulation and intentional errors, highlighting the tactile precision inherent in classical painting.
Defining Glitch Art in the Digital Era
Glitch art, emerging from digital errors and technological malfunctions, redefines traditional painting by embracing imperfections and randomness as creative tools. Unlike classical painting, which relies on deliberate brushstrokes on canvas, glitch art utilizes corrupted digital files, software bugs, and hardware failures to produce visually striking, unpredictable compositions. This art form challenges conventional aesthetics by transforming digital disruptions into innovative expressions of contemporary culture and technology.
Historical Evolution: From Canvas to Code
Painting has historically evolved from traditional canvas techniques using oils and acrylics to exploring digital mediums, reflecting shifts in artistic tools and cultural contexts. Glitch art emerges in the digital era, manipulating errors and corrupted data to create visual aesthetics, marking a departure from classical forms toward code-driven creativity. This transition highlights a broader technological influence on art, where historical evolution bridges tangible brushstrokes with algorithmic disruption.
Key Materials and Tools Used in Each Medium
Painting traditionally relies on materials such as canvas, oil, acrylic, and watercolor paints, along with brushes, palettes, and easels to create textured and layered visuals. Glitch Art utilizes digital tools and techniques including software like Adobe Photoshop, Audacity, or custom code to manipulate pixels, data, and corrupted files, often embracing errors and glitches as creative elements. While painting prioritizes tactile, physical materials, Glitch Art emphasizes virtual technology and digital manipulation for its unique aesthetic.
Artistic Intent and Conceptual Frameworks
Painting traditionally emphasizes deliberate brushwork and compositional harmony to convey artist intention through color, texture, and form, rooted within established art historical narratives. Glitch art deliberately embraces digital errors and anomalies as a conceptual framework, challenging notions of perfection and control while exploring themes of technological disruption and entropy. Both practices prioritize meaning-making, yet painting often seeks aesthetic beauty and mastery, whereas glitch art foregrounds process, randomness, and the critique of digital culture.
Visual Language: Color, Composition, and Form
Painting utilizes traditional color theory and brush techniques to create harmonious compositions often centered on balance and depth, emphasizing form through controlled strokes and layering. Glitch Art exploits digital errors and pixel distortion to generate unpredictable color shifts, fragmented forms, and chaotic compositions that challenge traditional visual language. Both mediums manipulate color, composition, and form but diverge in method--painting prioritizes intentional structure while glitch art embraces randomness and technological disruption.
Audience Perception: Engagement and Interpretation
Painting traditionally invites audiences to engage through tactile textures, color harmonies, and representational imagery that evoke emotional and cultural narratives. Glitch art challenges viewers by presenting digital disruptions and fragmented visuals, prompting active interpretation and reflection on technology's role in aesthetics. Audience perception varies, with painting often fostering appreciation of skill and storytelling, while glitch art elicits curiosity and critical dialogue about imperfection and digital decay.
Exhibit and Distribution Channels
Traditional painting exhibits prioritize gallery spaces, museums, and art fairs, leveraging physical presence to engage audiences and collectors. Glitch art, often distributed through digital platforms, online galleries, and social media, capitalizes on virtual accessibility and global reach, allowing for immediate and interactive audience engagement. The dichotomy between tactile exhibition and digital dissemination shapes the visibility and market dynamics of each art form distinctly.
Preservation and Longevity Challenges
Painting, rooted in traditional materials like canvas and oil, faces challenges such as fading, cracking, and environmental degradation that require specialized conservation techniques to preserve its longevity. Glitch art, created through digital corruption or manipulation of electronic media, confronts unique preservation issues including software obsolescence, data corruption, and hardware dependency, making its long-term archiving complex and unstable. Preservation strategies for glitch art often involve documentation of the process and migration to updated formats, whereas painting relies on physical restoration and climate-controlled environments to maintain its integrity.
The Future of Artistic Expression: Painting and Glitch Art
Painting remains a timeless medium, evolving through contemporary techniques and digital integration to retain its cultural significance. Glitch art harnesses digital errors and technological malfunctions, pushing boundaries of creativity and challenging conventional aesthetics. Both forms represent dynamic futures of artistic expression, merging tradition with innovation in the digital age.
Related Important Terms
Data Moshing
Data moshing, a technique central to glitch art, manipulates digital video compression artifacts by intentionally corrupting frame data, creating unpredictable visual distortions that contrast with the intentional brushstrokes and color theory found in traditional painting. While painting emphasizes tactile materials and controlled composition, data moshing leverages digital errors to challenge conventional aesthetics and explore the intersection of technology and visual expression.
Chromatic Aberration
Chromatic aberration in painting often enhances depth and texture through deliberate color shifts, while glitch art exploits this optical distortion to challenge traditional aesthetics by emphasizing pixelated color fringes and digital errors. This contrast highlights the intentional craftsmanship in painting versus the accidental beauty derived from malfunction in glitch art.
Algorithmic Brushstrokes
Algorithmic brushstrokes in painting simulate traditional techniques using coded patterns to create intricate textures and dynamic compositions. In glitch art, algorithmic manipulation intentionally disrupts digital data, producing fragmented and unpredictable visuals that challenge conventional aesthetics.
Generative Canvas
Generative Canvas leverages algorithmic processes to create dynamic, evolving artworks that contrast the traditional brushstrokes and textures of painting with the digital distortion of Glitch Art. While painting emphasizes manual skill and materiality, Glitch Art and Generative Canvas explore randomness and code-based disruptions, offering new dimensions in contemporary visual expression.
Pixel Smearing
Pixel smearing in painting involves deliberate brushwork to blend colors and create textured transitions, whereas in glitch art, pixel smearing results from digital errors that distort imagery by shifting or stretching pixels unpredictably. This contrast highlights painting's controlled manipulation of form versus glitch art's embrace of accidental pixel disruption as an aesthetic technique.
Digital Artefacting
Digital artefacting in painting often manifests as subtle texture inconsistencies and color banding due to compression, whereas glitch art intentionally exploits these digital imperfections to create aesthetic disruption and visual chaos. While traditional digital painting aims for realism and clarity, glitch art embraces errors like pixelation, data corruption, and algorithmic distortion as integral artistic elements.
Aesthetic Corruption
Painting embodies controlled aesthetic expression through deliberate brushstrokes and composition, creating harmony and intentional beauty. Glitch Art embraces aesthetic corruption by manipulating digital errors and distortions, challenging traditional perceptions of art and beauty through chaos and randomness.
Hyperreal Palette
Hyperreal Palette in painting emphasizes precise color gradients and realistic textures to create lifelike imagery, enhancing visual depth and emotional impact. In contrast, Glitch Art manipulates digital errors and pixel distortions to produce fragmented, abstract aesthetics, often employing unexpected color shifts that challenge traditional color harmony.
File Compression Distortion
Painting preserves visual integrity with each brushstroke, maintaining consistent texture and color depth, while glitch art intentionally exploits file compression distortion artifacts such as pixelation and color shifts to create unpredictable aesthetic disruptions, emphasizing digital error as a creative element. The manipulation of compression algorithms in glitch art contrasts with painting's reliance on physical media, highlighting the interplay between traditional artistry and digital degradation processes.
Analog-Digital Hybridization
Painting and glitch art converge through analog-digital hybridization, merging traditional brushwork with digital disruptions to create innovative visual experiences. This fusion challenges conventional aesthetics by blending tactile textures with algorithmic errors, redefining boundaries between handcrafted and machine-generated art.
Painting vs Glitch Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com