Sculpture traditionally emphasizes the manipulation of materials like stone, metal, or clay to create three-dimensional art forms that often reflect cultural or personal expression. Eco-installations prioritize environmental themes by integrating natural elements and sustainable practices to foster ecological awareness and interact with their surroundings. Both art forms challenge perceptions, but eco-installations uniquely merge creativity with environmental activism, promoting harmony between art and nature.
Table of Comparison
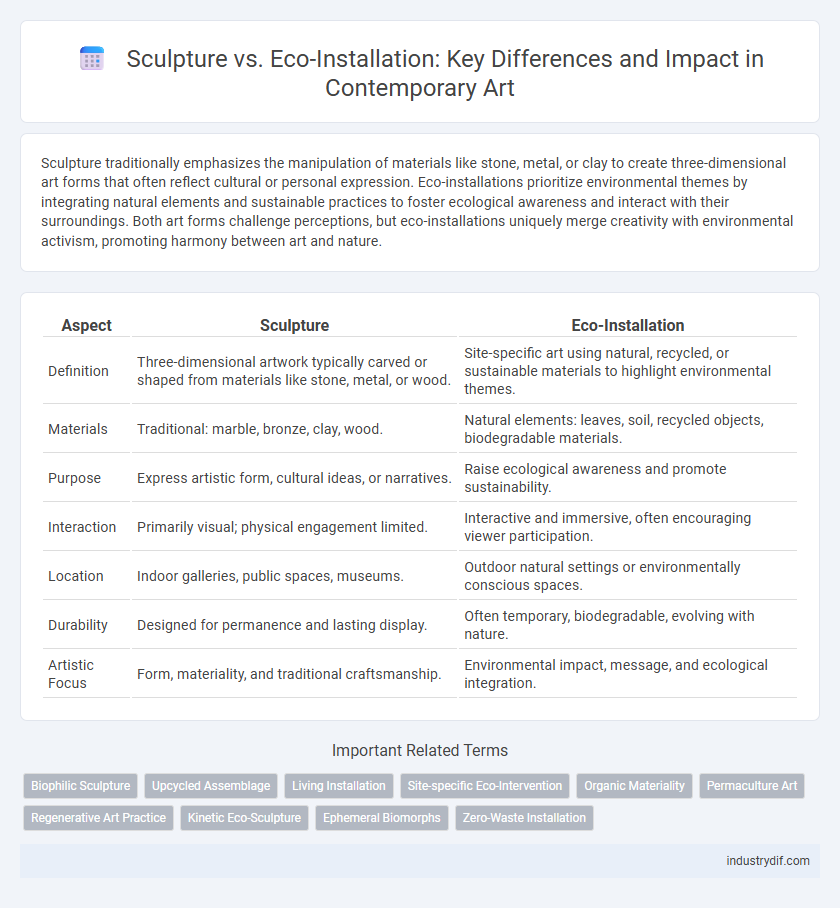
| Aspect | Sculpture | Eco-Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Three-dimensional artwork typically carved or shaped from materials like stone, metal, or wood. | Site-specific art using natural, recycled, or sustainable materials to highlight environmental themes. |
| Materials | Traditional: marble, bronze, clay, wood. | Natural elements: leaves, soil, recycled objects, biodegradable materials. |
| Purpose | Express artistic form, cultural ideas, or narratives. | Raise ecological awareness and promote sustainability. |
| Interaction | Primarily visual; physical engagement limited. | Interactive and immersive, often encouraging viewer participation. |
| Location | Indoor galleries, public spaces, museums. | Outdoor natural settings or environmentally conscious spaces. |
| Durability | Designed for permanence and lasting display. | Often temporary, biodegradable, evolving with nature. |
| Artistic Focus | Form, materiality, and traditional craftsmanship. | Environmental impact, message, and ecological integration. |
Defining Sculpture in Contemporary Art
Sculpture in contemporary art is defined by its three-dimensional form, often created through carving, modeling, or assembling materials such as stone, metal, or wood. Unlike eco-installations, which prioritize environmental interaction and sustainability, contemporary sculpture emphasizes materiality, form, and spatial presence. This distinction highlights traditional sculptural techniques while engaging with modern themes and innovative materials.
Understanding Eco-Installation: Core Principles
Eco-installations emphasize sustainability by integrating natural materials and environments to create immersive, site-specific artwork that promotes ecological awareness. Unlike traditional sculptures, these installations prioritize the interaction between the artwork, nature, and viewers, fostering a deeper connection to environmental issues. Core principles include biodegradability, minimal environmental impact, and often temporal existence, challenging conventional notions of permanence in art.
Historical Evolution of Sculptural Art
Sculptural art has evolved from classical marble and bronze figures symbolizing religious and cultural values to contemporary eco-installations that incorporate natural materials and environmental themes. Traditional sculpture emphasized form, permanence, and human craftsmanship, while eco-installations prioritize sustainability, interactivity, and ecological awareness. This shift reflects broader changes in artistic priorities and societal concerns over the last century.
The Rise of Environmental Themes in Art
Environmental themes in art have gained prominence as artists use sculpture and eco-installation to address ecological concerns and promote sustainability. Sculptures often incorporate natural materials or recycled objects to highlight environmental issues, while eco-installations immerse viewers in interactive spaces that emphasize the relationship between humans and nature. This rise reflects a broader cultural shift toward environmental awareness and a commitment to artistic practices that inspire ecological responsibility.
Materials: Traditional Sculpture vs. Sustainable Choices
Traditional sculpture often employs materials like marble, bronze, and wood, prized for their durability and aesthetic qualities but frequently sourced through environmentally taxing methods. Eco-installations prioritize sustainable materials such as reclaimed wood, recycled metals, and biodegradable elements to minimize ecological impact and promote environmental awareness. The shift towards eco-friendly materials reflects a growing commitment within the art community to blend creative expression with sustainability.
Techniques: Crafting vs. Assembling
Sculpture techniques emphasize meticulous crafting through carving, modeling, or casting to shape materials like stone, metal, or clay into enduring forms. Eco-installations prioritize assembling natural and recycled components, often using found objects, to create site-specific, environmentally conscious artworks. Both approaches highlight tactile engagement but differ in material manipulation and conceptual focus on permanence versus ecological interaction.
Audience Interaction: Static Display vs. Immersive Experience
Sculptures typically present a static display where audiences observe the artwork from a fixed perspective, emphasizing form, texture, and materiality. Eco-installations offer an immersive experience, inviting viewers to engage with natural elements and spatial dynamics, often blurring the boundaries between art and environment. This active participation fosters a deeper emotional and sensory connection, transforming the audience from passive observers into co-creators within the artistic ecosystem.
Conceptual Intent: Aesthetic Form vs. Environmental Message
Sculpture traditionally prioritizes aesthetic form, emphasizing shape, texture, and material to evoke emotional or intellectual responses through visual beauty or abstract expression. Eco-installations focus on conveying environmental messages, integrating natural elements or recycled materials to raise awareness about ecological issues and promote sustainability. The conceptual intent of sculptures centers on artistic innovation and sensory engagement, while eco-installations critically engage viewers in environmental discourse and activism.
Longevity and Ephemerality in Artworks
Sculpture typically embodies longevity through durable materials such as bronze, marble, and stone, allowing artworks to withstand time and environmental factors, often preserving artistic intent for centuries. Eco-installations emphasize ephemerality, using organic, biodegradable materials that interact with natural processes, highlighting themes of change, decay, and environmental cycles. The contrast between sculpture and eco-installation underscores differing artistic philosophies: permanence versus temporality, as well as fixed form versus dynamic transformation.
Future Trends: Merging Sculpture and Eco-Installation
Future trends in the arts reveal a growing fusion of sculpture and eco-installation, where traditional sculptural forms are enhanced with sustainable materials and environmental themes. Artists increasingly employ biodegradable elements, solar-powered components, and interactive ecosystems to create immersive experiences that raise ecological awareness. This merging not only redefines spatial aesthetics but also promotes environmental activism through innovative, multidisciplinary approaches.
Related Important Terms
Biophilic Sculpture
Biophilic sculpture integrates natural elements and organic forms to foster a connection between people and the environment, emphasizing sustainability and ecological awareness. Unlike traditional sculptures, eco-installations prioritize environmental interaction and living materials, creating immersive experiences that promote environmental stewardship and enhance well-being.
Upcycled Assemblage
Upcycled assemblage in sculpture transforms discarded materials into innovative art forms, emphasizing sustainability and creative reuse. Eco-installations integrate these upcycled elements into immersive environments, fostering environmental awareness through visually impactful, site-specific works.
Living Installation
Living installations in eco-art integrate organic materials and living organisms to create dynamic sculptures that evolve over time, emphasizing sustainability and environmental interaction. Unlike traditional static sculptures, these installations transform with natural growth, highlighting ecological processes and fostering a deeper connection between art and nature.
Site-specific Eco-Intervention
Site-specific eco-interventions integrate sustainable materials and environmental awareness directly into the landscape, contrasting traditional sculptures often isolated from ecological context. These eco-installations actively engage with the local ecosystem, promoting habitat restoration and reducing environmental impact while redefining artistic interaction with nature.
Organic Materiality
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes solid, enduring materials like stone, metal, and wood, while eco-installations prioritize organic materiality by integrating living plants, biodegradable elements, and natural processes to create transient, environmentally conscious art. This focus on organic materiality in eco-installations fosters a dynamic interaction between the artwork and its ecosystem, highlighting themes of sustainability and ecological interdependence.
Permaculture Art
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes form and material, while eco-installation integrates Permaculture Art principles, promoting sustainability and ecological harmony through living materials and regenerative design. Permaculture-based eco-installations transform spaces by embedding natural systems, encouraging biodiversity and environmental resilience within artistic expression.
Regenerative Art Practice
Sculpture traditionally emphasizes form and material permanence, while eco-installation integrates living elements to restore and harmonize natural ecosystems, embodying regenerative art practice. This approach not only creates aesthetic value but actively promotes environmental healing and sustainability through interactive, site-specific interventions.
Kinetic Eco-Sculpture
Kinetic eco-sculpture merges movement with environmental consciousness, utilizing renewable energy sources and natural materials to create dynamic artworks that interact with their surroundings. Unlike traditional sculpture, these installations prioritize sustainability and ecological impact while engaging viewers through evolving kinetic forms.
Ephemeral Biomorphs
Ephemeral biomorphs in sculpture emphasize transient forms crafted from natural materials, highlighting the interplay between organic decay and artistic expression. Eco-installations extend this concept by integrating living ecosystems, fostering sustainability and environmental awareness through immersive, temporally bound experiences.
Zero-Waste Installation
Zero-waste installations prioritize sustainability by using reclaimed materials and avoiding any waste production, contrasting with traditional sculpture which may involve resource-heavy processes and non-recyclable materials. Eco-installations emphasize environmental impact reduction, integrating natural elements and biodegradable components to create art that harmonizes with ecological principles.
Sculpture vs Eco-Installation Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com