Traditional art emphasizes handcrafted techniques and materials, showcasing the artist's direct skill and tactile connection to the medium. Generative art leverages algorithms and computational processes, creating dynamic, often unpredictable visual experiences that evolve with code. Both forms challenge perceptions of creativity, blending human intention with unique methods of expression.
Table of Comparison
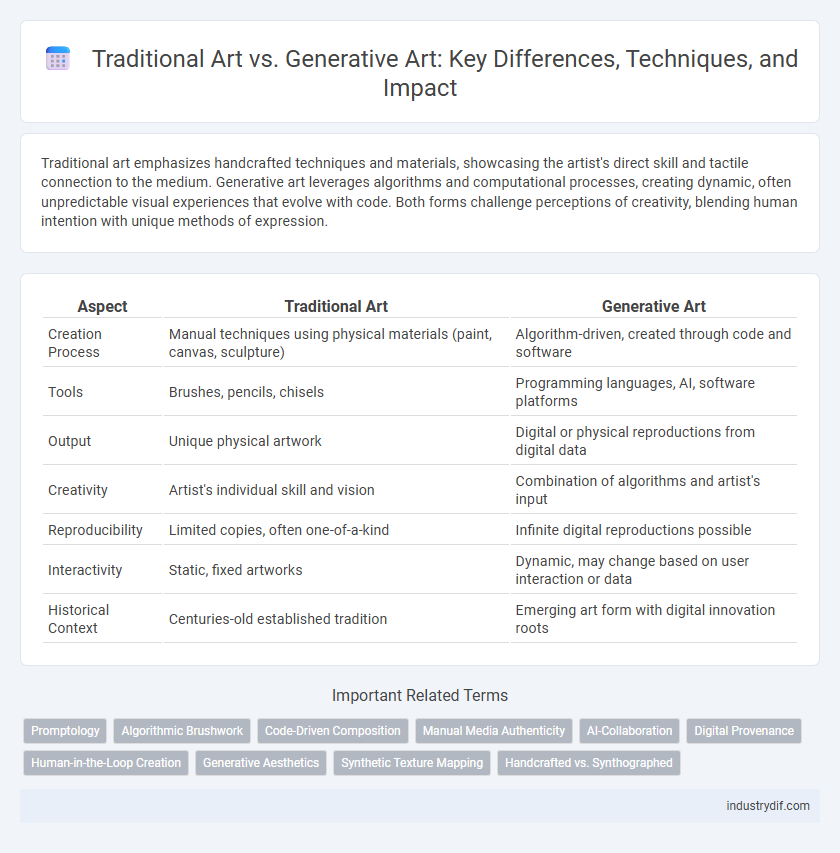
| Aspect | Traditional Art | Generative Art |
|---|---|---|
| Creation Process | Manual techniques using physical materials (paint, canvas, sculpture) | Algorithm-driven, created through code and software |
| Tools | Brushes, pencils, chisels | Programming languages, AI, software platforms |
| Output | Unique physical artwork | Digital or physical reproductions from digital data |
| Creativity | Artist's individual skill and vision | Combination of algorithms and artist's input |
| Reproducibility | Limited copies, often one-of-a-kind | Infinite digital reproductions possible |
| Interactivity | Static, fixed artworks | Dynamic, may change based on user interaction or data |
| Historical Context | Centuries-old established tradition | Emerging art form with digital innovation roots |
Defining Traditional Art and Generative Art
Traditional Art encompasses techniques such as painting, sculpture, and drawing that rely on manual skill and physical materials, reflecting centuries-old practices and cultural heritage. Generative Art involves the use of algorithms and computational processes to create artworks, often resulting in dynamic, evolving, or interactive pieces driven by software and artificial intelligence. Both forms redefine creative expression, with Traditional Art emphasizing human craftsmanship and Generative Art highlighting technological innovation.
Historical Evolution of Artistic Techniques
Traditional art techniques, such as oil painting, fresco, and sculpture, have evolved over centuries, reflecting cultural shifts and technological advancements from the Renaissance to the modern era. Generative art leverages algorithms, artificial intelligence, and computational processes, emerging prominently in the late 20th and early 21st centuries as digital technology advanced. This transition marks a significant shift in artistic creation, blending historical craftsmanship with innovative digital methodologies.
Core Principles and Aesthetics
Traditional art centers on manual techniques, emphasizing craftsmanship, tactile materials, and the artist's direct physical interaction with mediums like paint, clay, or fabric. Generative art leverages algorithms, code, and computational processes to create dynamic, often unpredictable visuals, prioritizing systems and variability over fixed forms. The aesthetics of traditional art reflect tangible textures and intentional human expression, while generative art highlights complexity, randomness, and machine-driven creativity.
Tools, Materials, and Creative Processes
Traditional art relies heavily on physical tools such as brushes, canvases, sculpting clay, and pigments, requiring hands-on techniques and tactile engagement to create textures and depth. Generative art utilizes digital software, algorithms, and AI-driven tools to produce artworks through code-driven processes, enabling rapid iteration and complex pattern generation beyond manual capabilities. Creative processes in traditional art emphasize skillful manipulation of materials, while generative art combines artistic intention with computational randomness, expanding possibilities for innovation and hybrid expressions.
Authorship and Artistic Intent
Traditional art emphasizes individual authorship and intentionality, with artists directly crafting each piece to convey personal vision and emotional depth. Generative art leverages algorithms and autonomous systems, shifting authorship from the artist alone to a collaboration between human creativity and machine processes. Artistic intent in generative art is often embedded in coding choices and parameters, allowing unpredictable and emergent aesthetics driven by computational logic.
Audience Engagement and Experience
Traditional art offers a tactile and intimate experience, allowing audiences to connect deeply through physical presence and texture, fostering personal reflection. Generative art leverages algorithms and interactivity to create dynamic, evolving pieces that engage viewers by requiring active participation and offering unique, repeatable experiences. Audiences of generative art often encounter personalized visual narratives, enhancing emotional engagement through real-time responsiveness and innovation.
Authenticity and Originality in Art
Traditional art emphasizes authenticity through the unique handcraftsmanship and historical context embedded in each piece, reflecting the artist's direct touch and cultural heritage. Generative art challenges conventional notions by using algorithms to produce originality, where the creative process is driven by code rather than solely by human intention. Authenticity in generative art emerges from the innovative integration of technology and artistic vision, redefining originality in the digital age.
Market Trends and Art Collecting
Traditional art continues to hold significant value in the art market, with collectors favoring established artists and tangible mediums such as oil paintings and sculptures. Generative art, driven by algorithms and AI, is rapidly gaining traction, appealing to tech-savvy collectors and attracting high-profile sales in digital auction platforms. Market data shows a growing investment in NFTs and blockchain-verified works, signaling a shift toward digital provenance and new forms of art ownership.
Ethical Considerations in Art Creation
Ethical considerations in traditional art revolve around authenticity, cultural appropriation, and the moral responsibilities of the artist towards their subject and audience. In generative art, concerns focus on algorithmic bias, intellectual property rights, and the transparency of the AI's role in the creative process. Addressing these ethical challenges requires ongoing dialogue between artists, technologists, and ethicists to ensure respectful and responsible art creation.
Future Trajectories of the Art World
Traditional art, rooted in manual techniques and historical craftsmanship, continues to influence contemporary aesthetics, while generative art leverages artificial intelligence and algorithmic processes to create dynamic, evolving pieces. Future trajectories suggest a hybridization where artists integrate AI tools to expand creative boundaries, fostering new art forms that challenge conventional narratives. The art world is poised for transformative shifts as technology enhances artistic expression, democratizes creation, and redefines authorship in both physical and digital realms.
Related Important Terms
Promptology
Promptology in generative art leverages algorithm-driven inputs and precise language to create dynamic artworks, contrasting with traditional art's reliance on manual techniques and physical materials. The evolving expertise in crafting detailed prompts enhances the complexity and originality of AI-generated pieces, reshaping creative processes and artistic expression.
Algorithmic Brushwork
Algorithmic brushwork in generative art employs computational algorithms to simulate painting techniques, producing intricate patterns and textures unattainable through traditional manual brushstrokes. Traditional art relies on the tactile precision and expressive nuances of human hand movements, while generative art leverages code-driven randomness and iteration to innovate visual aesthetics dynamically.
Code-Driven Composition
Traditional art relies on manual techniques and physical materials, emphasizing human craftsmanship and historical methods, while generative art uses algorithmic code and computational processes to create dynamic, often unpredictable compositions. Code-driven composition in generative art enables artists to explore complex patterns, automate creative decisions, and produce unique visual outputs that evolve with parameters set by the programmer.
Manual Media Authenticity
Traditional art embodies manual media authenticity through tactile techniques and direct human expression, preserving unique imperfections and textures that reflect the artist's individual touch. Generative art, while innovative in algorithmic creation, often lacks the intrinsic authenticity rooted in hands-on craftsmanship that defines traditional artistic value.
AI-Collaboration
Traditional art relies on manual techniques passed down through generations, emphasizing human creativity and tactile skills, while generative art incorporates AI algorithms to produce dynamic and evolving visuals, expanding the boundaries of artistic expression. Collaboration between artists and AI enables innovative hybrid artworks that blend human intuition with machine-driven patterns, fostering new creative possibilities in the art world.
Digital Provenance
Traditional art relies on physical provenance documented through certificates and gallery records, ensuring authenticity via tangible history tracing. Generative art leverages blockchain technology for immutable digital provenance, embedding creation data and ownership directly within the art's metadata to prevent forgery.
Human-in-the-Loop Creation
Human-in-the-loop creation in traditional art emphasizes direct artist intervention, craftsmanship, and emotional expression, preserving the authenticity and uniqueness of each piece. Generative art integrates algorithmic processes with human input, enabling artists to guide and refine AI-generated outputs, fostering innovative collaborations between human creativity and computational techniques.
Generative Aesthetics
Generative art utilizes algorithms and computational processes to create aesthetically complex works that evolve beyond traditional artistic methods, emphasizing dynamic patterns and emergent properties. This approach challenges conventional artistry by integrating randomness, iteration, and code-driven design, fostering unique visual outcomes rooted in generative aesthetics.
Synthetic Texture Mapping
Traditional art relies on manual techniques to create textures directly on physical surfaces, emphasizing tactile authenticity and organic variation. Generative art employs synthetic texture mapping using algorithms to simulate complex, dynamic surfaces, enabling infinite customization and consistency in digital artworks.
Handcrafted vs. Synthographed
Traditional art showcases the meticulous skills of artists through handcrafted techniques such as painting, sculpting, and drawing, emphasizing tactile interaction and unique imperfections. Generative art, or Synthographed art, leverages algorithms and artificial intelligence to create complex, data-driven visuals that evolve beyond human limitations, highlighting the fusion of technology and creativity.
Traditional Art vs Generative Art Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com