Email offers widespread accessibility and ease of use but often lacks robust security features, making sensitive information vulnerable to interception. Encrypted messaging provides enhanced privacy by protecting messages through end-to-end encryption, ensuring data remains confidential between sender and recipient. Choosing between email and encrypted messaging depends on the balance needed between convenience and security for effective communication.
Table of Comparison
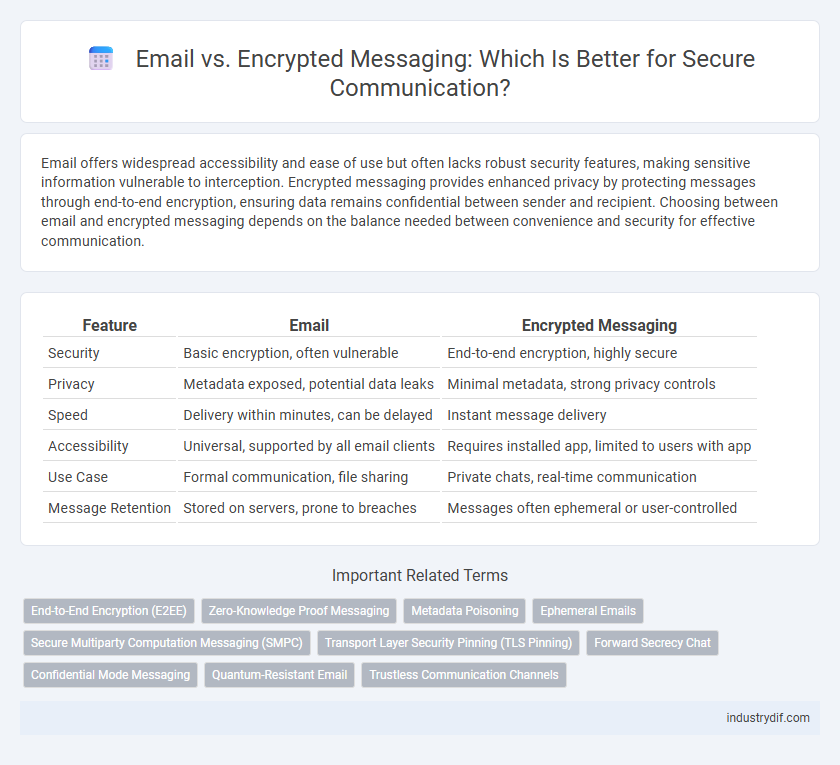
| Feature | Encrypted Messaging | |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Basic encryption, often vulnerable | End-to-end encryption, highly secure |
| Privacy | Metadata exposed, potential data leaks | Minimal metadata, strong privacy controls |
| Speed | Delivery within minutes, can be delayed | Instant message delivery |
| Accessibility | Universal, supported by all email clients | Requires installed app, limited to users with app |
| Use Case | Formal communication, file sharing | Private chats, real-time communication |
| Message Retention | Stored on servers, prone to breaches | Messages often ephemeral or user-controlled |
Overview of Email and Encrypted Messaging
Email enables the exchange of digital messages through centralized servers, making it accessible and widely used for both personal and professional communication. Encrypted messaging uses end-to-end encryption protocols to secure conversations, ensuring that only the sender and recipient can access the content. While email offers ease of use and broad compatibility, encrypted messaging prioritizes privacy and data security against unauthorized access.
Core Differences Between Email and Encrypted Messaging
Email transmits messages through servers with standard protocols, often lacking end-to-end encryption, making it vulnerable to interception. Encrypted messaging employs robust cryptographic techniques to secure content from sender to recipient, ensuring confidentiality and data integrity. Unlike email, encrypted messaging platforms typically include built-in authentication and real-time delivery features, enhancing privacy and user trust.
Security and Privacy: Email vs Encrypted Messaging
Email communication, while widely used, often lacks end-to-end encryption, exposing messages to potential interceptions and unauthorized access. Encrypted messaging platforms implement robust cryptographic protocols like Signal Protocol, ensuring that only intended recipients can read the content, significantly enhancing security and privacy. Employing encrypted messaging reduces risks of data breaches, making it the preferred choice for confidential and sensitive communications.
User Authentication and Identity Verification
User authentication in email typically relies on password protection and two-factor authentication to verify identity, though it remains vulnerable to phishing attacks and credential theft. Encrypted messaging platforms enhance security by incorporating end-to-end encryption combined with robust identity verification methods such as biometric authentication and cryptographic keys. This dual approach ensures that message content remains confidential while confirming the sender's and receiver's identities, significantly reducing the risk of impersonation or unauthorized access.
Encryption Protocols: Standards and Practices
Email typically relies on Transport Layer Security (TLS) for encryption during transmission, but standard email protocols like SMTP, IMAP, and POP3 lack end-to-end encryption, exposing messages to potential interception. Encrypted messaging apps use protocols such as Signal Protocol and Double Ratchet, providing robust end-to-end encryption, ensuring that only communicating users can decrypt messages. Industry standards like OpenPGP and S/MIME enhance email security through encryption and digital signatures but depend on user implementation and key management, which can complicate usability and adoption compared to integrated encrypted messaging solutions.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Email communication often faces challenges in meeting compliance standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and FINRA due to vulnerabilities in data transmission and storage. Encrypted messaging solutions provide enhanced security features like end-to-end encryption and advanced access controls, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements for data protection and privacy. Organizations prioritizing compliance frequently adopt encrypted messaging to mitigate risks of data breaches and regulatory penalties.
Use Cases in Corporate Communication
Email remains the predominant tool for formal corporate communication due to its compatibility with a wide range of business applications and archiving systems. Encrypted messaging is essential for transmitting sensitive information, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Organizations increasingly adopt hybrid communication strategies, employing email for routine correspondence and encrypted messaging platforms like Signal or Wickr for confidential discussions and real-time collaboration.
Integration with Existing Communication Systems
Email seamlessly integrates with most existing communication systems, leveraging established protocols like SMTP, IMAP, and POP3 to ensure broad compatibility across platforms and devices. Encrypted messaging often requires specialized applications or plugins, which may pose challenges for integration with legacy systems and enterprise communication infrastructures. Businesses prioritize solutions that balance strong security with ease of integration to maintain efficient workflows and data consistency.
Scalability and Cost Implications
Email systems offer high scalability due to established infrastructure and widespread user adoption, enabling cost-effective communication across large audiences with minimal incremental expenses. Encrypted messaging, while providing enhanced security and privacy through end-to-end encryption protocols like Signal and WhatsApp, can introduce higher costs related to infrastructure maintenance, encryption key management, and compliance with data protection regulations. Organizations must balance the scalability benefits of traditional email with the increased operational expenses of encrypted messaging platforms when prioritizing secure communication strategies.
Future Trends in Secure Digital Communication
Encrypted messaging is set to dominate future secure digital communication due to advanced end-to-end encryption protocols ensuring data privacy and protection against cyber threats. Email platforms are increasingly integrating encryption standards like TLS and S/MIME to enhance security but still lag behind instant, encrypted messaging apps in real-time confidentiality. Emerging technologies such as blockchain for decentralized verification and AI-driven threat detection are transforming secure communication landscapes, favoring encrypted messaging solutions.
Related Important Terms
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Email typically lacks default End-to-End Encryption (E2EE), making messages vulnerable to interception during transmission or on mail servers. Encrypted messaging platforms implement robust E2EE protocols, ensuring that only the sender and recipient can read the content, significantly enhancing communication privacy and security.
Zero-Knowledge Proof Messaging
Zero-Knowledge Proof Messaging enhances communication security by allowing message verification without revealing content, offering a stronger privacy layer compared to traditional email protocols. This cryptographic approach ensures that only authorized parties can access message data, eliminating risks of interception inherent in standard email exchanges.
Metadata Poisoning
Email communication is vulnerable to metadata poisoning, where attackers manipulate headers to obscure information or impersonate users, compromising message authenticity. Encrypted messaging protocols like Signal employ end-to-end encryption and minimize metadata exposure, significantly reducing risks associated with metadata poisoning attacks.
Ephemeral Emails
Ephemeral emails offer a secure alternative to traditional email by automatically deleting messages after a set time, reducing digital footprints and exposure to data breaches. Unlike encrypted messaging, which focuses on end-to-end encryption for privacy during transmission, ephemeral emails emphasize temporary accessibility, enhancing confidentiality in sensitive communications.
Secure Multiparty Computation Messaging (SMPC)
Secure Multiparty Computation Messaging (SMPC) enhances privacy by enabling multiple parties to jointly compute functions over their inputs while keeping those inputs private, surpassing traditional email encryption methods in confidentiality. Unlike standard encrypted email protocols, SMPC ensures that no individual participant gains access to the complete message data, making it ideal for highly sensitive communications.
Transport Layer Security Pinning (TLS Pinning)
Transport Layer Security (TLS) pinning enhances encrypted messaging by binding a specific server certificate to prevent man-in-the-middle attacks, offering a higher level of security compared to standard email protocols that often lack strict certificate validation. Unlike traditional email services vulnerable to interception, TLS pinning in encrypted messaging ensures end-to-end confidentiality and integrity by verifying the authenticity of communication endpoints during the transport layer handshake.
Forward Secrecy Chat
Forward Secrecy in encrypted messaging ensures that even if long-term keys are compromised, past communications remain secure by generating unique session keys for each conversation, a feature typically absent in traditional email systems. This enhanced security model protects sensitive information from retrospective decryption, making encrypted messaging more reliable for privacy-focused communication compared to standard email protocols.
Confidential Mode Messaging
Confidential Mode Messaging enhances email security by allowing senders to set expiration dates and revoke access, minimizing the risk of unauthorized forwarding, copying, or downloading of sensitive content. Unlike standard encrypted messaging apps that rely on end-to-end encryption for message privacy, confidential mode integrates seamlessly with traditional email platforms, providing an extra layer of control without requiring recipients to use specialized software.
Quantum-Resistant Email
Quantum-resistant email leverages advanced cryptographic algorithms such as lattice-based and hash-based encryption to protect messages from the threat of quantum computing attacks, ensuring long-term confidentiality and integrity. Unlike traditional encrypted messaging, this approach integrates seamlessly with existing email infrastructure, providing enhanced security without sacrificing usability or interoperability.
Trustless Communication Channels
Email relies on centralized servers vulnerable to interception, making encrypted messaging protocols like Signal and Matrix essential for trustless communication channels that ensure end-to-end encryption without requiring mutual trust in intermediaries. These decentralized messaging platforms use cryptographic keys to provide confidentiality, integrity, and authentication, eliminating risks inherent in traditional email systems.
Email vs Encrypted Messaging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com