Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and a deeper sense of connection through nonverbal cues such as body language and facial expressions. Asynchronous communication allows for flexible response times, facilitating thoughtful and well-crafted messages without the pressure of instant replies. Each mode offers distinct advantages that suit different contexts, making it essential to choose based on the communication goals and situational needs.
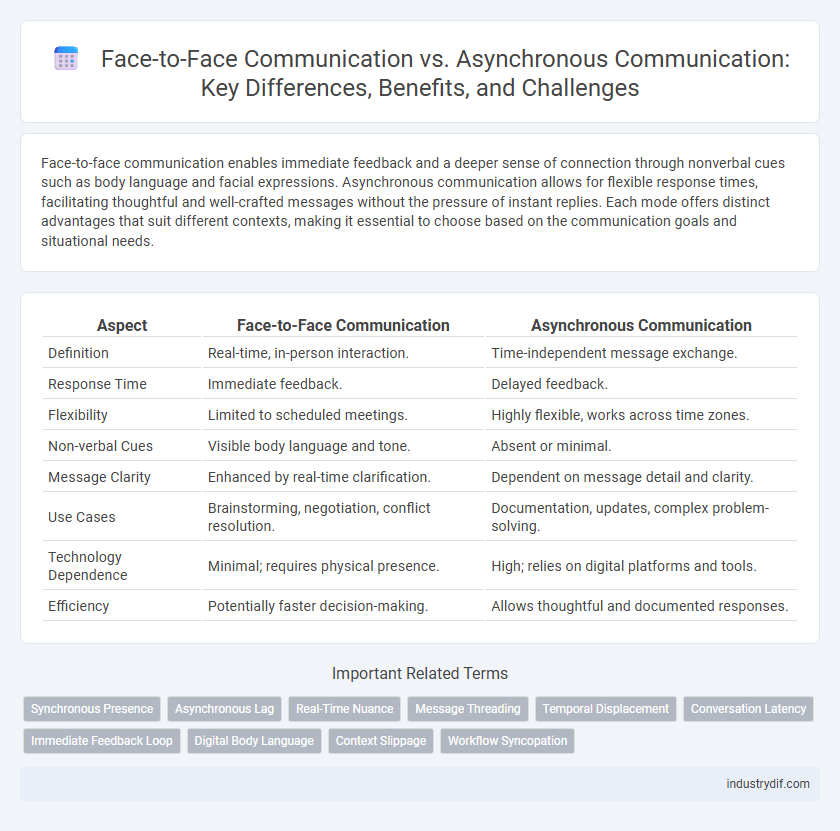
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Communication | Asynchronous Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, in-person interaction. | Time-independent message exchange. |
| Response Time | Immediate feedback. | Delayed feedback. |
| Flexibility | Limited to scheduled meetings. | Highly flexible, works across time zones. |
| Non-verbal Cues | Visible body language and tone. | Absent or minimal. |
| Message Clarity | Enhanced by real-time clarification. | Dependent on message detail and clarity. |
| Use Cases | Brainstorming, negotiation, conflict resolution. | Documentation, updates, complex problem-solving. |
| Technology Dependence | Minimal; requires physical presence. | High; relies on digital platforms and tools. |
| Efficiency | Potentially faster decision-making. | Allows thoughtful and documented responses. |
Defining Face-to-Face Communication
Face-to-face communication involves direct, real-time interaction between individuals in the same physical space, allowing for immediate feedback and nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. This mode of communication enhances clarity and emotional connection, fostering deeper understanding and trust between participants. Face-to-face communication is essential in contexts requiring collaboration, conflict resolution, and nuanced discussions where instant responses and personal engagement are critical.
Understanding Asynchronous Communication
Asynchronous communication enables individuals to exchange messages without needing real-time responses, allowing participants to process information at their convenience. This mode often relies on written formats such as emails, messaging apps, and forums, promoting thoughtful and deliberate interactions. Enhanced flexibility and reduced time-zone constraints make asynchronous communication especially valuable for distributed teams and remote collaboration.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Methods
Face-to-face communication enables real-time interaction with immediate feedback, enhancing non-verbal cue interpretation and fostering stronger personal connections. Asynchronous communication, such as email or messaging platforms, allows participants to respond at their convenience, facilitating flexibility across different time zones and reducing pressure for instant replies. Key differences include immediacy, with synchronous methods requiring simultaneous participation, while asynchronous methods support delayed responses and improved time management.
Benefits of Face-to-Face Communication in the Workplace
Face-to-face communication in the workplace enhances clarity through real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and reducing misunderstandings. It fosters stronger interpersonal relationships and trust among team members, which boosts collaboration and morale. Non-verbal cues such as body language and facial expressions further enrich understanding and improve conflict resolution.
Advantages of Asynchronous Communication for Remote Teams
Asynchronous communication allows remote teams to work across different time zones without the need for simultaneous presence, enhancing productivity and flexibility. It provides team members the opportunity to thoughtfully craft responses, reducing miscommunication and increasing clarity. This mode of communication also helps in maintaining comprehensive records, which facilitates better project tracking and accountability.
Challenges and Limitations of In-Person Interactions
Face-to-face communication often faces challenges such as time constraints and location dependence, limiting flexibility and accessibility for participants. Nonverbal cues may be misinterpreted, leading to misunderstandings and reduced message clarity. Furthermore, in-person interactions can be affected by environmental distractions and social anxiety, hindering effective information exchange.
Common Tools Used for Asynchronous Communication
Common tools used for asynchronous communication include email, messaging apps like Slack and Microsoft Teams, and project management platforms such as Asana and Trello. These tools enable users to send and receive messages, share files, and collaborate on tasks without requiring simultaneous participation. This mode of communication supports flexibility and time management by allowing participants to respond at their convenience.
Impact on Collaboration and Team Productivity
Face-to-face communication enhances collaboration by enabling immediate feedback, fostering trust, and facilitating real-time problem-solving, which significantly boosts team productivity. In contrast, asynchronous communication provides flexibility, allowing team members to contribute thoughtfully across different time zones, but may slow decision-making and hinder spontaneous idea exchange. Balancing both methods optimizes teamwork by combining the strengths of direct interaction with the convenience of time-independent communication.
Choosing the Right Communication Method for Your Organization
Face-to-face communication enhances clarity and builds trust through immediate feedback and nonverbal cues, making it ideal for complex discussions or sensitive topics within organizations. Asynchronous communication, leveraging emails, messaging apps, and shared documents, supports flexibility and productivity across different time zones and schedules, facilitating thoughtful responses and documentation. Selecting the right communication method depends on factors such as the urgency of the message, the need for collaboration, team dynamics, and the organization's culture and technological infrastructure.
Future Trends in Workplace Communication Dynamics
Future trends in workplace communication dynamics emphasize the integration of face-to-face communication with advanced asynchronous tools to enhance productivity and flexibility. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) are transforming virtual interactions to closely mimic in-person experiences while allowing time-shifted collaboration. Organizations increasingly prioritize hybrid communication models that balance real-time engagement with asynchronous methods to accommodate diverse work schedules and global teams.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Presence
Synchronous presence in face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback, richer emotional expression, and non-verbal cue interpretation, enhancing mutual understanding and collaboration. Asynchronous communication lacks real-time interaction, often delaying responses and reducing the ability to convey tone and urgency effectively.
Asynchronous Lag
Asynchronous communication often involves a time lag between messages, which can delay decision-making and reduce immediacy compared to face-to-face interactions. This lag impacts the flow of information, causing potential misunderstandings and decreasing collaborative efficiency in team environments.
Real-Time Nuance
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and captures real-time nuances such as tone, body language, and facial expressions, which enrich understanding and emotional connection. Asynchronous communication lacks this immediacy, often leading to delayed responses and potential misinterpretations due to the absence of immediate contextual cues.
Message Threading
Face-to-face communication allows immediate feedback and nonverbal cues, enhancing message clarity and reducing misunderstandings, while asynchronous communication relies heavily on message threading to maintain context and coherence over time. Effective message threading in asynchronous platforms organizes conversations into chronological or thematic sequences, enabling participants to track discussions and respond thoughtfully despite time delays.
Temporal Displacement
Face-to-face communication offers real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback and dynamic verbal and nonverbal cues, which fosters clearer understanding and quicker decision-making. Asynchronous communication, characterized by temporal displacement, allows participants to respond at their convenience, supporting flexibility but potentially delaying information exchange and reducing the immediacy of feedback.
Conversation Latency
Face-to-face communication exhibits minimal conversation latency, enabling instant feedback, spontaneous interaction, and nonverbal cues that enhance understanding and emotional connection. Asynchronous communication involves significant delays between messages, allowing flexible response times but potentially leading to misinterpretation and slower decision-making processes.
Immediate Feedback Loop
Face-to-face communication enables an immediate feedback loop, allowing participants to quickly clarify misunderstandings and adapt their messages based on nonverbal cues such as facial expressions and tone of voice. In contrast, asynchronous communication delays feedback, which can slow decision-making and reduce the effectiveness of real-time problem-solving in collaborative environments.
Digital Body Language
Digital body language in asynchronous communication includes response time, message length, and emoji usage, which convey emotions and intent without physical presence. Face-to-face communication relies on visual and auditory cues like facial expressions, tone, and posture, providing richer context for interpreting messages and enhancing interpersonal understanding.
Context Slippage
Face-to-face communication allows immediate feedback and rich contextual cues, reducing the risk of context slippage that commonly occurs in asynchronous communication, where delays and lack of nonverbal signals often lead to misunderstandings. Asynchronous communication, while flexible for time zones and schedules, requires explicit context reinforcement to maintain clarity and prevent message distortion.
Workflow Syncopation
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and real-time collaboration, minimizing workflow syncopation by aligning team members' understanding instantly. In contrast, asynchronous communication can cause delays and misalignment in workflow synchronization due to lag in response times and staggered information exchange.
Face-to-Face Communication vs Asynchronous Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com