Face-to-face communication allows for immediate feedback, rich nonverbal cues, and dynamic interaction, enhancing understanding and emotional connection. Asynchronous messaging provides flexibility and time to craft thoughtful responses, making it ideal for complex or non-urgent communication across different time zones. Combining both methods optimizes clarity and efficiency in personal and professional exchanges.
Table of Comparison
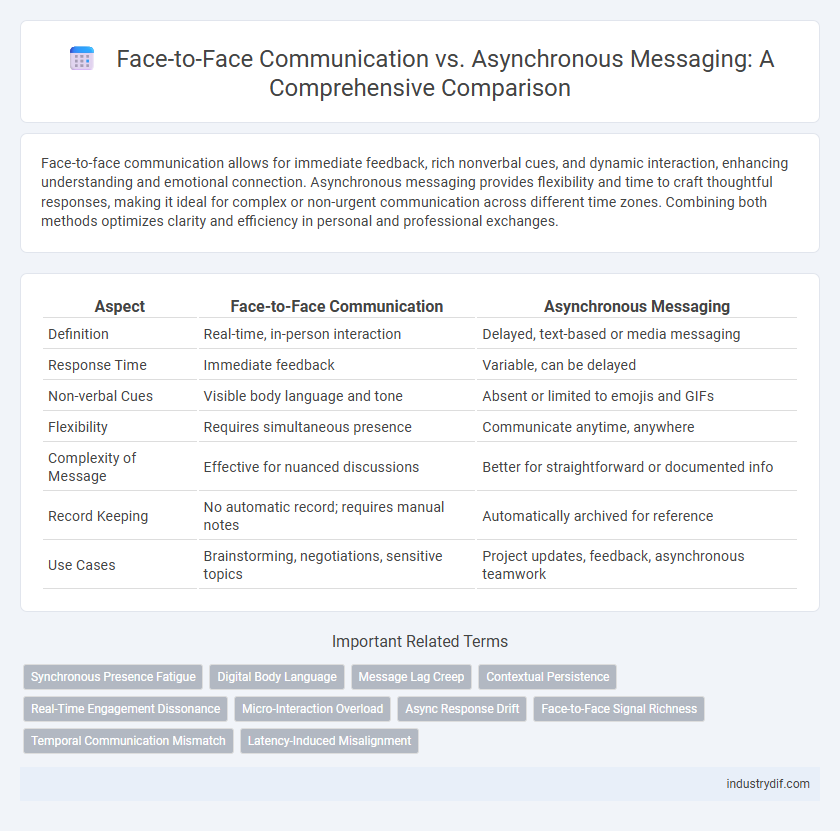
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Communication | Asynchronous Messaging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, in-person interaction | Delayed, text-based or media messaging |
| Response Time | Immediate feedback | Variable, can be delayed |
| Non-verbal Cues | Visible body language and tone | Absent or limited to emojis and GIFs |
| Flexibility | Requires simultaneous presence | Communicate anytime, anywhere |
| Complexity of Message | Effective for nuanced discussions | Better for straightforward or documented info |
| Record Keeping | No automatic record; requires manual notes | Automatically archived for reference |
| Use Cases | Brainstorming, negotiations, sensitive topics | Project updates, feedback, asynchronous teamwork |
Understanding Face-to-Face Communication
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and rich nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, tone, and body language, which enhance message clarity and emotional connection. It supports spontaneous interaction and dynamic conversation flow, reducing misunderstandings common in text-based exchanges. This direct form of communication is critical in building trust and rapport in personal and professional relationships.
Defining Asynchronous Messaging
Asynchronous messaging is a communication method where participants exchange messages without requiring simultaneous interaction, allowing responses at convenient times. This model supports flexibility across time zones and promotes thoughtful, well-crafted replies, enhancing clarity in professional and personal contexts. Common platforms include email, messaging apps, and collaboration tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams, which facilitate efficient workflow and reduce interruptions.
Real-Time Interaction: Pros and Cons
Face-to-face communication allows for real-time interaction, enabling immediate feedback, nonverbal cues, and emotional connection, which enhances understanding and trust. Asynchronous messaging offers flexibility, allowing participants to respond at their convenience, but it can lead to delays, misinterpretations, and a lack of emotional context. Balancing these communication methods depends on the urgency, complexity, and emotional tone required for effective information exchange.
Flexibility and Convenience in Messaging
Asynchronous messaging offers unmatched flexibility by allowing individuals to communicate across different time zones without the need for immediate responses, making it ideal for busy schedules. Unlike face-to-face communication, messaging provides convenience by enabling users to craft thoughtful replies and share multimedia content at their own pace. This adaptability enhances productivity and maintains connectivity without the constraints of synchronous interactions.
Nonverbal Cues and Their Impact
Nonverbal cues in face-to-face communication, such as facial expressions, gestures, and tone of voice, enhance message clarity and emotional connection. In asynchronous messaging, the absence of immediate visual and auditory signals can lead to misunderstandings and reduced empathy. Emoticons, emojis, and carefully crafted text attempts to compensate, but often cannot fully replicate the richness of real-time nonverbal interaction.
Message Clarity and Miscommunication Risks
Face-to-face communication offers immediate feedback and non-verbal cues, enhancing message clarity and reducing miscommunication risks. Asynchronous messaging lacks tone and instant response, increasing the likelihood of misunderstandings but allowing time for thoughtful replies. Choosing the appropriate channel depends on the complexity and urgency of the information being conveyed.
Collaboration Efficiency: Synchronous vs Asynchronous
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and dynamic interaction, enhancing collaboration efficiency in real-time decision-making and complex problem-solving scenarios. Asynchronous messaging supports flexibility by allowing participants to respond at their convenience, which can lead to better thought-out contributions but may delay project timelines. Organizations benefit from integrating both methods to balance instant collaboration with thoughtful communication, optimizing overall productivity and team responsiveness.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Face-to-face communication offers inherent privacy and security through direct, controlled interactions without digital footprints vulnerable to hacking or interception. Asynchronous messaging relies on encrypted platforms to ensure message confidentiality, but risks arise from data breaches, unauthorized access, and metadata exposure. Choosing between these modes requires evaluating the sensitivity of shared information, platform encryption standards like end-to-end encryption, and compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Workplace Productivity and Communication Tools
Face-to-face communication enhances workplace productivity by enabling immediate feedback, non-verbal cues, and clearer understanding, which reduces misunderstandings and accelerates decision-making. In contrast, asynchronous messaging tools such as email, Slack, and Microsoft Teams allow employees to communicate across different time zones and manage tasks flexibly, boosting efficiency in distributed teams. Effective use of a hybrid communication strategy leveraging real-time conversations and asynchronous platforms optimizes collaboration and streamlines workflow in modern workplaces.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Team
Selecting the optimal communication method for your team hinges on factors such as urgency, message complexity, and team dynamics. Face-to-face communication promotes immediate feedback and clearer understanding during complex discussions, while asynchronous messaging offers flexibility and allows thoughtful responses across different time zones. Assessing the context, team preferences, and project requirements ensures effective collaboration and maximizes productivity.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Presence Fatigue
Synchronous presence fatigue occurs when constant real-time interactions in face-to-face communication overwhelm cognitive resources, leading to decreased attention and productivity. In contrast, asynchronous messaging allows individuals to manage their response time, reducing mental fatigue by offering flexibility and control over communication flow.
Digital Body Language
Face-to-face communication offers rich digital body language cues such as facial expressions, gestures, and voice tone that enhance message clarity and emotional understanding. Asynchronous messaging lacks these immediate nonverbal signals, requiring users to rely on text cues like emojis, punctuation, and response timing to interpret intent and sentiment.
Message Lag Creep
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and reduces message lag creep, ensuring clarity and timely responses. In contrast, asynchronous messaging often experiences delays that accumulate over time, potentially leading to misunderstandings and decreased collaboration efficiency.
Contextual Persistence
Face-to-face communication offers immediate contextual persistence through real-time verbal and non-verbal cues, enhancing understanding and reducing misinterpretations. In contrast, asynchronous messaging provides long-term contextual persistence by preserving message history, enabling users to revisit and reference conversations at any time for clarity and accountability.
Real-Time Engagement Dissonance
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and nuanced nonverbal cues, fostering dynamic real-time engagement that asynchronous messaging lacks. The delay inherent in asynchronous messaging creates dissonance in conversational flow, often leading to misunderstandings and reduced emotional connection.
Micro-Interaction Overload
Face-to-face communication allows for natural micro-interactions like gestures and immediate feedback, reducing the cognitive load typically caused by asynchronous messaging platforms that often lead to micro-interaction overload through constant notifications and fragmented conversations. This overload in asynchronous messaging can diminish productivity and increase stress, as users struggle to manage multiple simultaneous interactions without real-time contextual cues.
Async Response Drift
Asynchronous messaging often leads to response drift, where delayed replies cause misunderstandings and disrupt conversational flow unlike immediate face-to-face communication that enables real-time feedback and clarification. This temporal disconnect in asynchronous communication can reduce message clarity and weaken interpersonal connection.
Face-to-Face Signal Richness
Face-to-face communication offers unparalleled signal richness through immediate feedback, vocal tone, facial expressions, and body language that create a more nuanced and effective exchange of information. Unlike asynchronous messaging, this mode reduces misunderstandings by allowing real-time clarification and emotional connection.
Temporal Communication Mismatch
Face-to-face communication enables immediate feedback and real-time interaction, reducing the risk of temporal communication mismatch. In contrast, asynchronous messaging can create delays that disrupt conversational flow and lead to misunderstandings due to the time lag between message exchanges.
Latency-Induced Misalignment
Face-to-face communication minimizes latency-induced misalignment by enabling immediate feedback, reducing misunderstandings and ensuring clearer exchanges. Asynchronous messaging often suffers from delayed responses, causing potential misinterpretations and disrupting the flow of effective communication.
Face-to-Face Communication vs Asynchronous Messaging Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com