Face-to-face communication fosters immediate, rich interactions through nonverbal cues and emotional resonance, creating a deeper sense of trust and understanding. Metaverse communication, while offering immersive and interactive virtual environments, may lack the subtlety of physical presence but enables global connectivity and innovative collaboration. Both modes serve unique purposes, with face-to-face excelling in intimacy and metaverse communication driving accessibility and creative engagement.
Table of Comparison
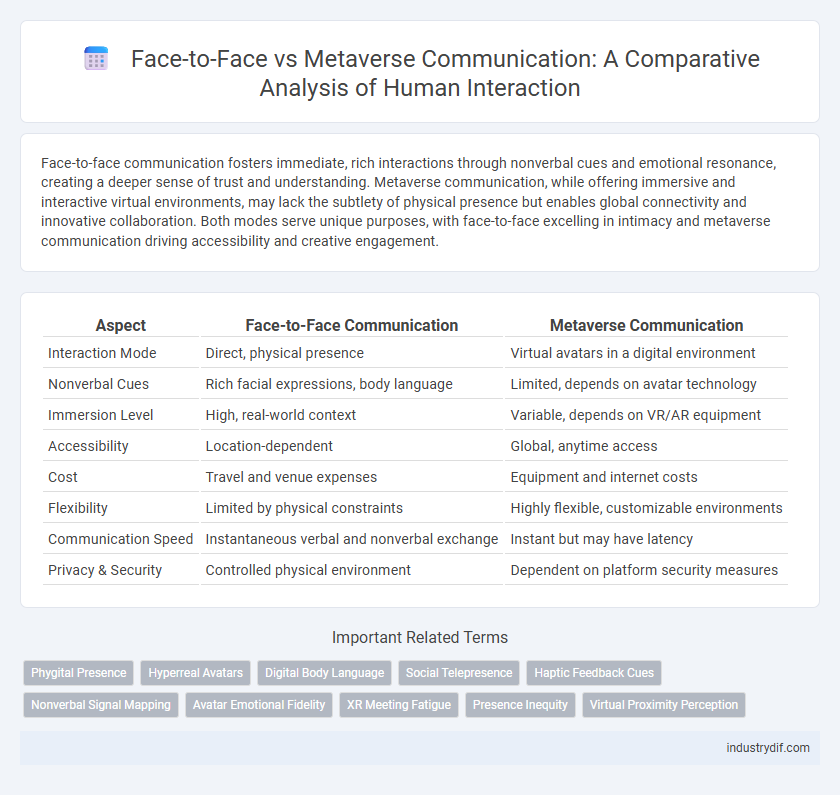
| Aspect | Face-to-Face Communication | Metaverse Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Interaction Mode | Direct, physical presence | Virtual avatars in a digital environment |
| Nonverbal Cues | Rich facial expressions, body language | Limited, depends on avatar technology |
| Immersion Level | High, real-world context | Variable, depends on VR/AR equipment |
| Accessibility | Location-dependent | Global, anytime access |
| Cost | Travel and venue expenses | Equipment and internet costs |
| Flexibility | Limited by physical constraints | Highly flexible, customizable environments |
| Communication Speed | Instantaneous verbal and nonverbal exchange | Instant but may have latency |
| Privacy & Security | Controlled physical environment | Dependent on platform security measures |
Introduction to Face-to-Face and Metaverse Communication
Face-to-face communication involves direct interpersonal interaction characterized by verbal and nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice, fostering immediate feedback and emotional connection. Metaverse communication occurs within virtual environments where users interact through avatars, leveraging digital tools and immersive technologies to simulate real-time conversation despite physical distances. Understanding these modes highlights the balance between the authentic engagement of in-person exchanges and the expansive, innovative potential of metaverse platforms.
Defining Key Communication Channels
Face-to-face communication relies on direct verbal and nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, tone, and body language, which enhance understanding and emotional connection. Metaverse communication utilizes virtual reality environments and avatars, enabling immersive interactions through digital gestures, spatial audio, and real-time collaboration tools. Both channels serve distinct roles in communication strategies, with face-to-face emphasizing personal presence and the metaverse offering scalable, interactive experiences across distances.
Nonverbal Cues in Physical vs Digital Environments
Face-to-face communication allows for rich nonverbal cues such as facial expressions, body language, and eye contact, which enhance understanding and emotional connection. In metaverse communication, these nonverbal signals are often represented by avatars, limiting the subtlety and authenticity of gestures and microexpressions. Advances in virtual reality technology aim to improve the accuracy of digital nonverbal communication, but current metaverse interactions still lack the full depth of physical presence cues.
Immediacy and Responsiveness in Real-Time Interactions
Face-to-face communication offers unparalleled immediacy and responsiveness, enabling participants to interpret non-verbal cues such as body language and facial expressions instantaneously. Metaverse communication, while enhancing accessibility across distances, often experiences latency issues that can delay real-time interactions and reduce the natural flow of conversation. Advanced virtual reality technologies within the Metaverse are progressively improving synchronization, yet they still struggle to fully replicate the immediacy inherent in physical, in-person communication.
Presence and Immersion: Comparing User Experience
Face-to-face communication offers unparalleled presence through direct eye contact, body language, and physical proximity, fostering authentic emotional connections and immediate feedback. Metaverse communication enhances immersion by utilizing virtual reality environments, avatars, and interactive digital settings, creating a customizable space that simulates real-world interactions but lacks physical sensory cues. User experience in face-to-face settings excels in genuine social bonding, whereas metaverse platforms prioritize expansive accessibility and novel immersive features that redefine social presence.
Accessibility and Inclusivity of Communication Platforms
Face-to-face communication offers natural accessibility through direct physical presence and nonverbal cues, enhancing inclusivity for participants regardless of technological proficiency. Metaverse communication platforms extend accessibility by allowing users from diverse geographic locations to interact in immersive digital environments, though they often require advanced hardware and stable internet connections that may exclude underserved populations. Balancing these platforms involves improving metaverse technology affordability and user interface design to promote equitable communication access and inclusivity across varied user demographics.
Emotional Intelligence: Challenges and Opportunities
Face-to-face communication enables richer emotional intelligence through real-time facial expressions, tone, and body language, fostering deeper empathetic connections. Metaverse communication challenges emotional intelligence by relying on avatars that limit nonverbal cues but offers opportunities for creative emotional expression via customizable digital environments. Advances in virtual reality technology aim to enhance emotional recognition and response, bridging the gap between physical presence and digital interaction.
Security, Privacy, and Trust in Both Mediums
Face-to-face communication offers inherent security and privacy benefits as it occurs in a controlled physical environment, minimizing risks of data interception and unauthorized access. In contrast, Metaverse communication relies on complex digital infrastructures that can be vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and identity spoofing, necessitating robust encryption and authentication protocols. Trust in face-to-face interactions is often established through direct personal cues, whereas Metaverse environments require users to depend on platform security measures and transparent privacy policies to build confidence in digital exchanges.
Productivity and Collaboration Outcomes
Face-to-face communication often enhances productivity and collaboration by enabling immediate feedback, nonverbal cues, and spontaneous brainstorming that foster trust and clarity. Metaverse communication offers immersive virtual environments that can connect remote teams globally, facilitating collaboration through shared digital workspaces and interactive 3D models. While metaverse platforms reduce geographical barriers, face-to-face interactions remain superior for nuanced discussions and building strong interpersonal relationships critical to high-performing teams.
Future Trends in Human Communication Evolution
Face-to-face communication remains crucial for emotional connection and nonverbal cues, but metaverse communication is rapidly evolving with immersive virtual environments and augmented reality enhancing interaction realism. Future trends indicate a hybrid model where AI-driven avatars and haptic feedback create seamless, multisensory experiences, bridging physical and digital presence. Advances in neural interfaces promise direct brain-to-brain communication, revolutionizing how humans share thoughts and emotions beyond traditional speech.
Related Important Terms
Phygital Presence
Phygital presence blends the tangible immediacy of face-to-face communication with the immersive, interactive environments of Metaverse communication, enhancing emotional connection and engagement. Integrating physical cues and virtual accessibility, this hybrid approach optimizes user experience by leveraging real-world social dynamics alongside digital innovation.
Hyperreal Avatars
Hyperreal avatars in metaverse communication create immersive environments that replicate nuanced facial expressions and gestures, enhancing emotional connection beyond traditional digital interactions. Face-to-face communication remains unparalleled for spontaneous feedback and authentic human presence, but hyperreal avatars significantly narrow this gap by delivering detailed nonverbal cues in virtual settings.
Digital Body Language
Digital body language in metaverse communication relies heavily on avatars' gestures, facial expressions, and spatial positioning to convey emotions and intent, compensating for the lack of physical presence inherent in face-to-face interactions. Unlike traditional face-to-face communication where subtle body cues and eye contact play a crucial role, metaverse platforms employ sophisticated tracking and AI-driven animations to interpret and express users' nonverbal signals effectively.
Social Telepresence
Face-to-face communication offers high social telepresence through direct eye contact, body language, and immediate feedback, fostering stronger emotional connections and trust. Metaverse communication leverages virtual environments and avatars to simulate presence, enhancing interaction flexibility while still striving to replicate the nuanced social cues found in physical settings.
Haptic Feedback Cues
Face-to-face communication offers immediate and rich haptic feedback cues such as handshakes, pats, or subtle touch, enhancing emotional connection and trust between participants. In contrast, metaverse communication leverages advanced haptic technology and wearable devices to simulate these tactile sensations, aiming to replicate the physical presence and improve immersive interaction in virtual environments.
Nonverbal Signal Mapping
Face-to-face communication enables accurate nonverbal signal mapping through direct observation of facial expressions, gestures, and body language, which are essential for interpreting emotions and intentions. In contrast, metaverse communication relies on avatars and digital environments, where nonverbal cues are often limited or simulated, challenging the richness and spontaneity of nonverbal signal interpretation.
Avatar Emotional Fidelity
Avatar emotional fidelity in metaverse communication enables users to convey nuanced expressions and body language through digital avatars, enhancing interpersonal connection beyond traditional text or voice. Face-to-face communication remains superior in capturing authentic emotional cues with natural facial microexpressions and tone variations, but advances in avatar technology are narrowing this gap.
XR Meeting Fatigue
Face-to-face communication fosters natural nonverbal cues and emotional connection, reducing cognitive strain compared to extended XR meetings in the metaverse, which often cause XR meeting fatigue due to sensory overload and prolonged headset use. This fatigue impacts productivity and engagement, highlighting the need for balanced integration of immersive technologies with traditional interpersonal interactions.
Presence Inequity
Face-to-face communication offers rich nonverbal cues and immediate feedback, fostering a stronger sense of presence and emotional connection compared to Metaverse communication, which often struggles with presence inequity due to avatar limitations and technological constraints. Enhanced virtual reality tools aim to bridge this gap by improving avatar expressiveness and spatial audio, yet the immersive authenticity of physical interactions remains unparalleled.
Virtual Proximity Perception
Virtual proximity perception in metaverse communication creates an immersive sense of presence that mimics face-to-face interactions by using spatial audio, avatars, and 3D environments to simulate physical closeness. Unlike traditional face-to-face communication, metaverse platforms can transcend geographical barriers while maintaining emotional and social cues, enhancing collaborative experiences despite physical distance.
Face-to-Face Communication vs Metaverse Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com