Focus groups provide direct, qualitative insights through structured discussions with targeted participants, allowing for in-depth exploration of opinions and emotions. Social listening captures real-time, unfiltered conversations across social media platforms, offering broader trends and sentiment analysis on a larger scale. Combining both approaches enhances understanding of consumer behavior by validating qualitative feedback with organic, data-driven observations.
Table of Comparison
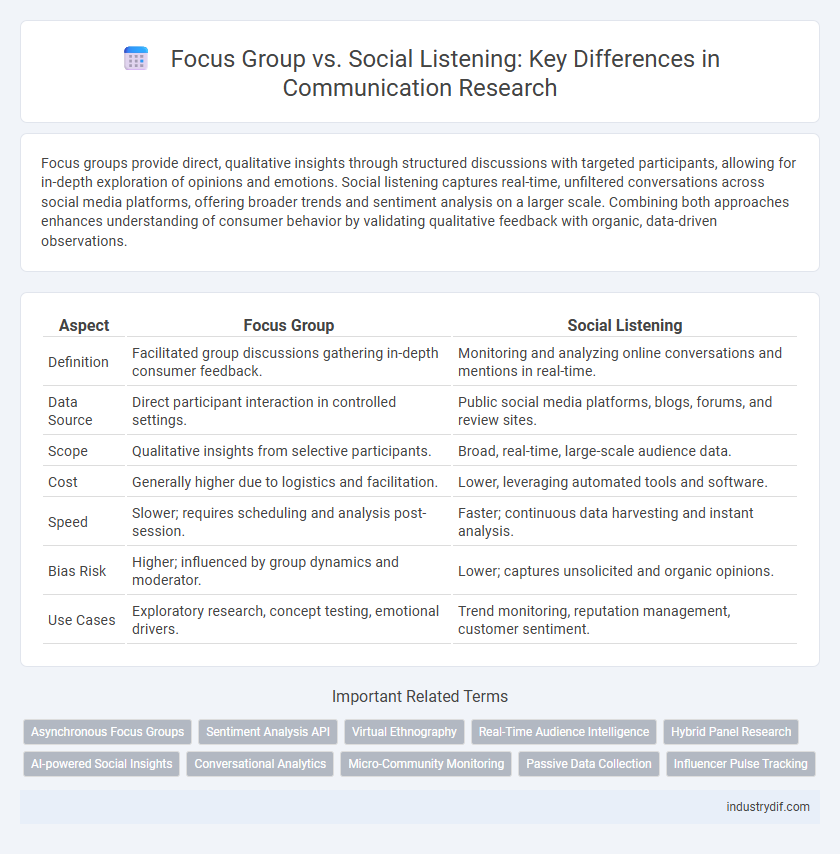
| Aspect | Focus Group | Social Listening |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Facilitated group discussions gathering in-depth consumer feedback. | Monitoring and analyzing online conversations and mentions in real-time. |
| Data Source | Direct participant interaction in controlled settings. | Public social media platforms, blogs, forums, and review sites. |
| Scope | Qualitative insights from selective participants. | Broad, real-time, large-scale audience data. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to logistics and facilitation. | Lower, leveraging automated tools and software. |
| Speed | Slower; requires scheduling and analysis post-session. | Faster; continuous data harvesting and instant analysis. |
| Bias Risk | Higher; influenced by group dynamics and moderator. | Lower; captures unsolicited and organic opinions. |
| Use Cases | Exploratory research, concept testing, emotional drivers. | Trend monitoring, reputation management, customer sentiment. |
Introduction to Communication Research Methods
Focus groups involve direct interactions with a targeted group to gather qualitative insights on perceptions and attitudes, enabling researchers to explore motivations behind communication behaviors. Social listening captures and analyzes real-time online conversations and trends across social media platforms, providing vast quantitative and contextual data without participant bias. Both methods complement each other in communication research by combining explicit feedback with naturally occurring audience expressions.
Defining Focus Groups in Industry Contexts
Focus groups serve as a qualitative research method where moderated discussions gather detailed consumer insights, opinions, and attitudes toward products or services within specific industry contexts. They enable companies to explore customer perceptions, test marketing messages, and refine product development strategies by directly interacting with targeted demographic segments. Unlike social listening, which analyzes unsolicited online conversations, focus groups provide structured environments for in-depth exploration of participant feedback and emotional responses.
Understanding Social Listening: Key Concepts
Social listening involves monitoring online conversations and sentiment across social media platforms to gather real-time insights about a brand, product, or topic. This technique leverages natural language processing and sentiment analysis to identify emerging trends, customer opinions, and potential crises. Unlike focus groups, social listening captures unfiltered consumer behavior and broader audience perspectives without direct interaction.
Core Differences: Focus Group vs Social Listening
Focus groups involve direct interaction with selected participants to gather in-depth insights through guided discussions, enabling real-time feedback on specific topics or products. Social listening, on the other hand, monitors and analyzes online conversations across social media platforms to track public sentiment, trends, and emerging issues without direct engagement. The core difference lies in focus groups providing qualitative, controlled feedback from a limited audience, while social listening offers large-scale, passive data collection from diverse online communities.
Advantages of Conducting Focus Groups
Focus groups provide direct, nuanced insights by allowing real-time interaction and discussion among participants, which uncovers emotions, motivations, and detailed opinions that social listening may overlook. They enable researchers to ask follow-up questions, clarify responses, and explore complex topics deeply, enhancing the quality of data collected. This controlled environment fosters understanding of target audience behaviors and preferences essential for tailored marketing and communication strategies.
Benefits of Leveraging Social Listening Tools
Social listening tools provide real-time insights into consumer sentiment, enabling brands to identify trends and address issues promptly. These tools aggregate data from multiple platforms, offering a broader and more diverse understanding of audience opinions than traditional focus groups. Leveraging social listening enhances decision-making with data-driven strategies that improve customer engagement and brand reputation.
Data Collection Techniques: Qualitative vs Quantitative
Focus groups employ qualitative data collection techniques by facilitating direct interaction and in-depth discussions among participants, revealing nuanced attitudes and motivations. Social listening utilizes quantitative data collection by analyzing large volumes of online conversations and social media metrics to identify trends and sentiment patterns. Combining both methods enhances comprehensive communication insights through balanced qualitative depth and quantitative breadth.
Industry Applications: When to Use Each Method
Focus groups provide in-depth qualitative insights through direct interaction, making them ideal for product development, advertising concepts, and testing new services in industries like retail, healthcare, and technology. Social listening captures real-time consumer sentiment and emerging trends by analyzing online conversations, which is valuable for brand management, crisis monitoring, and market research in sectors such as finance, hospitality, and media. Combining both methods enhances strategic decision-making, with focus groups delivering contextual feedback and social listening offering broad public perception data.
Challenges and Limitations in Communication Analysis
Focus groups face challenges such as limited participant diversity and potential groupthink, which can bias communication analysis and obscure authentic insights. Social listening struggles with interpreting contextual nuances and sentiment accurately due to the complexity of language and online noise. Both methods encounter limitations in capturing the full depth of communication dynamics, making it essential to combine approaches for comprehensive analysis.
Future Trends in Communication Research Methods
Focus groups remain valuable for in-depth qualitative insights but are increasingly complemented by social listening, which leverages real-time data from digital platforms for broader sentiment analysis. Future trends emphasize integrating AI-driven analytics to enhance the accuracy and scalability of social listening while maintaining the contextual depth provided by moderated discussions. Hybrid methodologies combining these approaches will dominate communication research, enabling more dynamic and responsive strategies.
Related Important Terms
Asynchronous Focus Groups
Asynchronous focus groups enable participants to engage in discussions at their convenience over an extended period, providing deeper insights into consumer attitudes compared to traditional synchronous methods. This format contrasts with social listening, which passively analyzes real-time online conversations, whereas asynchronous groups actively gather structured, qualitative feedback for richer data analysis.
Sentiment Analysis API
Focus Group sentiment analysis relies on structured feedback from selected participants, providing in-depth qualitative insights, while Social Listening leverages real-time data from diverse online sources, offering broader quantitative sentiment trends. Integrating a Sentiment Analysis API enhances the accuracy and scalability of evaluating mood and opinions across both methodologies, enabling more comprehensive communication strategies.
Virtual Ethnography
Virtual ethnography integrates social listening to capture natural online behaviors and attitudes, while focus groups provide structured, interactive discussions for deeper insight into participant perspectives. Combining these methods enhances communication research by balancing real-time digital observations with targeted participant feedback.
Real-Time Audience Intelligence
Focus groups provide structured, controlled environments for gathering qualitative insights from selected participants, enabling in-depth understanding of consumer attitudes. Social listening captures real-time audience intelligence by monitoring live online conversations across multiple platforms, offering unfiltered data on trends and sentiment as they evolve.
Hybrid Panel Research
Hybrid panel research integrates focus group insights with social listening data, enhancing understanding of consumer sentiment through real-time online behavior and in-depth qualitative feedback. This method provides a comprehensive communication strategy by combining structured group discussions and organic social media interactions for richer audience analysis.
AI-powered Social Insights
AI-powered social insights leverage advanced algorithms to analyze real-time, large-scale unstructured data from social media, providing deeper, unbiased consumer sentiment than traditional focus groups. Unlike focus groups, which rely on limited participant feedback in controlled settings, AI-driven social listening offers dynamic, continuous monitoring to detect emerging trends and authentic public opinions across diverse demographics.
Conversational Analytics
Focus groups provide direct, qualitative insights through participant interactions, capturing nuanced opinions and emotional responses, while social listening leverages AI-driven conversational analytics to analyze large volumes of online discussions, identifying trends and sentiment patterns in real-time. Conversational analytics enhances social listening by extracting actionable data from unstructured text, enabling businesses to understand customer needs and market dynamics at scale.
Micro-Community Monitoring
Focus Group research offers in-depth qualitative insights from targeted participants, enabling direct feedback within a controlled environment, while Social Listening captures real-time, organic conversations across digital platforms, providing broader trends and sentiment analysis. Micro-Community Monitoring leverages both methods by focusing on niche online groups, combining structured dialogue with continuous digital monitoring to understand specific audience behaviors and preferences in communication strategies.
Passive Data Collection
Passive data collection through social listening captures authentic, real-time consumer conversations across digital platforms, offering deeper insights without direct interaction bias. Focus groups rely on active participation, which can influence responses, whereas social listening uncovers genuine sentiment and emerging trends by analyzing naturally occurring online discussions.
Influencer Pulse Tracking
Focus group research provides direct feedback from selected participants, allowing for in-depth understanding of influencer impact on specific audiences, while social listening analyzes large-scale online conversations to identify trends and sentiment around influencers in real time. Influencer pulse tracking leverages social listening tools to continuously monitor influencer effectiveness, engagement rates, and brand alignment across multiple social platforms, offering dynamic insights that focus groups cannot capture with the same immediacy.
Focus Group vs Social Listening Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com