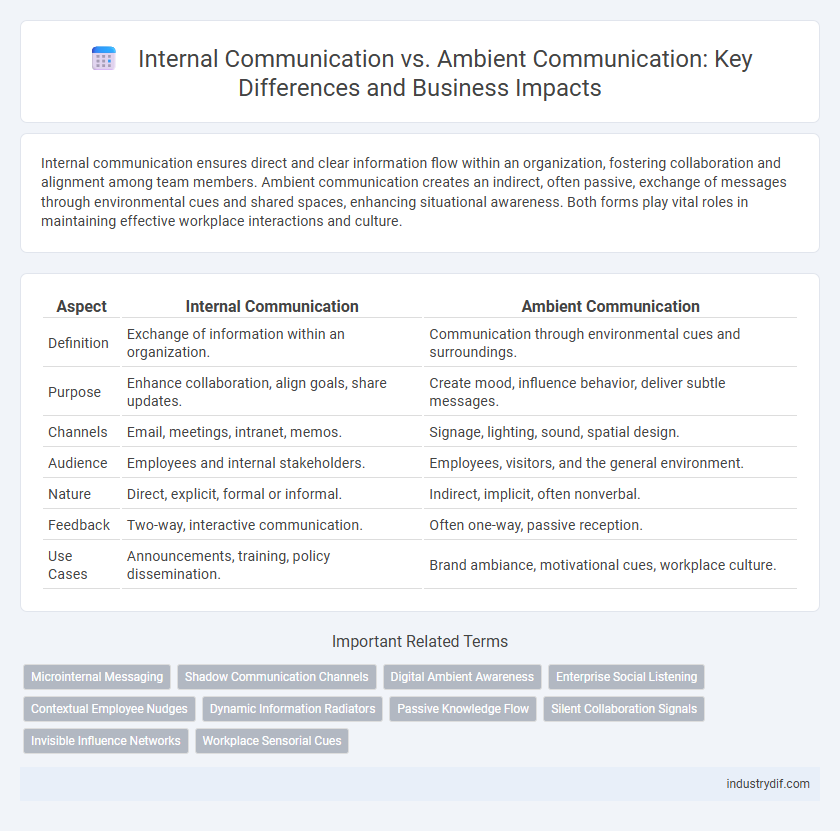
Internal communication ensures direct and clear information flow within an organization, fostering collaboration and alignment among team members. Ambient communication creates an indirect, often passive, exchange of messages through environmental cues and shared spaces, enhancing situational awareness. Both forms play vital roles in maintaining effective workplace interactions and culture.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Internal Communication | Ambient Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exchange of information within an organization. | Communication through environmental cues and surroundings. |
| Purpose | Enhance collaboration, align goals, share updates. | Create mood, influence behavior, deliver subtle messages. |
| Channels | Email, meetings, intranet, memos. | Signage, lighting, sound, spatial design. |
| Audience | Employees and internal stakeholders. | Employees, visitors, and the general environment. |
| Nature | Direct, explicit, formal or informal. | Indirect, implicit, often nonverbal. |
| Feedback | Two-way, interactive communication. | Often one-way, passive reception. |
| Use Cases | Announcements, training, policy dissemination. | Brand ambiance, motivational cues, workplace culture. |
Understanding Internal Communication
Internal communication is the structured exchange of information within an organization aimed at aligning employees with company goals and enhancing collaboration. It involves formal channels such as emails, meetings, and intranets to ensure clarity, consistency, and timely dissemination of messages. Effective internal communication boosts employee engagement, reduces misunderstandings, and supports organizational culture development.
Defining Ambient Communication
Ambient communication refers to the subtle, non-intrusive exchange of information embedded within an environment, enabling individuals to absorb messages effortlessly as part of their surroundings. Unlike internal communication, which relies on direct and deliberate interactions within an organization, ambient communication leverages ambient cues such as visual displays, background sounds, or shared digital spaces to facilitate continuous information flow. This form of communication enhances awareness and engagement by integrating messages naturally into daily environments, promoting a seamless and passive information experience.
Core Differences Between Internal and Ambient Communication
Internal communication involves targeted, direct exchanges of information within an organization, focusing on clarity, employee engagement, and efficient collaboration among teams. Ambient communication encompasses indirect, background messages delivered through environmental cues like signage, displays, or digital interfaces that subtly influence behavior and awareness without interrupting primary tasks. The core difference lies in intentionality and immediacy: internal communication is explicit and purposeful, while ambient communication is subtle and passive, shaping organizational culture and information flow through contextual presence.
Key Objectives of Internal Communication
Key objectives of internal communication include fostering employee engagement, aligning team goals with organizational strategy, and ensuring timely dissemination of critical information. It aims to build a transparent culture where feedback flows seamlessly between management and staff, enhancing collaboration and productivity. Effective internal communication drives motivation, reduces misunderstandings, and supports change management within the company.
The Role of Ambient Communication in the Workplace
Ambient communication in the workplace enhances employee engagement by subtly integrating information into the environment, promoting continuous awareness without disrupting workflow. Its role extends to fostering a cohesive culture through non-intrusive visual cues, digital displays, and environmental signals that reinforce organizational values and goals. Compared to traditional internal communication, ambient communication supports real-time, passive information sharing that boosts collaboration and productivity.
Benefits of Effective Internal Communication
Effective internal communication boosts employee engagement, enhances collaboration, and increases productivity by ensuring that team members clearly understand company goals and expectations. It fosters a transparent work environment, reducing misunderstandings and promoting trust across all levels of an organization. Streamlined communication tools facilitate real-time information sharing, enabling quicker decision-making and stronger alignment with organizational strategies.
Ambient Communication: Advantages and Limitations
Ambient communication enhances workplace interactions by integrating subtle, continuous messaging through environmental cues such as digital displays, ambient sound, and visual motifs, fostering a shared organizational culture without interrupting workflow. Its advantages include reinforcing organizational values, increasing engagement through non-intrusive means, and enabling informal knowledge sharing across departments. Limitations involve potential information overload if poorly managed, reduced message clarity compared to direct communication, and challenges in measuring communication effectiveness due to its implicit nature.
Strategic Integration: Balancing Internal and Ambient Communication
Strategic integration of internal and ambient communication ensures cohesive messaging by aligning employee-focused dialogues with external environmental cues. Leveraging internal communication platforms fosters transparency and engagement, while ambient communication subtly reinforces brand values and organizational culture across diverse touchpoints. Balancing these communication types enhances overall organizational coherence and drives unified stakeholder experiences.
Technology’s Impact on Communication Modalities
Internal communication leverages technology such as intranets, collaboration platforms like Microsoft Teams, and video conferencing tools to enhance direct, structured exchanges within organizations. Ambient communication relies on sensor-driven environments, IoT devices, and AI-powered context-aware systems to facilitate indirect, background information flow. Advances in machine learning and real-time data processing amplify the efficiency of both modalities by adapting messages to user preferences and situational contexts.
Best Practices for Enhancing Organizational Communication
Effective internal communication fosters transparency and employee engagement by utilizing targeted channels such as intranets, team meetings, and direct messaging platforms. Ambient communication enhances workplace culture through subtle cues like digital signage, ambient noise control, and shared collaborative spaces that promote spontaneous interactions. Integrating both approaches with consistent messaging and feedback loops maximizes information flow and strengthens organizational alignment.
Related Important Terms
Microinternal Messaging
Microinternal messaging enhances internal communication by delivering concise, targeted messages that improve employee engagement and information retention. Unlike ambient communication, which relies on environmental cues, microinternal messaging ensures precise, direct channels that foster clarity and immediate response within organizations.
Shadow Communication Channels
Shadow communication channels emerge as informal pathways within internal communication systems, often bypassing official channels and influencing workplace dynamics. These covert interactions impact ambient communication by shaping unspoken cultural norms and affecting transparency across organizational layers.
Digital Ambient Awareness
Digital Ambient Awareness enhances internal communication by providing continuous, low-effort updates on colleagues' activities and status, fostering a sense of presence and collaboration without direct interaction. This contrasts with traditional internal communication methods that rely on scheduled messages, as ambient communication leverages real-time, context-rich data streams to improve situational awareness within digital workspaces.
Enterprise Social Listening
Enterprise social listening enhances internal communication by enabling organizations to monitor, analyze, and respond to employee feedback in real-time, fostering a transparent and engaged workplace culture. Ambient communication leverages passive data from digital interactions to capture unspoken sentiments and trends, providing deeper insights beyond traditional feedback channels.
Contextual Employee Nudges
Internal communication leverages direct channels like emails and meetings to deliver targeted messages, whereas ambient communication uses subtle environmental cues to influence employee behavior unconsciously; contextual employee nudges embedded in ambient settings enhance engagement by aligning prompts with real-time tasks. Effective integration of these communication types optimizes message relevance and timing, driving productivity and reinforcing organizational culture through seamless behavioral cues.
Dynamic Information Radiators
Dynamic information radiators in internal communication enhance team collaboration by providing real-time updates and visualizing key metrics directly within workspaces. In contrast, ambient communication leverages subtle environmental cues, enabling passive information absorption without disrupting workflow or requiring direct interaction.
Passive Knowledge Flow
Internal communication facilitates structured, direct exchanges within an organization, ensuring targeted message delivery, whereas ambient communication enables passive knowledge flow through informal interactions and environmental cues, fostering spontaneous information sharing and collaborative awareness. Passive knowledge flow in internal communication relies on deliberate channels like emails and meetings, while in ambient communication, it thrives through social presence and contextual signals embedded in the workplace environment.
Silent Collaboration Signals
Silent collaboration signals in internal communication involve structured, intentional cues such as written updates and digital task boards that keep teams synchronized without disrupting workflow. Ambient communication relies on subtle environmental cues like office layout and background sounds to foster spontaneous interactions, enhancing team awareness and collaboration effortlessly.
Invisible Influence Networks
Internal communication leverages structured channels within an organization to facilitate clear, direct exchanges of information, while ambient communication operates through subtle, often unconscious interactions that shape invisible influence networks and organizational culture. These invisible influence networks, formed by ambient communication, play a critical role in disseminating informal knowledge and driving employee behavior beyond formal communication pathways.
Workplace Sensorial Cues
Internal communication in the workplace relies on direct, explicit exchanges such as emails, meetings, and memos to convey messages, ensuring clarity and precision among employees. Ambient communication utilizes sensorial cues like lighting, sound, and spatial arrangements to subtly influence mood and behavior, fostering an unconscious flow of information that complements internal messaging.
Internal Communication vs Ambient Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com