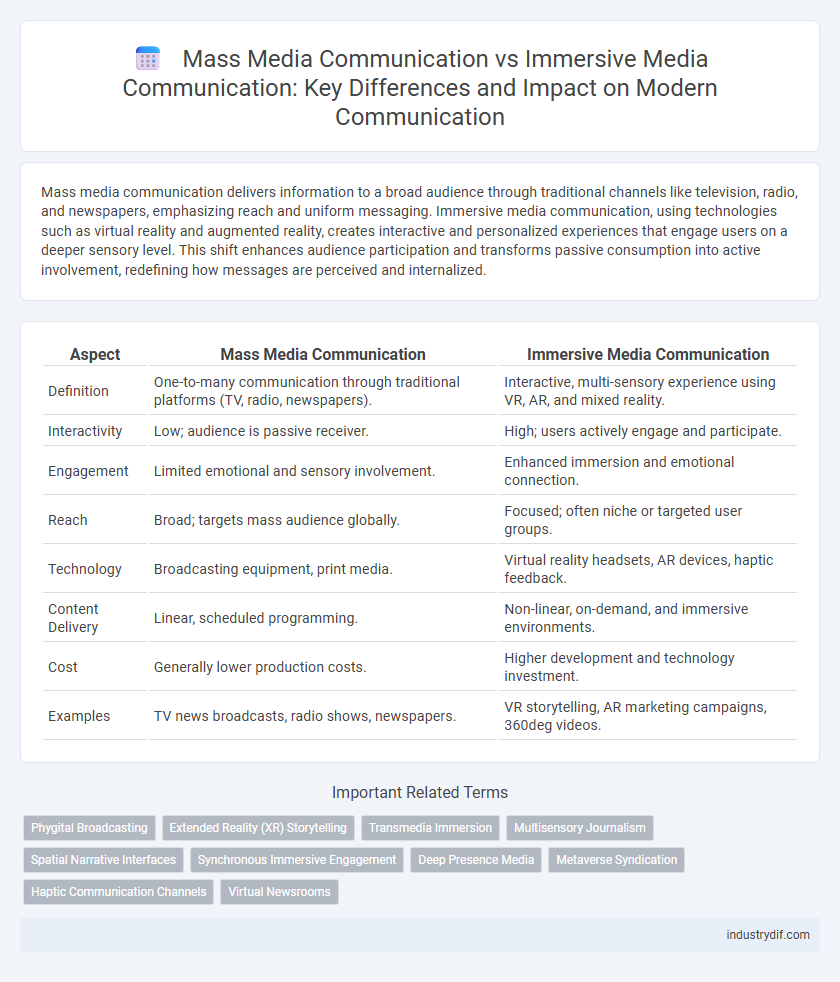
Mass media communication delivers information to a broad audience through traditional channels like television, radio, and newspapers, emphasizing reach and uniform messaging. Immersive media communication, using technologies such as virtual reality and augmented reality, creates interactive and personalized experiences that engage users on a deeper sensory level. This shift enhances audience participation and transforms passive consumption into active involvement, redefining how messages are perceived and internalized.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Mass Media Communication | Immersive Media Communication |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | One-to-many communication through traditional platforms (TV, radio, newspapers). | Interactive, multi-sensory experience using VR, AR, and mixed reality. |
| Interactivity | Low; audience is passive receiver. | High; users actively engage and participate. |
| Engagement | Limited emotional and sensory involvement. | Enhanced immersion and emotional connection. |
| Reach | Broad; targets mass audience globally. | Focused; often niche or targeted user groups. |
| Technology | Broadcasting equipment, print media. | Virtual reality headsets, AR devices, haptic feedback. |
| Content Delivery | Linear, scheduled programming. | Non-linear, on-demand, and immersive environments. |
| Cost | Generally lower production costs. | Higher development and technology investment. |
| Examples | TV news broadcasts, radio shows, newspapers. | VR storytelling, AR marketing campaigns, 360deg videos. |
Defining Mass Media Communication
Mass Media Communication refers to the process of disseminating information to large, diverse audiences through traditional channels such as television, radio, newspapers, and magazines. It relies on one-to-many communication models where the sender broadcasts messages to a broad public without direct interaction. This form of communication is characterized by its wide reach, standardized content, and the ability to influence public opinion and culture on a large scale.
Understanding Immersive Media Communication
Immersive media communication leverages virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality to create interactive, multisensory experiences that deepen audience engagement beyond traditional mass media's one-way information flow. This form transforms passive viewers into active participants, enhancing message retention and emotional connection through personalized and spatial storytelling techniques. Understanding immersive media communication helps marketers and communicators design impactful campaigns that utilize sensory immersion and real-time feedback to drive user involvement and behavior change.
Historical Evolution of Communication Channels
Mass media communication evolved from print newspapers and radio broadcasts to television and digital platforms, shaping public discourse through one-way information dissemination. Immersive media communication incorporates virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and interactive environments, enabling two-way engagement and real-time user interaction. The historical evolution from mass media's centralized distribution to immersive media's personalized, participatory experiences reflects advancements in technology and shifting audience expectations.
Key Components of Mass Media
Mass media communication relies on key components such as large-scale broadcasting channels, one-way content delivery, and standardized messaging targeting broad audiences. It emphasizes reach through newspapers, television, and radio, prioritizing mass appeal and rapid distribution. This contrasts sharply with immersive media communication, which centers on interactive, personalized, and multi-sensory experiences.
Technologies Driving Immersive Media
Emerging technologies such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) are revolutionizing immersive media communication by creating highly interactive and engaging environments. Advanced hardware like head-mounted displays, haptic feedback devices, and spatial audio systems enhance sensory experiences, fostering deeper user involvement compared to traditional mass media communication channels. The integration of AI-driven content personalization and 5G connectivity further accelerates real-time responsiveness and seamless user interaction within immersive media platforms.
Audience Engagement: Mass vs. Immersive Approaches
Mass media communication relies on broad content distribution to engage large audiences through passive consumption, often limiting personalized interaction and emotional connection. In contrast, immersive media communication employs interactive technologies like virtual reality and augmented reality to create deeply engaging, multisensory experiences that foster active participation and stronger emotional bonds. These immersive approaches enhance audience engagement by personalizing content and encouraging dynamic interaction, transforming viewers into participants.
Content Delivery Methods Compared
Mass media communication delivers content through broad channels like television, radio, and newspapers, targeting large audiences simultaneously with mostly one-way messaging. Immersive media communication employs virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive platforms to create personalized, two-way engagements that enhance user involvement. The contrast lies in mass media's passive reception and immersive media's active participation, transforming content delivery into an experiential process.
Impact on Consumer Behavior
Mass media communication delivers broad messages to large audiences, shaping consumer behavior through repeated exposure to advertisements and brand narratives via television, radio, and print media. Immersive media communication leverages virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive environments to create personalized, engaging experiences that significantly enhance emotional connections and influence purchasing decisions. The enhanced sensory engagement and interactivity of immersive media result in higher consumer involvement and stronger brand loyalty compared to traditional mass media channels.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Medium
Mass media communication faces challenges like one-way information flow, limited audience engagement, and difficulties in tailoring messages to diverse demographics, leading to potential message dilution. Immersive media communication encounters limitations such as high production costs, technological accessibility barriers, and user experience variability caused by hardware differences and digital literacy. Both mediums struggle with privacy concerns and the need to maintain credible content amidst rapidly evolving digital landscapes.
Future Trends in Media Communication
Mass media communication continues to evolve with advancements in AI-driven content personalization and 5G technology, enabling faster and more targeted dissemination of information to large audiences. Immersive media communication, leveraging virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), is expected to transform user engagement by creating interactive and experiential environments for education, entertainment, and marketing. The convergence of these technologies predicts a future where hybrid media platforms deliver seamless, multi-sensory communication experiences that cater to individual preferences while maintaining mass reach.
Related Important Terms
Phygital Broadcasting
Phygital broadcasting merges mass media communication's wide reach with immersive media communication's interactive experiences, creating seamless engagement across digital and physical platforms. This hybrid approach enhances viewer immersion by integrating real-time data, virtual reality, and augmented reality technologies, transforming passive audiences into active participants.
Extended Reality (XR) Storytelling
Mass media communication relies on broad dissemination through traditional channels like television and radio, delivering one-way narratives to a mass audience, whereas immersive media communication leverages Extended Reality (XR) technologies to create interactive, multi-sensory storytelling experiences that deeply engage users. XR storytelling uses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) to immerse audiences in dynamic, personalized narratives, transforming passive viewers into active participants and enhancing emotional connection and retention.
Transmedia Immersion
Mass media communication delivers content through traditional platforms like television and radio, reaching broad audiences with one-way messaging, whereas immersive media communication enhances user engagement by integrating interactive elements across multiple platforms, creating a cohesive transmedia immersion experience. Transmedia immersion leverages storytelling techniques in virtual reality, augmented reality, and interactive web environments to deepen audience participation and foster emotional connections beyond conventional media boundaries.
Multisensory Journalism
Mass media communication primarily delivers information through traditional channels like television, radio, and print, often relying on visual and auditory senses. Immersive media communication, particularly multisensory journalism, enhances storytelling by engaging multiple senses such as touch, smell, and spatial awareness, creating deeper emotional connections and more impactful audience experiences.
Spatial Narrative Interfaces
Mass media communication relies on traditional spatial narrative interfaces such as television screens and printed pages, delivering linear and passive content to broad audiences. Immersive media communication utilizes advanced spatial narrative interfaces, including virtual and augmented reality environments, enabling interactive, multi-dimensional storytelling that enhances user engagement and personalized experiences.
Synchronous Immersive Engagement
Synchronous immersive engagement in media communication enables real-time interaction and heightened sensory involvement, contrasting with traditional mass media communication's one-way broadcast model that limits immediate audience feedback. Technologies like virtual reality and augmented reality facilitate dynamic, shared experiences that enhance user presence and foster deeper emotional connections during synchronous interactions.
Deep Presence Media
Mass media communication delivers information to broad audiences through traditional channels like television, radio, and print, emphasizing reach and uniform messaging. Immersive media communication, especially Deep Presence Media, enhances user engagement by creating interactive, multi-sensory experiences that simulate real-life environments, fostering deeper emotional connections and personalized content absorption.
Metaverse Syndication
Mass media communication delivers information to a broad audience through traditional channels like television, radio, and newspapers, emphasizing one-way dissemination. Immersive media communication in the metaverse syndicates interactive, multi-sensory experiences that enable real-time user engagement and personalized content within virtual environments.
Haptic Communication Channels
Mass media communication primarily utilizes visual and auditory channels to reach broad audiences, whereas immersive media communication integrates haptic communication channels to provide tactile feedback, enhancing sensory engagement and user interaction. Haptic communication channels in immersive media enable real-time touch sensations, improving realism and emotional connection in virtual environments compared to traditional mass media formats.
Virtual Newsrooms
Mass media communication delivers news through traditional platforms like television, radio, and newspapers, reaching broad audiences with limited interaction. Immersive media communication, exemplified by virtual newsrooms, enhances audience engagement by integrating virtual reality and real-time collaboration, creating dynamic, interactive news experiences.
Mass Media Communication vs Immersive Media Communication Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com