Public speaking remains a powerful tool for authentic communication, relying on voice modulation, body language, and real-time audience interaction to convey trust and credibility. Audio deepfakes, however, pose significant challenges by mimicking voices with high precision, threatening to erode trust in spoken messages and complicate the verification of audio authenticity. Effective communication strategies must now integrate technology to detect deepfakes while reinforcing the value of genuine, live public speaking engagements.
Table of Comparison
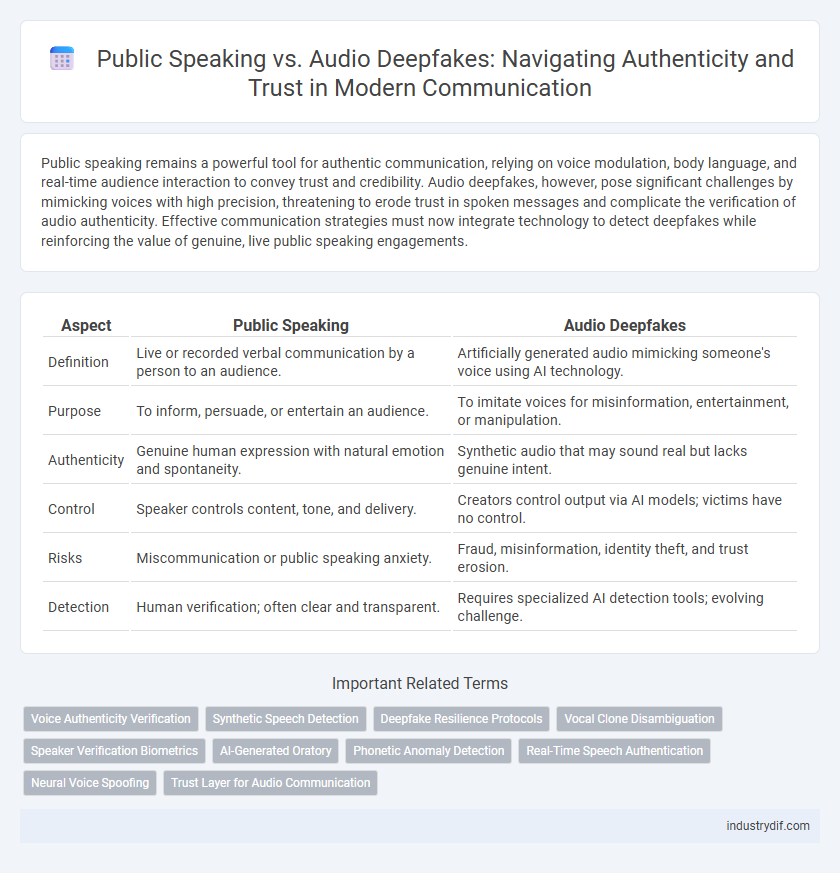
| Aspect | Public Speaking | Audio Deepfakes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Live or recorded verbal communication by a person to an audience. | Artificially generated audio mimicking someone's voice using AI technology. |
| Purpose | To inform, persuade, or entertain an audience. | To imitate voices for misinformation, entertainment, or manipulation. |
| Authenticity | Genuine human expression with natural emotion and spontaneity. | Synthetic audio that may sound real but lacks genuine intent. |
| Control | Speaker controls content, tone, and delivery. | Creators control output via AI models; victims have no control. |
| Risks | Miscommunication or public speaking anxiety. | Fraud, misinformation, identity theft, and trust erosion. |
| Detection | Human verification; often clear and transparent. | Requires specialized AI detection tools; evolving challenge. |
Defining Public Speaking in Modern Communication
Public speaking in modern communication involves the deliberate delivery of messages to an audience using verbal and non-verbal techniques to inform, persuade, or entertain. It emphasizes authenticity, clarity, and audience engagement, contrasting sharply with audio deepfakes that manipulate voices to create deceptive content. Mastering public speaking enhances trust and credibility in digital and physical interactions, making it a crucial skill in an era marked by increasing misinformation.
Understanding Audio Deepfakes: Technology and Terminology
Audio deepfakes utilize advanced machine learning algorithms, including generative adversarial networks (GANs) and neural text-to-speech models, to synthesize realistic human speech. Key terminology encompasses voice cloning, spectrogram manipulation, and synthetic speech generation, which enable the creation of highly convincing audio fabrications. Understanding the underlying technology reveals the challenges in detecting these deepfakes, crucial for maintaining trust in public speaking and communication contexts.
Authenticity in Public Speaking vs Audio Deepfakes
Authenticity in public speaking is defined by genuine voice modulation, emotional expression, and real-time interaction, fostering trust and credibility among audiences. Audio deepfakes, however, compromise authenticity by manipulating vocal elements to create deceptive or artificial representations, undermining the speaker's true intent. Maintaining authenticity in public communication is essential to preserve message integrity and build lasting audience relationships.
Impact on Audience Perception and Trust
Public speaking relies on authentic vocal delivery and body language, fostering immediate audience connection and trust through genuine emotional cues. Audio deepfakes, by contrast, can distort or fabricate speech, undermining trust and skewing audience perception with deceptive realism. The key challenge lies in audiences discerning credible communication from manipulated audio, impacting overall confidence in spoken messages.
Ethical Considerations in Public Speaking and Audio Deepfakes
Ethical considerations in public speaking emphasize honesty, transparency, and respect for the audience's trust, ensuring that speakers present accurate information without manipulation. In contrast, audio deepfakes pose significant ethical challenges by enabling the creation of deceptive and fabricated speeches that can undermine credibility and spread misinformation. Addressing these issues requires stringent ethical standards, advanced detection technologies, and public awareness to preserve the integrity of communication.
Detection and Prevention of Audio Deepfakes in Communication
Audio deepfakes pose significant challenges in public speaking by undermining trust and authenticity in communication. Advanced detection methods leverage machine learning models to analyze audio inconsistencies, voice biometrics, and spectral artifacts unique to synthetic speech. Preventive strategies include implementing real-time verification tools, watermarking authentic recordings, and promoting awareness about deepfake technologies among communication professionals.
Professional Applications: Benefits and Risks
Public speaking enhances professional credibility by fostering authentic engagement and trust, essential for effective leadership and team collaboration. Audio deepfakes offer innovative tools for training simulations and personalized communication but pose significant risks including misinformation, ethical concerns, and potential damage to reputation. Balancing the benefits and risks requires stringent verification protocols and ethical guidelines to ensure responsible use in professional settings.
Legal Frameworks Surrounding Audio Manipulation
Legal frameworks surrounding audio manipulation address the challenges posed by audio deepfakes in public speaking by establishing regulations that prevent unauthorized creation and distribution of deceptive audio content. Laws such as the Audio-Visual Copyright Directive and emerging anti-deepfake statutes emphasize consent, authenticity, and accountability to protect speakers' rights and maintain public trust. Enforcement mechanisms include criminal penalties, civil liabilities, and technological solutions to detect and verify manipulated audio, ensuring the integrity of communication in public discourse.
The Future of Public Speaking Amid Advancing Deepfake Technology
The future of public speaking faces significant challenges as advancing audio deepfake technology enables highly convincing impersonations, threatening speaker authenticity and audience trust. Public speakers will increasingly rely on enhanced verification tools and live interaction techniques to maintain credibility and engagement. Innovations in blockchain-based voice authentication and AI-driven real-time detection promise to safeguard the integrity of spoken communication in sensitive and influential contexts.
Best Practices for Ensuring Communication Integrity
Ensuring communication integrity in public speaking requires clear articulation, genuine emotion, and consistent body language to build trust and authenticity with the audience. In contrast, combating audio deepfakes demands advanced verification tools such as voice biometrics, blockchain timestamps, and AI-driven detection algorithms to authenticate the speaker's identity. Combining human vigilance with technological safeguards forms the best practice framework to maintain transparency and prevent misinformation.
Related Important Terms
Voice Authenticity Verification
Voice authenticity verification employs advanced AI algorithms and biometric voice recognition to accurately distinguish genuine public speaking from audio deepfakes, protecting speakers' credibility and preventing misinformation. This technology analyzes vocal patterns, tone, and acoustic features to detect synthetic alterations, ensuring reliable identification of authentic voices in real-time communication.
Synthetic Speech Detection
Public speaking relies on authentic vocal expression to engage audiences, while audio deepfakes use synthetic speech that challenges trust and credibility. Advanced synthetic speech detection techniques analyze acoustic patterns and linguistic anomalies to differentiate genuine human voices from artificial imitations, ensuring communication integrity.
Deepfake Resilience Protocols
Public speaking remains a trusted form of communication due to its authenticity and ability to convey emotion, but rising concerns over audio deepfakes have led to the development of Deepfake Resilience Protocols, which employ advanced AI detection algorithms and voice biometrics to verify speaker identity. These protocols enhance security by analyzing speech patterns, acoustic features, and contextual inconsistencies, mitigating the risks of misinformation and protecting the integrity of live and recorded communications.
Vocal Clone Disambiguation
Public speaking relies on authentic vocal presence and nuanced emotional delivery to establish trust, while audio deepfakes employ advanced vocal clone disambiguation techniques to detect synthetic replication of a speaker's voice, ensuring communication credibility. Leveraging machine learning algorithms and acoustic feature analysis enhances the accuracy of distinguishing genuine speech from cloned audio, crucial for preventing misinformation and maintaining public trust in communication.
Speaker Verification Biometrics
Speaker verification biometrics enhances public speaking authenticity by using unique vocal traits to confirm a speaker's identity, mitigating risks posed by audio deepfakes designed to mimic voice patterns. Advanced algorithms analyze voice frequency, pitch, and speech dynamics to detect fraudulent audio, ensuring reliable communication integrity in sensitive or high-stakes environments.
AI-Generated Oratory
AI-generated oratory leverages advanced deep learning models to create highly realistic audio mimicking public speaking styles, challenging traditional notions of authenticity in communication. While public speaking emphasizes genuine human expression and audience engagement, audio deepfakes introduce risks of misinformation by producing convincingly fabricated speeches with precise vocal intonations.
Phonetic Anomaly Detection
Phonetic anomaly detection plays a critical role in distinguishing genuine public speaking from audio deepfakes by analyzing irregularities in speech patterns, intonation, and articulation. Advanced machine learning algorithms enhance this technology's ability to identify subtle inconsistencies in voice modulation and phoneme delivery, thereby improving the accuracy of authentic speech verification.
Real-Time Speech Authentication
Real-time speech authentication leverages advanced voice biometrics and neural network algorithms to distinguish genuine public speaking from audio deepfakes, ensuring integrity in communication. This technology analyzes vocal timbre, speech patterns, and contextual nuances instantaneously to prevent misinformation and enhance trust during live interactions.
Neural Voice Spoofing
Neural voice spoofing leverages advanced deep learning models to create highly convincing audio deepfakes that mimic a speaker's voice, posing significant challenges for authentic public speaking and communication. These synthetic voices can deceive listeners and automated systems, raising critical concerns about trust, security, and the integrity of spoken information in digital communication platforms.
Trust Layer for Audio Communication
Public speaking establishes trust through genuine vocal tone and emotional cues, fostering authentic audience connection. Audio deepfakes undermine this trust layer by mimicking voice characteristics, making it difficult to verify authenticity and compromising the reliability of audio communication.
Public Speaking vs Audio Deepfakes Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com