Armored vehicles provide robust protection and superior firepower, making them ideal for frontline defense and heavy combat scenarios. Robotic mules offer versatility and agility, capable of transporting supplies efficiently across challenging terrains without risking human lives. Choosing between the two depends on mission requirements, balancing the trade-off between armored security and operational mobility.
Table of Comparison
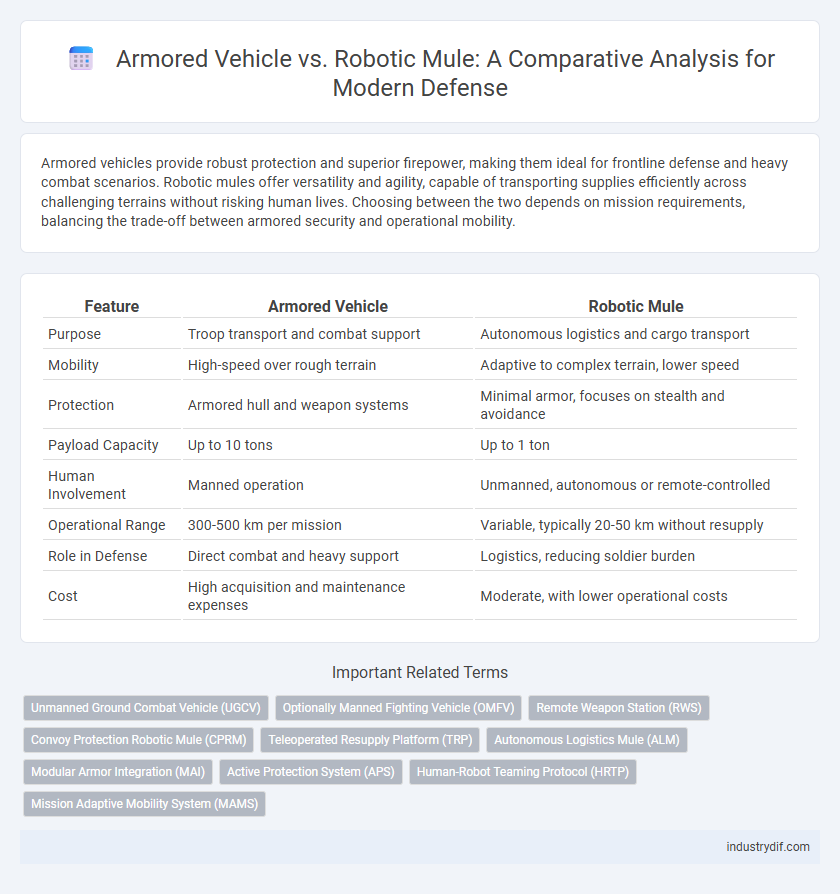
| Feature | Armored Vehicle | Robotic Mule |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Troop transport and combat support | Autonomous logistics and cargo transport |
| Mobility | High-speed over rough terrain | Adaptive to complex terrain, lower speed |
| Protection | Armored hull and weapon systems | Minimal armor, focuses on stealth and avoidance |
| Payload Capacity | Up to 10 tons | Up to 1 ton |
| Human Involvement | Manned operation | Unmanned, autonomous or remote-controlled |
| Operational Range | 300-500 km per mission | Variable, typically 20-50 km without resupply |
| Role in Defense | Direct combat and heavy support | Logistics, reducing soldier burden |
| Cost | High acquisition and maintenance expenses | Moderate, with lower operational costs |
Introduction to Armored Vehicles and Robotic Mules
Armored vehicles are military transport units designed with reinforced hulls to protect personnel and equipment against ballistic threats and explosive devices. Robotic mules, on the other hand, are autonomous or remotely controlled quadruped machines engineered to carry supplies over rough terrain without exposing soldiers to danger. Both platforms enhance battlefield mobility but serve distinct operational roles: armored vehicles prioritize crew protection and firepower, while robotic mules focus on logistical support and stealth.
Historical Evolution in Military Mobility
Armored vehicles revolutionized military mobility by providing enhanced protection, firepower, and all-terrain capability since their introduction in World War I. The development of robotic mules marks a significant evolution, offering autonomous logistical support to reduce soldier burden while navigating complex terrains. This shift reflects advancements in automation and unmanned systems, complementing traditional armored platforms by improving operational efficiency and reducing human risk.
Core Technologies: Armored Protection vs. Autonomous Systems
Armored vehicles rely on advanced composite materials and reactive armor technologies to provide superior ballistic protection and survivability against projectiles and explosive threats on the battlefield. In contrast, robotic mules utilize cutting-edge autonomous navigation systems, including LiDAR, computer vision, and AI-driven decision-making algorithms, enabling adaptive movement across complex terrains without direct human control. The integration of these core technologies highlights a strategic balance between physical defense capabilities in armored vehicles and the operational flexibility offered by autonomous robotic systems in modern defense applications.
Key Operational Roles and Mission Profiles
Armored vehicles serve as heavily protected platforms primarily designed for troop transport, direct fire support, and frontline combat roles, excelling in high-threat environments with enhanced armor and firepower. Robotic mules focus on logistical support, carrying supplies, ammunition, and equipment across challenging terrains, reducing soldier load and increasing mission endurance without risking human personnel. The complementary use of armored vehicles for combat operations and robotic mules for sustainment ensures optimized battlefield mobility, force protection, and operational efficiency in modern military missions.
Survivability and Threat Response Capabilities
Armored vehicles provide robust survivability through reinforced armor plating and active defense systems, enabling effective threat engagement in high-intensity combat zones. Robotic mules enhance operational flexibility by offering stealthy, low-profile logistics support with adaptive threat detection but lack the heavy armor to withstand direct hits. Combining both platforms leverages the armored vehicle's resilience and the robotic mule's agility, optimizing threat response and survivability in diverse battlefield scenarios.
Tactical Mobility and Transport Efficiency
Armored vehicles provide superior tactical mobility on rugged battlefields due to their heavy armor and powerful engines, allowing them to traverse difficult terrain while protecting personnel. Robotic mules enhance transport efficiency by autonomously carrying supplies and equipment, reducing the logistical burden on infantry units and enabling rapid resupply without exposing soldiers to danger. The integration of robotic mules with armored vehicles optimizes mission effectiveness by balancing protection, mobility, and real-time logistical support.
Payload Capacity and Mission Versatility
Armored vehicles typically offer a payload capacity ranging from 2,000 to 10,000 kilograms, enabling them to carry heavy weaponry, troops, and essential supplies for diverse combat scenarios. Robotic mules, with payload capabilities between 100 to 500 kilograms, excel in transporting tactical gear, ammunition, and medical supplies in challenging terrains without risking human lives. The mission versatility of armored vehicles encompasses frontline assault, troop transport, and heavy fire support, while robotic mules specialize in logistic resupply, reconnaissance accompaniment, and casualty evacuation in high-risk environments.
Human-Machine Integration and Crew Requirements
Armored vehicles maintain traditional human-machine integration by providing armored protection and advanced control systems that require trained crews to operate complex weaponry and navigation. Robotic mules reduce crew requirements by autonomously carrying heavy loads, enhancing soldier mobility without the need for constant human intervention. Integrating robotic mules with manned armored vehicles optimizes operational efficiency by combining autonomous logistics support with crewed combat capabilities.
Maintenance, Logistics, and Lifecycle Costs
Armored vehicles require extensive maintenance due to their complex mechanical and armored systems, leading to high lifecycle costs driven by fuel consumption, spare parts, and regular repairs. Robotic mules offer reduced logistical burdens with lower maintenance demands, relying on modular components and electric powertrains that decrease operational expenses over time. Lifecycle cost analysis reveals robotic mules as a cost-effective alternative, enhancing supply chain efficiency and minimizing downtime in defense operations.
Future Trends in Defense Ground Platforms
Future trends in defense ground platforms emphasize increased integration of autonomous systems, with armored vehicles evolving to incorporate advanced sensor arrays, AI-driven threat detection, and enhanced network connectivity for real-time battlefield data sharing. Robotic mules are being developed with improved payload capacity, terrain adaptability, and AI navigation to support infantry by transporting supplies and conducting reconnaissance in hazardous environments. The convergence of these technologies promises to create hybrid combat units combining heavy firepower and robotic mobility, significantly boosting operational efficiency and soldier protection.
Related Important Terms
Unmanned Ground Combat Vehicle (UGCV)
Unmanned Ground Combat Vehicles (UGCVs) like robotic mules provide enhanced battlefield mobility and logistics support without risking human personnel, offering advanced payload capabilities and stealth compared to traditional armored vehicles. These systems integrate autonomous navigation, sensor fusion, and remote control technologies to execute reconnaissance, supply transport, and fire support missions, making them indispensable in modern defense strategies.
Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicle (OMFV)
Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicles (OMFV) combine the heavy armor and firepower of traditional armored vehicles with the autonomous capabilities of robotic mules to enhance battlefield versatility and reduce soldier risk. These hybrid systems leverage advanced AI, sensor integration, and remote operation to perform reconnaissance, logistics support, and direct combat roles while adapting to dynamic combat environments.
Remote Weapon Station (RWS)
Remote Weapon Stations (RWS) on armored vehicles enhance battlefield survivability by allowing operators to engage targets from within protected compartments, integrating advanced targeting sensors and stabilization systems for increased accuracy. In contrast, robotic mules equipped with RWS provide flexible, unmanned firepower support in reconnaissance and supply roles, reducing human risk while offering rapid deployment and adaptive mission capabilities.
Convoy Protection Robotic Mule (CPRM)
The Convoy Protection Robotic Mule (CPRM) enhances convoy security by autonomously detecting threats and navigating complex terrain, reducing risk to personnel compared to traditional armored vehicles. Equipped with advanced sensors and AI-driven threat assessment, the CPRM offers real-time situational awareness and rapid response capabilities, transforming convoy defense strategies.
Teleoperated Resupply Platform (TRP)
The Teleoperated Resupply Platform (TRP) enhances battlefield logistics by combining the heavy armor protection of traditional armored vehicles with the agility and remote-operation capabilities of robotic mules. Designed to transport supplies and equipment under hostile conditions, the TRP reduces soldier exposure to enemy fire while maintaining operational efficiency through advanced teleoperation systems and rugged terrain adaptability.
Autonomous Logistics Mule (ALM)
The Autonomous Logistics Mule (ALM) offers enhanced battlefield mobility and logistical support by navigating complex terrains autonomously, contrasting with traditional armored vehicles that require human operation and present higher risk in hostile environments. ALMs reduce soldier burden and increase supply chain efficiency through real-time data integration and AI-driven pathfinding, revolutionizing military resupply and casualty evacuation operations.
Modular Armor Integration (MAI)
Modular Armor Integration (MAI) enhances armored vehicles by allowing rapid attachment and replacement of diverse armor panels tailored for specific threat environments, significantly improving battlefield adaptability and crew protection. In contrast, robotic mules primarily prioritize mobility and payload transport with limited armor capabilities, making MAI less applicable but highlighting the strategic value of modular armor in manned versus unmanned defense platforms.
Active Protection System (APS)
Armored vehicles equipped with Active Protection Systems (APS) utilize radar and infrared sensors to detect and intercept incoming threats such as anti-tank guided missiles and rocket-propelled grenades, enhancing crew survivability on the battlefield. In contrast, robotic mules, often designed for logistical support, incorporate lighter APS configurations prioritizing mobility and sensor integration to avoid enemy fire rather than direct engagement, reflecting their role in autonomous supply delivery within contested environments.
Human-Robot Teaming Protocol (HRTP)
Human-Robot Teaming Protocol (HRTP) enhances operational efficiency by enabling seamless coordination between armored vehicles and robotic mules through standardized communication, synchronization, and decision-making processes. This protocol ensures real-time data sharing and adaptive task allocation, maximizing battlefield maneuverability and reducing soldier workload while maintaining mission-critical safety standards.
Mission Adaptive Mobility System (MAMS)
The Mission Adaptive Mobility System (MAMS) enhances armored vehicle capabilities by providing modular adaptability for diverse terrains, enabling rapid mission-specific configuration changes. Compared to robotic mules, MAMS offers greater payload capacity and integrated combat support, optimizing operational mobility and survivability in dynamic defense environments.
Armored Vehicle vs Robotic Mule Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com