Armored vehicles provide robust protection and firepower for defense operations, ensuring crew safety in hostile environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles offer strategic advantages by performing reconnaissance, bomb disposal, and tactical support without risking human lives. Combining both platforms enhances battlefield efficiency and reduces operational risks.
Table of Comparison
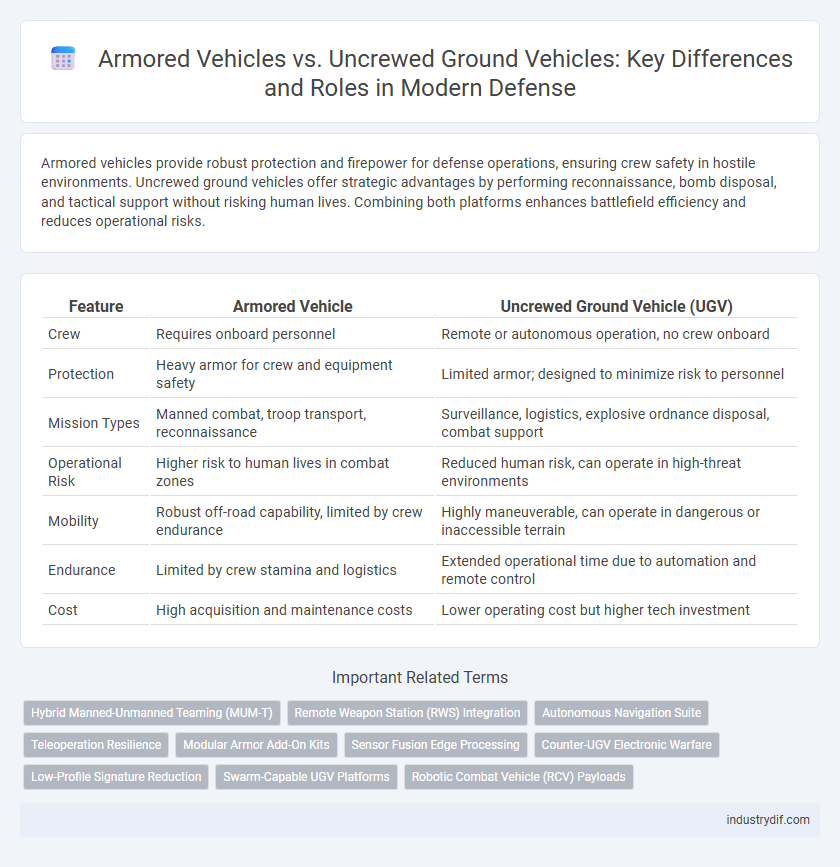
| Feature | Armored Vehicle | Uncrewed Ground Vehicle (UGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Crew | Requires onboard personnel | Remote or autonomous operation, no crew onboard |
| Protection | Heavy armor for crew and equipment safety | Limited armor; designed to minimize risk to personnel |
| Mission Types | Manned combat, troop transport, reconnaissance | Surveillance, logistics, explosive ordnance disposal, combat support |
| Operational Risk | Higher risk to human lives in combat zones | Reduced human risk, can operate in high-threat environments |
| Mobility | Robust off-road capability, limited by crew endurance | Highly maneuverable, can operate in dangerous or inaccessible terrain |
| Endurance | Limited by crew stamina and logistics | Extended operational time due to automation and remote control |
| Cost | High acquisition and maintenance costs | Lower operating cost but higher tech investment |
Overview of Armored Vehicles in Modern Defense
Armored vehicles remain a cornerstone of modern defense, providing essential protection and mobility for troops on the battlefield. These vehicles feature reinforced steel or composite armor designed to withstand projectiles, explosives, and chemical agents, ensuring crew survivability in high-threat environments. Integration of advanced targeting systems and communication technology enhances their operational effectiveness compared to uncrewed ground vehicles, which primarily focus on reconnaissance and support roles.
Introduction to Uncrewed Ground Vehicles (UGVs)
Uncrewed Ground Vehicles (UGVs) represent a transformative shift in defense technology by delivering autonomous or remotely operated capabilities that enhance battlefield versatility and reduce soldier risk. Unlike traditional armored vehicles requiring crew presence, UGVs leverage advanced sensors, artificial intelligence, and communication systems to perform reconnaissance, logistics, and combat missions in complex environments. Their integration within military operations drives increased situational awareness and operational efficiency while minimizing exposure to hostile threats.
Key Differences: Manned vs. Uncrewed Ground Systems
Armored vehicles rely on human crews for operation, offering real-time decision-making and adaptability in complex combat scenarios. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) operate autonomously or via remote control, reducing risk to personnel and enabling deployment in hazardous environments. Key differences include human situational awareness and direct control in manned systems versus increased endurance, reduced logistical support, and risk mitigation in uncrewed platforms.
Survivability and Protection Technologies
Armored vehicles utilize advanced composite armor, reactive armor, and active protection systems (APS) to enhance survivability against kinetic and explosive threats, maintaining crew safety in high-threat environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) rely on low-profile designs, stealth technologies, and sensor fusion for threat detection and avoidance, reducing vulnerability without exposing personnel. Integration of modular armor kits and AI-driven threat response systems further augments protection capabilities across both platforms, adapting to evolving battlefield conditions.
Mobility and Terrain Adaptability
Armored vehicles exhibit superior mobility on rugged terrain due to heavier armor and tracked or wheeled systems optimized for stability under fire, enabling sustained operations in diverse combat environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) offer enhanced terrain adaptability with autonomous navigation technologies and lightweight designs, allowing access to narrow or hazardous areas unsuitable for manned vehicles. Advanced sensor integration in UGVs improves obstacle detection and real-time terrain analysis, maximizing operational flexibility across complex battlefield conditions.
Firepower and Mission Capabilities
Armored vehicles typically provide superior firepower with heavy-caliber cannons and integrated weapon systems designed for direct combat engagement. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) offer enhanced mission flexibility by performing reconnaissance, target acquisition, and support roles without exposing personnel to danger. Firepower in UGVs is generally limited compared to manned armored vehicles but compensated by advanced sensors, remote operation, and the ability to operate in hazardous environments.
Cost Efficiency and Operational Logistics
Armored vehicles require significant investment in crew training, maintenance, and fuel consumption, which drives up operational costs and logistical complexity. Uncrewed ground vehicles reduce personnel risk and lower long-term expenses through autonomous operation and simplified supply chains. Their modular design enables rapid reconfiguration, enhancing mission adaptability and minimizing downtime in the field.
Integration with Network-Centric Warfare
Armored vehicles equipped with advanced communication systems provide robust protection and firepower while maintaining secure links within network-centric warfare environments, enhancing battlefield awareness and coordination. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) integrate seamlessly with network-centric operations through autonomous data sharing and real-time sensor fusion, enabling remote reconnaissance, target acquisition, and force multiplier effects without exposing personnel to direct threats. Effective integration of both platforms within command, control, communications, computers, intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (C4ISR) architectures maximizes operational efficiency and battlefield dominance.
Human Factors and Remote Operation Challenges
Armored vehicles provide crew protection and situational awareness through direct human control, but their weight and size limit operational agility in complex environments. Uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) reduce risk to personnel by enabling remote operation, yet face challenges in communication latency, limited sensory feedback, and operator cognitive load that impact decision-making accuracy. Effective integration of human factors in UGV control systems is critical to enhance remote situational awareness and reduce operational errors during defense missions.
Future Trends: Hybrid Solutions and Autonomous Combat Platforms
Future defense trends emphasize the integration of hybrid armored vehicles combining robust protection with agility, alongside advanced uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) featuring autonomous combat capabilities powered by AI-driven decision systems. Hybrid solutions enhance mission versatility by merging manned control with remote operation, optimizing battlefield responsiveness and survivability. Autonomous combat platforms leverage machine learning and sensor fusion to execute complex tasks, enabling real-time adaptive tactics and reducing human risk in high-threat environments.
Related Important Terms
Hybrid Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Hybrid Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) integrates armored vehicles with uncrewed ground vehicles to enhance battlefield situational awareness, survivability, and operational flexibility. This synergy leverages the armored vehicle's protection and firepower alongside the uncrewed ground vehicle's reconnaissance, target acquisition, and risk-reduction capabilities for coordinated defense missions.
Remote Weapon Station (RWS) Integration
Armored vehicles equipped with Remote Weapon Stations (RWS) enhance crew protection by enabling weapon operation from within the armored hull, whereas uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) leverage RWS integration to conduct high-risk reconnaissance and combat missions without endangering personnel. The advanced RWS systems in both platforms incorporate stabilized sensors and fire control systems, optimizing target engagement accuracy and tactical versatility in diverse combat environments.
Autonomous Navigation Suite
Armored vehicles equipped with advanced autonomous navigation suites utilize integrated LiDAR, radar, and GPS sensors for real-time terrain mapping and obstacle avoidance, ensuring enhanced operational safety and mission effectiveness. In contrast, uncrewed ground vehicles (UGVs) leverage AI-driven algorithms combined with machine learning capabilities to dynamically adapt to unpredictable environments, offering superior precision in autonomous path planning and threat detection.
Teleoperation Resilience
Teleoperation resilience in armored vehicles is enhanced by robust secure communication links and autonomous fallback systems that maintain mission continuity during signal disruption. Uncrewed ground vehicles leverage adaptive AI algorithms and redundant control channels to sustain operational effectiveness and ensure real-time decision-making under contested electronic warfare environments.
Modular Armor Add-On Kits
Modular Armor Add-On Kits significantly enhance the survivability of armored vehicles by providing adaptable protection against evolving threats such as IEDs, RPGs, and ballistic impacts. Uncrewed ground vehicles benefit from these modular kits to maintain mission flexibility and reduce the risk to human operators in high-threat combat zones.
Sensor Fusion Edge Processing
Armored vehicles rely on integrated sensor fusion and edge processing systems to enhance battlefield awareness, combining data from radar, lidar, and thermal sensors to provide real-time threat detection and target tracking. Uncrewed ground vehicles leverage advanced sensor fusion algorithms and edge computing to autonomously navigate complex environments, optimizing situational awareness while reducing the cognitive load on remote operators.
Counter-UGV Electronic Warfare
Counter-UGV electronic warfare employs advanced jamming and spoofing technologies to disrupt communication and navigation systems of uncrewed ground vehicles, neutralizing threats before they reach armored vehicles. Integrating these electronic countermeasures enhances the survivability of armored units by preventing UGVs from executing reconnaissance or attack missions on the battlefield.
Low-Profile Signature Reduction
Low-profile signature reduction in armored vehicles relies on advanced stealth coatings and shape optimization to minimize radar and thermal detection, enhancing battlefield survivability. Uncrewed ground vehicles leverage compact design and adaptive camouflage technologies to further reduce visual and infrared signatures, enabling covert operations in hostile environments.
Swarm-Capable UGV Platforms
Swarm-capable uncrewed ground vehicle (UGV) platforms offer enhanced tactical flexibility and reduced risk to personnel compared to traditional armored vehicles by enabling coordinated autonomous operations in complex environments. These UGV swarms leverage advanced AI algorithms for real-time decision-making and collective task execution, transforming battlefield reconnaissance, target acquisition, and support missions with scalable and resilient force multipliers.
Robotic Combat Vehicle (RCV) Payloads
Robotic Combat Vehicle (RCV) payloads integrate advanced sensor suites, weapon systems, and electronic warfare modules to enhance battlefield autonomy and lethality compared to traditional armored vehicles which rely heavily on crew operation. These uncrewed ground vehicles leverage AI-driven targeting and modular payload configurations to execute precision strikes and reconnaissance with reduced risk to personnel.
Armored vehicle vs Uncrewed ground vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com