Armored vehicles offer robust protection and heavy firepower, making them ideal for frontline defense in combat zones. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance tactical flexibility by performing high-risk reconnaissance and support missions without endangering personnel. Combining armored vehicles with UGVs creates a versatile defense strategy that balances protection, automation, and operational efficiency.
Table of Comparison
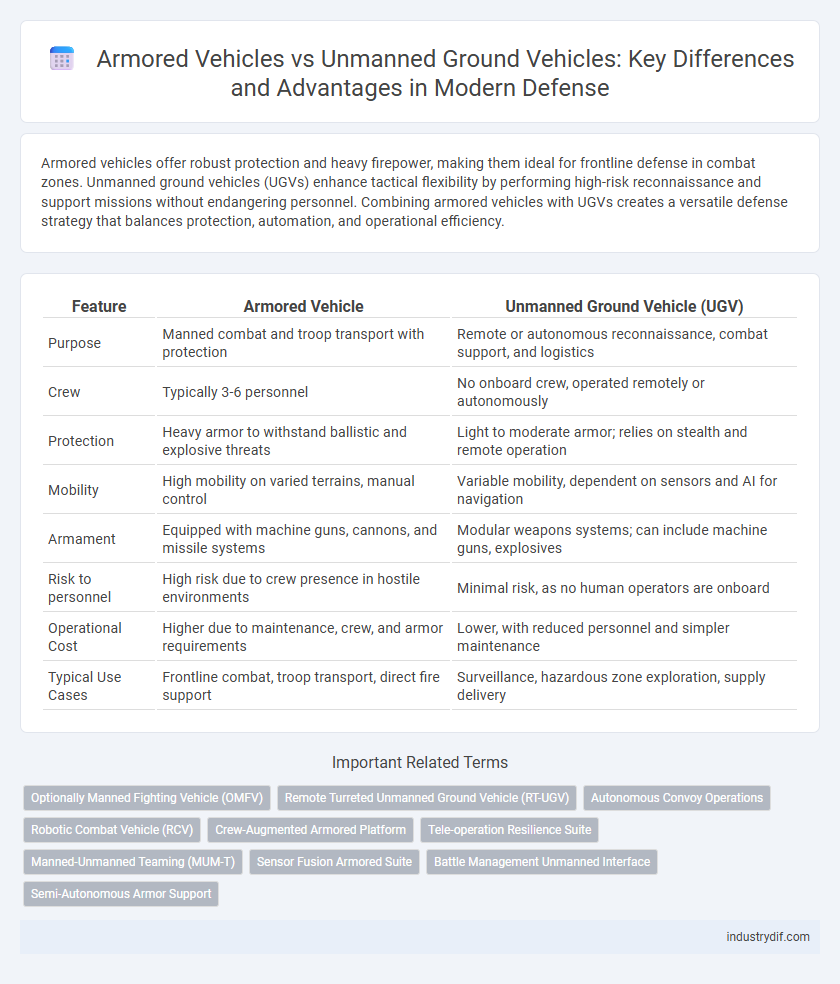
| Feature | Armored Vehicle | Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manned combat and troop transport with protection | Remote or autonomous reconnaissance, combat support, and logistics |
| Crew | Typically 3-6 personnel | No onboard crew, operated remotely or autonomously |
| Protection | Heavy armor to withstand ballistic and explosive threats | Light to moderate armor; relies on stealth and remote operation |
| Mobility | High mobility on varied terrains, manual control | Variable mobility, dependent on sensors and AI for navigation |
| Armament | Equipped with machine guns, cannons, and missile systems | Modular weapons systems; can include machine guns, explosives |
| Risk to personnel | High risk due to crew presence in hostile environments | Minimal risk, as no human operators are onboard |
| Operational Cost | Higher due to maintenance, crew, and armor requirements | Lower, with reduced personnel and simpler maintenance |
| Typical Use Cases | Frontline combat, troop transport, direct fire support | Surveillance, hazardous zone exploration, supply delivery |
Introduction: Armored Vehicles and Unmanned Ground Vehicles Defined
Armored vehicles are heavily protected military transport designed to withstand small arms fire, explosive blasts, and harsh combat environments, often equipped with advanced weaponry and reinforced armor plating. Unmanned Ground Vehicles (UGVs) are autonomous or remotely controlled machines used for reconnaissance, logistics, or combat support, eliminating risk to personnel. Both platforms enhance battlefield effectiveness, with armored vehicles providing direct firepower and protection, while UGVs offer versatility in high-risk or inaccessible terrain.
Historical Evolution of Armored and Unmanned Ground Vehicles
Armored vehicles have evolved since World War I, transitioning from basic steel-plated tanks to advanced main battle tanks equipped with composite armor and high-caliber weaponry. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) emerged in the late 20th century, initially designed for reconnaissance and explosive ordnance disposal, now integrating AI-driven navigation and combat capabilities. The historical evolution reflects increasing emphasis on crew protection, automation, and multifunctionality within defense strategies.
Core Technologies: Armor and Autonomy
Armored vehicles leverage advanced composite and reactive armor technologies to provide enhanced protection against kinetic and explosive threats, ensuring crew survivability in high-threat environments. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) integrate cutting-edge autonomy systems, including machine learning algorithms and sensor fusion, to enable precise navigation and target identification without human intervention. The convergence of robust armor materials with sophisticated autonomous controls defines the next generation of battlefield mobility and force protection capabilities.
Operational Roles and Mission Profiles
Armored vehicles provide robust protection and firepower, excelling in frontline combat and troop transport under hostile conditions. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance reconnaissance, surveillance, and logistics by operating in dangerous environments without risking personnel. Their complementary operational roles enable integrated mission profiles combining manned firepower with remote sensing and support capabilities.
Survivability and Protection Capabilities
Armored vehicles utilize reinforced steel plating and reactive armor systems to maximize survivability against ballistic threats and improvised explosive devices, offering high crew protection in hostile environments. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance protection capabilities by removing personnel from direct danger zones while employing advanced detection sensors and modular armor kits to withstand explosive and kinetic attacks. Integration of active protection systems in both platforms increases their ability to intercept incoming projectiles, significantly improving battlefield survivability.
Mobility, Endurance, and Terrain Navigation
Armored vehicles offer robust mobility with powerful engines and reinforced suspension systems designed for rugged terrain, while unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) excel in endurance through longer operational hours supported by efficient power management and autonomous systems. Terrain navigation in armored vehicles relies heavily on human crew adaptability and sensor integration, whereas UGVs utilize advanced AI algorithms, real-time mapping, and obstacle avoidance for precise maneuvering in complex environments. The combination of armored vehicles' physical resilience and UGVs' extended mission capability highlights their complementary roles in modern defense strategies.
Weapon Systems and Payload Integration
Armored vehicles feature integrated weapon systems such as cannons, machine guns, and missile launchers designed for robust, direct combat engagements. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) provide flexible payload integration options, allowing for specialized modules including remote weapon stations, reconnaissance sensors, and electronic warfare equipment. The modular design of UGVs facilitates rapid mission adaptation, whereas traditional armored vehicles emphasize heavily armored protection with fixed armament configurations.
Human Factors: Crew vs Remote Operation
Armored vehicles require onboard crews, exposing personnel to physical risks and cognitive stress from prolonged missions in hostile environments. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enable remote operation, reducing human exposure to battlefield dangers but increasing reliance on remote sensory inputs and communication links, which may introduce latency and situational awareness challenges. Human factors in UGVs emphasize operator training for remote control interfaces and mitigating cognitive load caused by limited direct environmental feedback.
Cost, Logistics, and Maintenance Considerations
Armored vehicles require significant investment in fuel, regular maintenance, and specialized repair crews, leading to high lifecycle costs and logistical demands on supply chains. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) drastically reduce personnel risk and can be deployed with lower operational expenses, but they depend heavily on advanced electronics and software, which may increase costs related to technical support and system upgrades. Maintenance for UGVs involves specialized technical skills and access to sophisticated diagnostic tools, whereas armored vehicles rely on traditional mechanical expertise, influencing overall maintenance infrastructure and training needs.
Future Trends and Integration on the Modern Battlefield
Future trends emphasize the integration of armored vehicles with unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) to enhance battlefield versatility, situational awareness, and force protection. Advanced sensor fusion, AI-driven autonomy, and secure communication networks enable seamless coordination between manned and unmanned platforms, improving mission effectiveness and reducing risk to personnel. Military modernization programs prioritize hybrid combat teams combining armored vehicles and UGVs for reconnaissance, logistics, and combat support in complex operational environments.
Related Important Terms
Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicle (OMFV)
Optionally Manned Fighting Vehicles (OMFV) integrate advanced armor protection with adaptable unmanned systems, enhancing battlefield versatility and survivability compared to traditional armored vehicles and fully unmanned ground vehicles. These platforms optimize crew safety by allowing remote operation in high-risk scenarios while retaining manned control for complex missions, blending human decision-making with autonomous capabilities.
Remote Turreted Unmanned Ground Vehicle (RT-UGV)
Remote Turreted Unmanned Ground Vehicles (RT-UGVs) enhance battlefield capabilities by integrating advanced sensor arrays and weapon systems without risking crew lives, offering superior reconnaissance and precision firepower compared to traditional armored vehicles. These RT-UGVs leverage real-time data links and autonomous navigation algorithms to deliver rapid response in high-threat environments, optimizing force protection and operational efficiency in modern defense strategies.
Autonomous Convoy Operations
Autonomous convoy operations using unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) enhance mission efficiency and reduce personnel risk in defense scenarios compared to traditional armored vehicles. UGVs equipped with advanced sensors and AI enable seamless, coordinated movement and threat detection, optimizing force protection and operational resilience.
Robotic Combat Vehicle (RCV)
Robotic Combat Vehicles (RCVs) offer enhanced strategic flexibility and reduced soldier risk compared to traditional armored vehicles by integrating autonomous navigation, advanced sensors, and remote weapon systems. Equipped with AI-driven threat detection and precision targeting, RCVs improve battlefield situational awareness and operational efficiency in high-threat combat environments.
Crew-Augmented Armored Platform
Crew-augmented armored platforms integrate human crew members with unmanned ground vehicle technologies to enhance situational awareness, decision-making, and combat effectiveness on the battlefield. These hybrid systems combine the protection and firepower of traditional armored vehicles with the advanced reconnaissance, target acquisition, and remote operational capabilities of unmanned ground vehicles.
Tele-operation Resilience Suite
The Tele-operation Resilience Suite enhances armored vehicles by providing robust remote control capabilities that maintain mission continuity under electronic warfare and signal disruption conditions. Unmanned ground vehicles equipped with this suite benefit from increased operational reliability and secure communication links, ensuring effective deployment in contested environments.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) integrates armored vehicles with unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) to enhance battlefield situational awareness and force protection by combining human decision-making with autonomous sensor capabilities. This synergy improves threat detection, target acquisition, and mission flexibility while reducing crew risk and increasing operational effectiveness in complex defense scenarios.
Sensor Fusion Armored Suite
Sensor Fusion Armored Suite integrates multiple sensor modalities such as radar, lidar, infrared, and acoustic sensors to enhance situational awareness and threat detection in both armored vehicles and unmanned ground vehicles. This advanced fusion technology improves target identification, reduces false alarms, and enables real-time decision-making, significantly increasing operational efficiency and survivability on the battlefield.
Battle Management Unmanned Interface
Battle Management Unmanned Interface (BMUI) enhances operational efficiency by integrating real-time data from armored vehicles and unmanned ground vehicles, enabling synchronized command and control across diverse battlefield assets. This interface leverages advanced sensor fusion and autonomous navigation, improving situational awareness and minimizing human risk while maximizing mission adaptability.
Semi-Autonomous Armor Support
Semi-autonomous armor support integrates advanced sensors and AI-driven control systems within armored vehicles to enhance targeting accuracy and battlefield adaptability while reducing crew risk. Unmanned ground vehicles (UGVs) equipped with semi-autonomous capabilities offer remote surveillance, reconnaissance, and fire support, complementing manned armored units and expanding operational reach in high-threat environments.
Armored vehicle vs Unmanned ground vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com