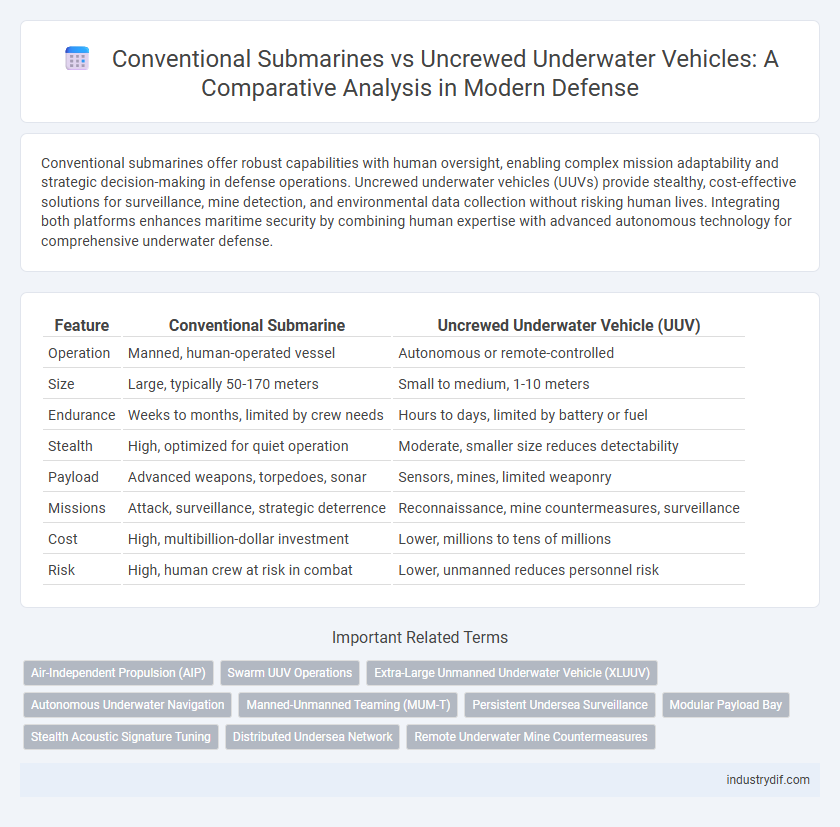
Conventional submarines offer robust capabilities with human oversight, enabling complex mission adaptability and strategic decision-making in defense operations. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) provide stealthy, cost-effective solutions for surveillance, mine detection, and environmental data collection without risking human lives. Integrating both platforms enhances maritime security by combining human expertise with advanced autonomous technology for comprehensive underwater defense.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Conventional Submarine | Uncrewed Underwater Vehicle (UUV) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Manned, human-operated vessel | Autonomous or remote-controlled |
| Size | Large, typically 50-170 meters | Small to medium, 1-10 meters |
| Endurance | Weeks to months, limited by crew needs | Hours to days, limited by battery or fuel |
| Stealth | High, optimized for quiet operation | Moderate, smaller size reduces detectability |
| Payload | Advanced weapons, torpedoes, sonar | Sensors, mines, limited weaponry |
| Missions | Attack, surveillance, strategic deterrence | Reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, surveillance |
| Cost | High, multibillion-dollar investment | Lower, millions to tens of millions |
| Risk | High, human crew at risk in combat | Lower, unmanned reduces personnel risk |
Introduction to Conventional Submarines and Uncrewed Underwater Vehicles
Conventional submarines operate with human crews, relying on diesel-electric or nuclear propulsion systems to perform stealthy underwater missions such as patrol, surveillance, and strategic deterrence. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) are autonomous or remotely operated platforms designed for tasks including reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and data collection, offering reduced risk to personnel and extended operational endurance. Both systems play critical roles in modern naval defense by complementing human-operated platforms with enhanced surveillance capabilities and operational flexibility.
Key Design Differences: Crewed vs. Uncrewed Platforms
Conventional submarines feature robust crew accommodations, life-support systems, and extensive control interfaces, enabling human operation during extended missions. In contrast, uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) prioritize compact, automated designs with autonomous navigation and sensor integration, eliminating the need for life-support infrastructure. This fundamental distinction drives differences in size, endurance, operational risk, and mission flexibility between crewed submarines and UUVs.
Propulsion Systems and Endurance Comparisons
Conventional submarines typically utilize nuclear or diesel-electric propulsion systems, offering substantial endurance with the ability to operate submerged for weeks or even months, depending on fuel and crew supplies. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) often rely on battery-powered or hybrid propulsion systems, which limit their operational endurance to hours or days but provide increased stealth and reduced detection risk. Advances in energy storage technologies for UUVs are closing the endurance gap, enabling longer missions while maintaining quieter propulsion compared to traditional submarines.
Stealth Capabilities and Signature Management
Conventional submarines utilize advanced acoustic dampening technologies and anechoic coatings to minimize sonar detection, maintaining stealth through low noise propulsion systems and thermal signature control. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) leverage smaller size and electric propulsion to reduce acoustic footprints, enabling covert operations in high-risk environments with minimal electromagnetic emissions. Signature management in UUVs emphasizes modular sensor packages and adaptive camouflage, enhancing survivability and operational discretion in contested maritime domains.
Sensor Suites and Intelligence Gathering
Conventional submarines are equipped with advanced sensor suites including passive and active sonar systems, electronic support measures (ESM), and periscopes for multi-spectrum intelligence gathering and stealth operations. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) utilize compact, specialized sensors like synthetic aperture sonar (SAS), magnetic anomaly detectors (MAD), and environmental monitoring systems designed for discreet reconnaissance and data collection in high-risk environments. While conventional submarines excel in long-duration missions with comprehensive onboard analysis, UUVs provide enhanced operational flexibility and reduced risk by enabling remote, real-time intelligence gathering in contested or inaccessible areas.
Weapons Integration and Combat Roles
Conventional submarines feature advanced torpedo tubes and missile launch systems enabling multi-role offensive operations, including anti-ship, anti-submarine, and strategic strike capabilities. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) integrate modular payloads such as sonar arrays, mine countermeasures, and small arms launchers designed primarily for reconnaissance, surveillance, and support roles rather than direct combat. The synergy between conventional submarines' heavy armament and UUVs' stealth and versatility enhances underwater warfare effectiveness through coordinated missions and extended operational reach.
Cost Efficiency and Lifecycle Considerations
Conventional submarines involve higher acquisition and maintenance costs due to complex crew accommodations and extensive support systems, impacting their lifecycle expenses significantly. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) offer enhanced cost efficiency through reduced personnel requirements and simpler logistics, leading to lower operational expenditures over time. Lifecycle considerations favor UUVs for missions requiring prolonged deployment and minimal human risk, while conventional submarines maintain strategic value for complex, multi-faceted military operations.
Operational Flexibility and Mission Profiles
Conventional submarines offer extensive operational flexibility with prolonged endurance, the ability to conduct a wide range of missions including stealth reconnaissance, anti-submarine warfare, and strategic deterrence. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) excel in specialized, risk-intensive operations such as mine detection, underwater surveillance, and intelligence gathering, providing persistent presence without endangering crew. The integration of UUVs enhances mission profiles by allowing manned submarines to extend reach and operational capabilities while reducing human exposure in hostile environments.
Maintenance, Logistics, and Support Challenges
Conventional submarines demand extensive maintenance involving complex mechanical systems, requiring specialized personnel and regular dockyard overhauls, which increases logistical burdens. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) offer reduced maintenance needs due to fewer moving parts and modular designs, though their advanced electronics and autonomous systems require specialized technical support and software updates. Logistics for conventional submarines emphasize fuel, torpedo resupply, and crew provisions, whereas UUVs focus on battery charging, sensor calibration, and remote operational support, presenting distinct challenges in sustainment and deployment efficiency.
Future Trends in Underwater Defense Technologies
Conventional submarines remain critical for strategic deterrence and deep-sea combat capabilities, leveraging advanced stealth technologies and nuclear propulsion for extended missions. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) are rapidly advancing with autonomous navigation, AI-powered threat detection, and swarm tactics, enhancing reconnaissance and mine countermeasure operations. Future underwater defense strategies emphasize integrating UUV fleets with manned platforms to achieve superior situational awareness and operational flexibility in contested maritime environments.
Related Important Terms
Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP)
Conventional submarines equipped with Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) systems can remain submerged for weeks, significantly enhancing stealth capabilities without surfacing for oxygen. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) leveraging AIP technology benefit from extended covert operations and reduced detection risks, offering strategic advantages in intelligence gathering and naval warfare.
Swarm UUV Operations
Swarm UUV operations enable coordinated strikes and intelligence gathering by deploying multiple uncrewed underwater vehicles simultaneously, offering greater stealth and persistence compared to conventional submarines. These unmanned systems enhance maritime domain awareness and increase operational flexibility in contested environments without risking crewed assets.
Extra-Large Unmanned Underwater Vehicle (XLUUV)
Extra-Large Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (XLUUVs) offer extended endurance and stealth capabilities compared to conventional submarines, enabling persistent intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and mine countermeasure missions without risking human crews. These autonomous platforms integrate advanced sensor suites, modular payloads, and long-range communication systems, revolutionizing undersea warfare by enhancing operational flexibility and reducing deployment costs.
Autonomous Underwater Navigation
Conventional submarines rely heavily on skilled crew members for navigation and decision-making, which can be limited by human endurance and real-time situational awareness. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) utilize advanced autonomous underwater navigation systems featuring AI-driven sensors, inertial measurement units, and sonar mapping, enabling precise and prolonged operations with reduced risk of detection.
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T)
Manned-unmanned teaming (MUM-T) in defense leverages the complementary strengths of conventional submarines and uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) to enhance reconnaissance, surveillance, and tactical operations in contested underwater environments. Integrating UUVs with manned submarines enables real-time data sharing, extended operational reach, and reduced risk to human crews while maintaining strategic stealth and decision-making capabilities.
Persistent Undersea Surveillance
Conventional submarines provide stealth and mobility for undersea missions but are limited by crew endurance and maintenance requirements, whereas uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) offer persistent undersea surveillance with extended operational durations and reduced risk to personnel. UUVs equipped with advanced sensors and communication systems enhance maritime domain awareness by continuously monitoring strategic areas without the need for surface support or crew accommodations.
Modular Payload Bay
Conventional submarines feature spacious modular payload bays allowing flexible integration of torpedoes, sonar systems, and special operations equipment, enabling multi-mission adaptability. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) employ compact modular payload bays designed for rapid sensor swaps and specialized mission packages, enhancing stealth and operational versatility in contested environments.
Stealth Acoustic Signature Tuning
Conventional submarines utilize advanced hull designs and sound-isolating machinery to minimize acoustic signatures, enabling stealth operations in contested waters. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) feature modular acoustic signature tuning technologies that allow adaptive noise reduction, enhancing their covert capabilities in diverse maritime environments.
Distributed Undersea Network
Conventional submarines rely on stealth and onboard sensors for intelligence gathering and combat operations, whereas Uncrewed Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) enhance a Distributed Undersea Network by providing persistent surveillance and real-time data relay across vast oceanic regions. Integrating UUVs with manned submarines expands situational awareness and enables coordinated, network-centric warfare in contested undersea environments.
Remote Underwater Mine Countermeasures
Conventional submarines rely on stealth and human-operated systems for remote underwater mine countermeasures, often facing limitations in maneuverability and risk to personnel. Uncrewed underwater vehicles (UUVs) offer enhanced precision and safety by remotely detecting, mapping, and neutralizing underwater mines using autonomous sensors and advanced sonar technology.
Conventional submarine vs Uncrewed underwater vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com