Conventional submarines possess advanced stealth capabilities, longer operational endurance, and can carry diverse weaponry, making them vital for strategic defense missions. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) offer enhanced risk mitigation, extended surveillance capabilities, and cost-effectiveness for mine detection and reconnaissance tasks. Combining the strengths of both platforms enhances underwater defense operations by leveraging human control and autonomous technology.
Table of Comparison
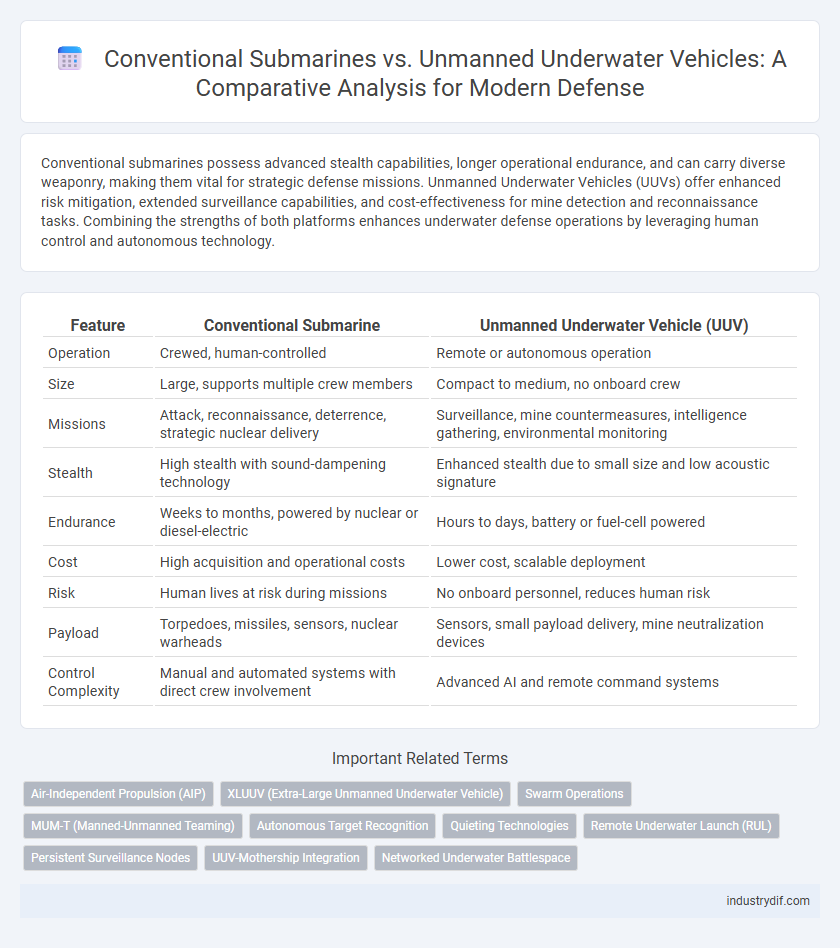
| Feature | Conventional Submarine | Unmanned Underwater Vehicle (UUV) |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Crewed, human-controlled | Remote or autonomous operation |
| Size | Large, supports multiple crew members | Compact to medium, no onboard crew |
| Missions | Attack, reconnaissance, deterrence, strategic nuclear delivery | Surveillance, mine countermeasures, intelligence gathering, environmental monitoring |
| Stealth | High stealth with sound-dampening technology | Enhanced stealth due to small size and low acoustic signature |
| Endurance | Weeks to months, powered by nuclear or diesel-electric | Hours to days, battery or fuel-cell powered |
| Cost | High acquisition and operational costs | Lower cost, scalable deployment |
| Risk | Human lives at risk during missions | No onboard personnel, reduces human risk |
| Payload | Torpedoes, missiles, sensors, nuclear warheads | Sensors, small payload delivery, mine neutralization devices |
| Control Complexity | Manual and automated systems with direct crew involvement | Advanced AI and remote command systems |
Introduction to Modern Undersea Warfare
Conventional submarines remain pivotal in modern undersea warfare due to their stealth, endurance, and strategic strike capabilities, equipped with advanced sonar and missile systems. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) enhance undersea operations by providing intelligence, surveillance, reconnaissance, and mine countermeasures without risking crew lives. The integration of UUVs alongside manned submarines is transforming naval tactics, allowing for more flexible and cost-effective maritime dominance.
Defining Conventional Submarines
Conventional submarines are manned naval vessels powered predominantly by diesel-electric engines, designed for underwater operations involving stealth, surveillance, and strategic deterrence. These submarines rely on human crews to execute complex missions, including intelligence gathering, anti-ship warfare, and special operations support. Their capabilities contrast with unmanned underwater vehicles, which operate autonomously or via remote control for reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and data collection without onboard personnel.
Understanding Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs)
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) are autonomous or remotely operated systems that enhance maritime defense capabilities through stealthy reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and environmental monitoring. Unlike conventional submarines, UUVs offer extended operational endurance with reduced risk to personnel and lower detection probability due to their smaller size and quieter operation. Advanced sensor integration and AI-driven navigation enable UUVs to conduct complex underwater missions, making them critical assets for modern naval warfare and surveillance.
Key Differences: Submarine vs UUV Capabilities
Conventional submarines offer advanced stealth, long endurance, and substantial payload capacity, enabling multi-mission operations including strategic deterrence and intelligence gathering. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) provide enhanced operational flexibility, remote deployment, and reduced risk to personnel, excelling in surveillance, mine countermeasures, and reconnaissance. The key differences lie in human crew presence, mission duration, and technological adaptability, with submarines prioritizing sustained combat capabilities and UUVs focusing on tactical versatility and cost efficiency.
Stealth and Survivability: Human vs Unmanned Assets
Conventional submarines leverage advanced stealth technology and human decision-making to enhance survivability in complex underwater combat environments. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) offer reduced detectability through smaller acoustic signatures and can perform high-risk missions without endangering personnel. Integrating UUVs with manned submarines creates a force multiplier, combining human strategic control with autonomous stealth capabilities for superior underwater defense operations.
Mission Profiles: Roles in Maritime Defense
Conventional submarines excel in strategic deterrence, intelligence gathering, and anti-submarine warfare due to their extended endurance and stealth capabilities. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) perform specialized missions such as mine detection, reconnaissance, and underwater surveillance with reduced risk to personnel. Integrating UUVs with manned submarines enhances maritime domain awareness and force multiplication in complex naval operations.
Technological Edge: Sensors and Weapon Systems
Conventional submarines are equipped with advanced sonar arrays, torpedo tubes, and missile launch systems that provide comprehensive strike and stealth capabilities in deep-water operations. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) leverage cutting-edge sensor suites including synthetic aperture sonar, magnetic anomaly detectors, and acoustic sensors for enhanced underwater reconnaissance and mine detection. The technological edge in UUVs lies in their autonomous weapon delivery systems, enabling precise, remote engagement of targets with minimized risk to human crews.
Cost Comparison and Operational Sustainability
Conventional submarines generally incur significantly higher acquisition and maintenance costs compared to Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs), with expenses reaching billions for nuclear-powered vessels versus millions for advanced UUV deployment. Operational sustainability favors UUVs due to lower crew requirements, reduced risk exposure, and extended mission durations enabled by autonomous technology and modular power systems. Budget allocation within naval defense increasingly prioritizes the cost-effective deployment of UUVs for reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and persistent surveillance over the resource-intensive operation of manned submarines.
Crew Requirements and Human Risk Factors
Conventional submarines require a full crew onboard to operate complex navigation, weaponry, and maintenance systems, which increases the risk of human error and exposure to hazardous environments during missions. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) eliminate the need for onboard personnel, significantly reducing human risk factors such as physical danger, fatigue, and psychological stress in hostile or deep-sea conditions. The autonomous or remotely operated nature of UUVs enhances operational endurance and mission safety by minimizing human involvement in high-risk underwater defense operations.
Future Trends in Undersea Military Platforms
Future trends in undersea military platforms highlight the increasing integration of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) alongside conventional submarines to enhance stealth, surveillance, and operational flexibility. Advances in autonomous navigation and AI-driven decision-making enable UUVs to perform complex reconnaissance and mine countermeasure missions with reduced risk to personnel. Conventional submarines continue to evolve with improved propulsion systems and stealth technology, ensuring they remain pivotal in strategic deterrence and multi-domain warfare.
Related Important Terms
Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP)
Conventional submarines equipped with Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP) systems offer prolonged underwater endurance and stealth by reducing the need to surface for oxygen, significantly enhancing their strategic value in naval defense operations. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) utilizing AIP technology enable extended missions with reduced human risk, providing critical capabilities in underwater reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and surveillance without compromising stealth.
XLUUV (Extra-Large Unmanned Underwater Vehicle)
Conventional submarines provide strategic stealth and extended endurance with human-operated decision-making, while XLUUVs (Extra-Large Unmanned Underwater Vehicles) offer enhanced mission flexibility, reduced risk, and persistent surveillance capabilities in contested maritime environments. The integration of XLUUVs into naval fleets enables force multiplication, covert reconnaissance, and payload delivery without exposing personnel to frontline hazards.
Swarm Operations
Conventional submarines offer stealth and endurance for deep-sea missions, while unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) excel in swarm operations by providing scalable and coordinated reconnaissance with reduced risk to human life. Swarm UUVs enhance situational awareness and force multiplication through autonomous, networked collaboration, challenging traditional submarine roles in modern naval warfare.
MUM-T (Manned-Unmanned Teaming)
Manned-Unmanned Teaming (MUM-T) integrates conventional submarines and unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) to enhance maritime defense capabilities through synchronized operations that leverage human decision-making and autonomous sensor systems. This synergy improves situational awareness, extends surveillance reach, and enables covert intelligence gathering, transforming undersea warfare with increased operational flexibility and reduced risk to human crews.
Autonomous Target Recognition
Conventional submarines rely heavily on human-operated sonar systems and manual target identification, limiting real-time decision-making speed, whereas Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) equipped with advanced Autonomous Target Recognition (ATR) systems utilize machine learning algorithms and sensor fusion to detect, classify, and track targets with high precision and minimal human intervention. The integration of ATR in UUVs enhances stealth capabilities, operational endurance, and situational awareness in underwater defense missions, significantly improving threat detection and engagement effectiveness.
Quieting Technologies
Conventional submarines utilize advanced anechoic coatings, raft-mounted machinery, and pump-jet propulsors to minimize acoustic signatures, ensuring stealth in hostile environments. Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) prioritize lightweight, low-vibration electric propulsion and noise-dampening materials to achieve quiet operation during extended surveillance missions.
Remote Underwater Launch (RUL)
Conventional submarines offer strategic advantages in endurance and payload capacity, but Remote Underwater Launch (RUL) technology in Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) enables stealthy, flexible deployment of sensors and munitions without risking crew safety. RUL enhances mission adaptability by allowing autonomous underwater platforms to launch payloads remotely, expanding tactical options in surveillance, mine countermeasures, and offensive operations.
Persistent Surveillance Nodes
Conventional submarines provide strategic depth and stealth capabilities vital for national defense, but their endurance is limited by crew fatigue and logistical support needs. Unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) enhance persistent surveillance nodes by enabling continuous, risk-free monitoring of maritime environments, extending mission duration and operational reach without exposing personnel to danger.
UUV-Mothership Integration
The integration of Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) with conventional submarines enhances naval operational capabilities by enabling extended surveillance, reconnaissance, and mine countermeasure missions beyond the reach of manned platforms. This UUV-mothership synergy leverages the stealth and endurance of conventional submarines while deploying autonomous systems for risk mitigation and expanded mission adaptability in contested underwater environments.
Networked Underwater Battlespace
Conventional submarines offer stealth and extended endurance with human decision-making capabilities crucial for complex underwater networks, while unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) enhance networked underwater battlespace by providing distributed sensing, real-time data sharing, and force multiplication in contested environments. Integrating UUVs with manned submarines creates a resilient, adaptive underwater communication and sensor network essential for modern anti-submarine warfare and maritime domain awareness.
Conventional Submarine vs Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com