Cyber defense strategies emphasize protecting networks through perimeter-based security measures, while Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," enforcing strict identity verification regardless of location. ZTA minimizes attack surfaces by continuously validating user access and device security, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Integrating Zero Trust principles enhances traditional cyber defense by providing granular, real-time threat detection and response capabilities.
Table of Comparison
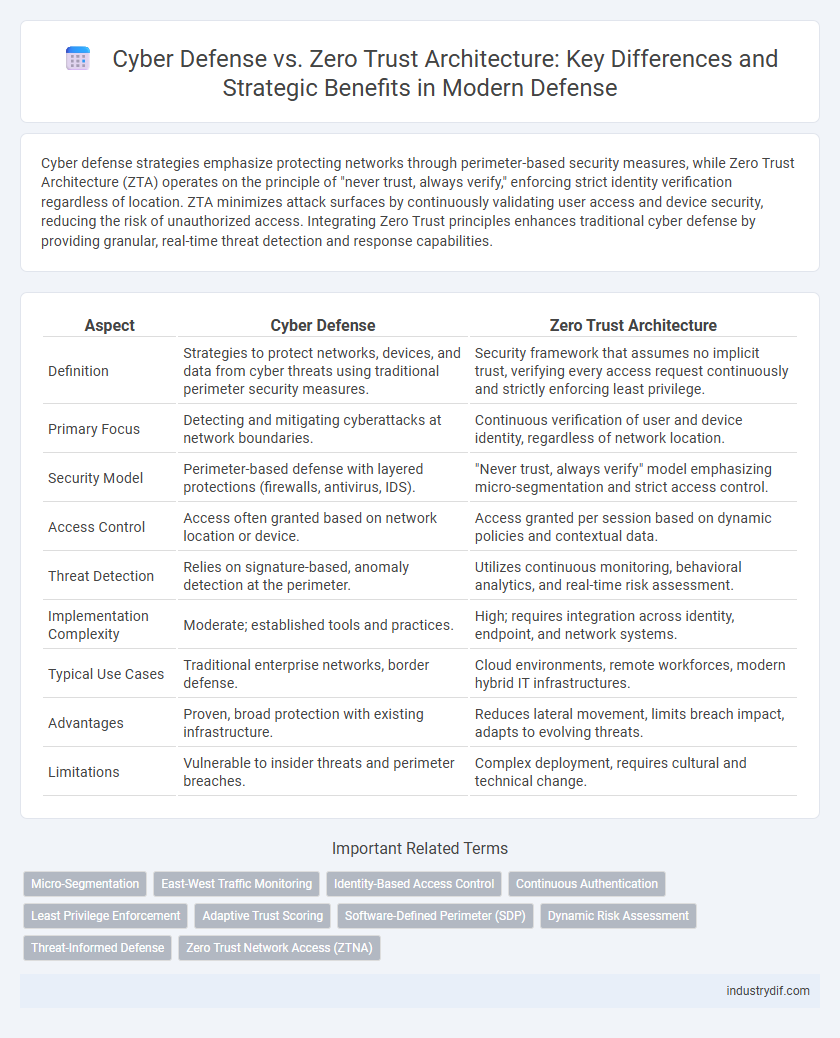
| Aspect | Cyber Defense | Zero Trust Architecture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategies to protect networks, devices, and data from cyber threats using traditional perimeter security measures. | Security framework that assumes no implicit trust, verifying every access request continuously and strictly enforcing least privilege. |
| Primary Focus | Detecting and mitigating cyberattacks at network boundaries. | Continuous verification of user and device identity, regardless of network location. |
| Security Model | Perimeter-based defense with layered protections (firewalls, antivirus, IDS). | "Never trust, always verify" model emphasizing micro-segmentation and strict access control. |
| Access Control | Access often granted based on network location or device. | Access granted per session based on dynamic policies and contextual data. |
| Threat Detection | Relies on signature-based, anomaly detection at the perimeter. | Utilizes continuous monitoring, behavioral analytics, and real-time risk assessment. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate; established tools and practices. | High; requires integration across identity, endpoint, and network systems. |
| Typical Use Cases | Traditional enterprise networks, border defense. | Cloud environments, remote workforces, modern hybrid IT infrastructures. |
| Advantages | Proven, broad protection with existing infrastructure. | Reduces lateral movement, limits breach impact, adapts to evolving threats. |
| Limitations | Vulnerable to insider threats and perimeter breaches. | Complex deployment, requires cultural and technical change. |
Understanding Cyber Defense: Core Principles
Cyber defense centers on proactive threat detection, continuous monitoring, and rapid incident response to safeguard critical defense infrastructures from cyberattacks. Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification and micro-segmentation, reducing attack surfaces by assuming no implicit trust within or outside the network perimeter. Integrating core cyber defense principles with Zero Trust frameworks enhances resilience against sophisticated nation-state cyber threats and advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Zero Trust Architecture: A Paradigm Shift
Zero Trust Architecture represents a paradigm shift in cyber defense by eliminating implicit trust and continuously verifying every access request, thereby minimizing attack surfaces. Unlike traditional cybersecurity models relying on perimeter defenses, Zero Trust enforces strict identity verification, micro-segmentation, and least-privilege access controls across all network resources. This approach significantly enhances protection against sophisticated threats, insider attacks, and lateral movement within networks.
Key Differences Between Cyber Defense and Zero Trust
Cyber Defense encompasses a broad range of strategies and technologies aimed at protecting digital assets from cyber threats, focusing on perimeter security, threat detection, and incident response. Zero Trust Architecture operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify," enforcing strict identity verification and access controls regardless of network location. Key differences include Cyber Defense's emphasis on traditional security perimeters versus Zero Trust's granular, continuous authentication and least-privilege access model.
Historical Evolution of Security Frameworks
Cyber defense has evolved from perimeter-based security models to Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), which assumes no implicit trust within or outside the network. Early frameworks like the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria (TCSEC) laid groundwork by defining basic access controls, but growing cyber threats necessitated ZTA's principle of "never trust, always verify." This shift reflects an adaptive response to advanced persistent threats, emphasizing continuous authentication, micro-segmentation, and strict access policies to enhance defense-in-depth strategies.
Advantages of Traditional Cyber Defense
Traditional cyber defense relies on established perimeter security measures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems, providing a proven first line of defense against external threats. It allows organizations to monitor and control network traffic effectively, leveraging centralized security management for incident response. These methods often require less complex implementation compared to Zero Trust Architecture, making them cost-effective for organizations with limited resources or smaller attack surfaces.
Zero Trust Implementation in Modern Environments
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) enhances cyber defense by strict verification of every user and device, regardless of location, ensuring continuous authentication and authorization within modern enterprise environments. Implementation of Zero Trust involves micro-segmentation, multi-factor authentication, and real-time monitoring to minimize attack surfaces and prevent lateral movement of threats. Modern environments benefit from ZTA by integrating cloud-native security tools and AI-driven analytics to adapt dynamically to emerging cyber threats.
Challenges in Transitioning to Zero Trust
Transitioning to Zero Trust Architecture in cyber defense confronts significant challenges including the complexity of integrating legacy systems with modern security protocols and ensuring continuous authentication across diverse endpoints. Organizations face difficulties in reallocating resources to manage granular access controls while maintaining operational performance and user productivity. Moreover, the cultural shift required for Zero Trust adoption demands extensive training and commitment to ongoing policy enforcement to mitigate evolving cyber threats effectively.
Case Studies: Cyber Defense vs Zero Trust in Action
Case studies reveal that organizations leveraging Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) significantly reduce cyber defense breach incidents by enforcing strict identity verification and micro-segmentation. Enterprises adopting ZTA report a 50% decrease in lateral movement during cyber-attacks, highlighting enhanced containment compared to traditional perimeter-based cyber defense. Real-world deployments in defense sectors demonstrate ZTA's superior effectiveness in mitigating insider threats and advanced persistent threats (APTs) through continuous monitoring and adaptive access controls.
Industry Best Practices for Enterprise Protection
Cyber defense strategies prioritize continuous monitoring, threat intelligence integration, and proactive incident response to safeguard enterprise assets against evolving cyber threats. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) enforces strict access controls by verifying every user and device identity, regardless of network location, significantly reducing attack surfaces. Implementing industry best practices involves combining comprehensive network segmentation, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and real-time analytics to enhance protection and ensure compliance with security frameworks such as NIST and ISO 27001.
Future Trends in Cybersecurity Architectures
Future trends in cybersecurity architectures emphasize the integration of Cyber Defense strategies with Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) principles to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. Advanced machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics are increasingly incorporated to enforce continuous verification of users and devices, minimizing attack surfaces and insider threats. Adoption of cloud-native ZTA frameworks is expanding, enabling scalable, resilient, and context-aware security postures critical for defending against evolving cyber threats.
Related Important Terms
Micro-Segmentation
Cyber defense strategies employing micro-segmentation within Zero Trust Architecture drastically reduce attack surfaces by isolating network segments and enforcing strict access controls. This granular approach limits lateral movement of threats, enhancing overall security posture in defense environments.
East-West Traffic Monitoring
Cyber defense strategies that emphasize East-West traffic monitoring enhance threat detection within internal networks by scrutinizing lateral movement between systems. Zero Trust Architecture complements this approach by enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification, minimizing the risk of insider threats and unauthorized East-West traffic.
Identity-Based Access Control
Cyber defense strategies increasingly prioritize Zero Trust Architecture, which employs Identity-Based Access Control to verify user identities rigorously before granting network access. This approach minimizes insider threats and lateral movement, ensuring strict authentication and authorization protocols within defense systems.
Continuous Authentication
Cyber defense strategies increasingly prioritize continuous authentication within Zero Trust Architecture to ensure persistent verification of user identities and device integrity, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access. Continuous authentication leverages behavioral biometrics, adaptive risk assessments, and real-time monitoring to enforce dynamic security policies that align with Zero Trust principles, enhancing overall threat mitigation.
Least Privilege Enforcement
Cyber defense strategies increasingly rely on Zero Trust Architecture to enforce least privilege principles by ensuring users and devices access only necessary resources, minimizing attack surfaces. Implementing granular access controls and continuous verification within Zero Trust frameworks enhances security posture against sophisticated cyber threats.
Adaptive Trust Scoring
Adaptive Trust Scoring in Cyber Defense enhances Zero Trust Architecture by continuously evaluating user behavior and contextual factors to dynamically adjust access privileges, reducing the risk of unauthorized intrusions. This approach leverages machine learning algorithms and real-time data analytics to assign risk scores, ensuring granular and responsive security postures aligned with evolving threat landscapes.
Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP)
Cyber defense leverages Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP) within Zero Trust Architecture to enforce dynamic, identity-based access controls that isolate network resources and reduce attack surfaces. SDP enhances security by creating encrypted, invisible perimeters that prevent unauthorized lateral movement and minimize risks from compromised credentials.
Dynamic Risk Assessment
Dynamic Risk Assessment in Cyber Defense continuously evaluates threat vectors and system vulnerabilities in real-time, enabling adaptive security measures tailored to evolving risks. Zero Trust Architecture integrates this dynamic approach by enforcing strict identity verification and least-privilege access, reducing attack surfaces and minimizing potential breaches through constant micro-segmentation and behavioral analytics.
Threat-Informed Defense
Cyber Defense integrates Threat-Informed Defense by continuously analyzing real-time threat intelligence to proactively adapt security measures, whereas Zero Trust Architecture enforces strict identity verification and micro-segmentation to minimize attack surfaces. Leveraging Threat-Informed Defense within Zero Trust frameworks enhances detection accuracy and response effectiveness by aligning validation policies with evolving adversary tactics and indicators of compromise.
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) strengthens cyber defense by enforcing strict identity verification and least-privilege access across all network resources, reducing the risk of lateral movement in case of breaches. Unlike traditional perimeter-based security models, ZTNA dynamically verifies users and devices before granting access, ensuring continuous protection in modern, hybrid, and cloud environments.
Cyber Defense vs Zero Trust Architecture Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com