Human soldiers benefit from synthetic training environments by experiencing realistic combat scenarios that enhance situational awareness and decision-making skills without the risks of live training. These environments utilize advanced simulations and AI-driven enemy tactics to replicate diverse battlefield conditions, improving adaptability and stress management. Integrating synthetic training with traditional methods accelerates skill acquisition and prepares soldiers for complex, unpredictable missions.
Table of Comparison
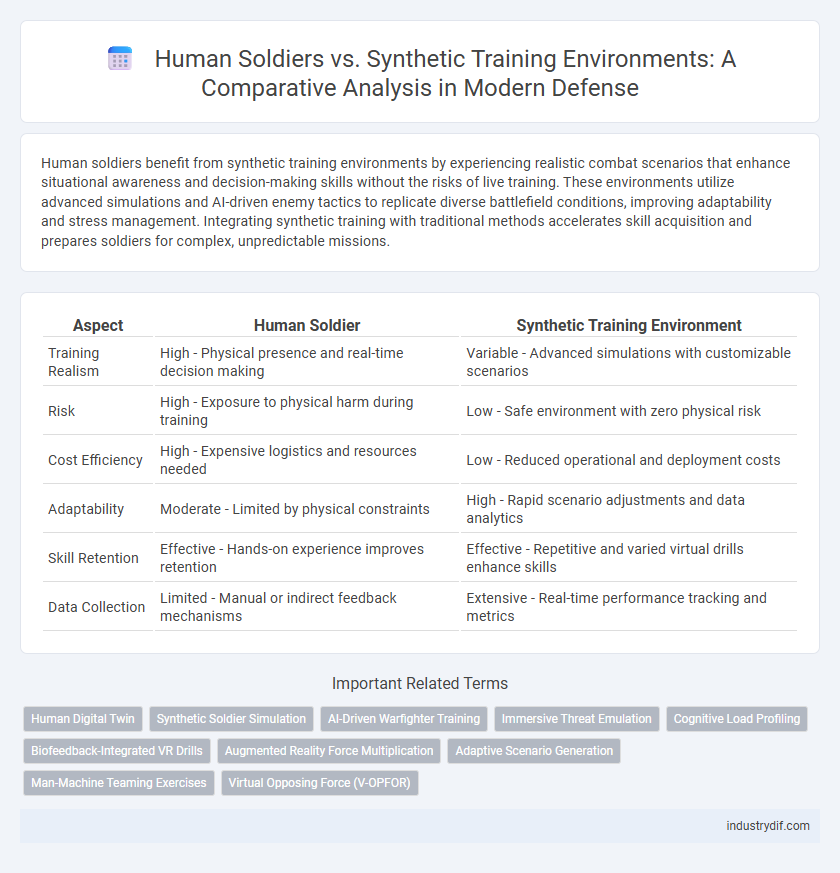
| Aspect | Human Soldier | Synthetic Training Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Training Realism | High - Physical presence and real-time decision making | Variable - Advanced simulations with customizable scenarios |
| Risk | High - Exposure to physical harm during training | Low - Safe environment with zero physical risk |
| Cost Efficiency | High - Expensive logistics and resources needed | Low - Reduced operational and deployment costs |
| Adaptability | Moderate - Limited by physical constraints | High - Rapid scenario adjustments and data analytics |
| Skill Retention | Effective - Hands-on experience improves retention | Effective - Repetitive and varied virtual drills enhance skills |
| Data Collection | Limited - Manual or indirect feedback mechanisms | Extensive - Real-time performance tracking and metrics |
Introduction to Human Soldiers in Modern Defense
Human soldiers remain a pivotal component of modern defense strategies due to their adaptability, critical thinking, and ethical decision-making capabilities that synthetic training environments cannot fully replicate. Advanced synthetic environments enhance soldier readiness by providing immersive simulations that develop combat skills and situational awareness without physical risk. Integrating human expertise with synthetic training technologies optimizes operational effectiveness and mission success in complex defense scenarios.
Overview of Synthetic Training Environments (STE)
Synthetic Training Environments (STE) utilize advanced virtual reality, augmented reality, and artificial intelligence to simulate diverse combat scenarios for human soldiers. These environments enhance decision-making, tactical skills, and situational awareness without physical risks, enabling controlled repetition and performance analysis. STE accelerates readiness by integrating real-time data and adaptive threat models to mirror evolving battlefield conditions accurately.
Key Differences: Human-Centric vs. Virtual Training
Human soldier training emphasizes real-world sensory experiences, decision-making under physical stress, and adaptive problem-solving in unpredictable environments. Synthetic training environments offer scalable, controlled scenarios with instant feedback, enabling repetition and data-driven performance analysis. The key difference lies in human-centric embodied learning versus virtual, algorithm-driven simulation training.
Cognitive Performance and Stress Adaptation
Human soldiers exhibit nuanced cognitive performance and adaptive stress responses honed through real-world experience, while synthetic training environments enhance situational awareness and decision-making under controlled stress simulations. Advances in virtual reality and AI-driven scenarios offer scalable, repeatable stress adaptations that complement traditional training, enabling optimized cognitive resilience. Integration of biometric feedback and neurocognitive assessments in synthetic platforms provides data-driven insights to refine soldier readiness and mental endurance against battlefield stressors.
Realism and Immersion in Synthetic Environments
Synthetic training environments leverage advanced virtual reality and AI-driven simulations to enhance realism and immersion, closely replicating battlefield conditions for human soldiers. High-fidelity graphics, haptic feedback, and dynamic scenario adjustments create an adaptive training platform that improves decision-making and situational awareness. These technologies bridge the gap between live training exercises and controlled simulations, optimizing preparedness while minimizing risk and logistical constraints.
Cost Efficiency and Resource Allocation
Synthetic training environments offer significant cost efficiency by reducing the need for physical materials, travel, and facility usage associated with human soldier training exercises. These virtual platforms allow for scalable resource allocation, enabling defense agencies to optimize manpower and equipment deployment without compromising training quality. Leveraging advanced simulation technologies ultimately maximizes budget utilization while maintaining mission readiness.
Data Analytics and Feedback in STE
Synthetic Training Environments (STE) utilize advanced data analytics to monitor human soldier performance in real-time, capturing metrics such as reaction time, accuracy, and decision-making patterns. These environments provide immediate, precise feedback through AI-driven assessments, enabling tailored training adjustments that enhance skill acquisition and mission readiness. Integration of big data analytics in STE supports continuous improvement by identifying performance trends and optimizing training scenarios based on empirical soldier data.
Limitations of Human Training and STE
Human soldier training faces limitations such as physical fatigue, risk of injury, and inconsistent skill replication, which hinder optimal readiness. Synthetic Training Environments (STE) offer controlled, repeatable scenarios that enhance cognitive skills without physical constraints but may lack full realism in sensory feedback. Integrating STE with human training addresses these gaps by combining immersive simulation with real-world experience for comprehensive soldier preparedness.
Integration of Human Factors with Synthetic Technologies
Integrating human factors with synthetic training technologies enhances soldier performance through realistic simulations that replicate cognitive and physical stressors. Advanced synthetic environments utilize biometric feedback and adaptive AI to tailor scenarios, improving decision-making and situational awareness under combat conditions. This synergy between human intuition and synthetic adaptability accelerates skill acquisition and operational readiness in modern defense training programs.
Future Outlook: Hybrid Training Models in Defense
Hybrid training models in defense combine human soldiers' experiential judgment with synthetic environments' adaptability and scalability, enhancing combat readiness and decision-making skills. These models leverage virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and AI-driven simulations to create immersive, realistic scenarios that improve cognitive and physical training outcomes. The integration of real-time data analytics and machine learning ensures continuous feedback and customization, accelerating skill acquisition and operational effectiveness.
Related Important Terms
Human Digital Twin
Human Digital Twin technology revolutionizes defense training by creating precise virtual replicas of soldiers, enabling personalized performance analysis and adaptive skill development in synthetic training environments. This innovation enhances mission readiness through real-time physiological and cognitive data integration, optimizing training effectiveness and minimizing physical risk.
Synthetic Soldier Simulation
Synthetic soldier simulation enhances defense training by providing realistic, scalable, and programmable combat scenarios that allow soldiers to rehearse tactics without physical constraints or risk. These virtual environments leverage AI-driven avatars and advanced sensor integration to replicate diverse battlefield conditions, improving decision-making and operational readiness more efficiently than traditional live exercises.
AI-Driven Warfighter Training
AI-driven warfighter training leverages synthetic environments that replicate complex combat scenarios with high fidelity, enabling soldiers to develop critical decision-making skills and muscle memory in safe, controlled settings. These advanced simulations use machine learning algorithms to adapt in real-time, providing personalized feedback and enhancing the effectiveness of traditional human soldier training methods.
Immersive Threat Emulation
Immersive threat emulation within synthetic training environments enhances human soldier preparedness by replicating realistic combat scenarios using advanced virtual reality and AI-driven adversaries. These simulations improve decision-making, situational awareness, and stress resilience through dynamic, adaptive threat representations that traditional live training cannot consistently provide.
Cognitive Load Profiling
Human soldiers exhibit varying cognitive load responses when training in synthetic environments, with real-time profiling enabling tailored scenario adjustments to optimize decision-making and situational awareness. Advanced cognitive load profiling tools integrate biometric sensors and AI analytics to enhance training efficiency by identifying stress points and cognitive bottlenecks specific to individual trainees.
Biofeedback-Integrated VR Drills
Biofeedback-integrated VR drills enhance human soldier training by providing real-time physiological data to adapt scenarios for stress management and performance optimization. This synthetic training environment improves combat readiness and resilience through immersive simulation of battlefield conditions monitored by heart rate, respiration, and galvanic skin response sensors.
Augmented Reality Force Multiplication
Augmented reality force multiplication in synthetic training environments enhances human soldiers' situational awareness and decision-making accuracy by overlaying real-time data and interactive simulations, accelerating skill acquisition and mission preparedness. This technology bridges the gap between live exercises and virtual scenarios, reducing training costs while intensifying combat readiness through immersive, adaptive, and scalable training modules.
Adaptive Scenario Generation
Adaptive scenario generation in synthetic training environments leverages real-time algorithms to create dynamic battlefield simulations that respond to a soldier's tactical decisions and skill level, enhancing situational awareness and decision-making under pressure. These advanced systems enable personalized training by continuously adjusting variables such as enemy behavior, environmental conditions, and mission objectives, resulting in improved operational readiness and battlefield performance.
Man-Machine Teaming Exercises
Man-machine teaming exercises in defense utilize synthetic training environments to enhance soldier performance by integrating real-time AI-driven simulations that replicate complex battlefield scenarios. These environments enable human soldiers to develop adaptive decision-making skills and seamless coordination with autonomous systems, optimizing operational effectiveness and mission success.
Virtual Opposing Force (V-OPFOR)
Virtual Opposing Force (V-OPFOR) leverages advanced synthetic training environments to simulate realistic combat scenarios, providing human soldiers with adaptive adversaries that enhance situational awareness and tactical decision-making. These immersive virtual opponents utilize artificial intelligence to replicate diverse enemy tactics, driving improved preparedness and operational effectiveness in defense training programs.
Human Soldier vs Synthetic Training Environment Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com