Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online learning, offering flexibility and personalized pacing for students. Cohort-based learning groups learners together to progress through a curriculum simultaneously, fostering collaboration and peer support. Choosing between these methods depends on the desired balance of interaction and self-directed study in educational settings.
Table of Comparison
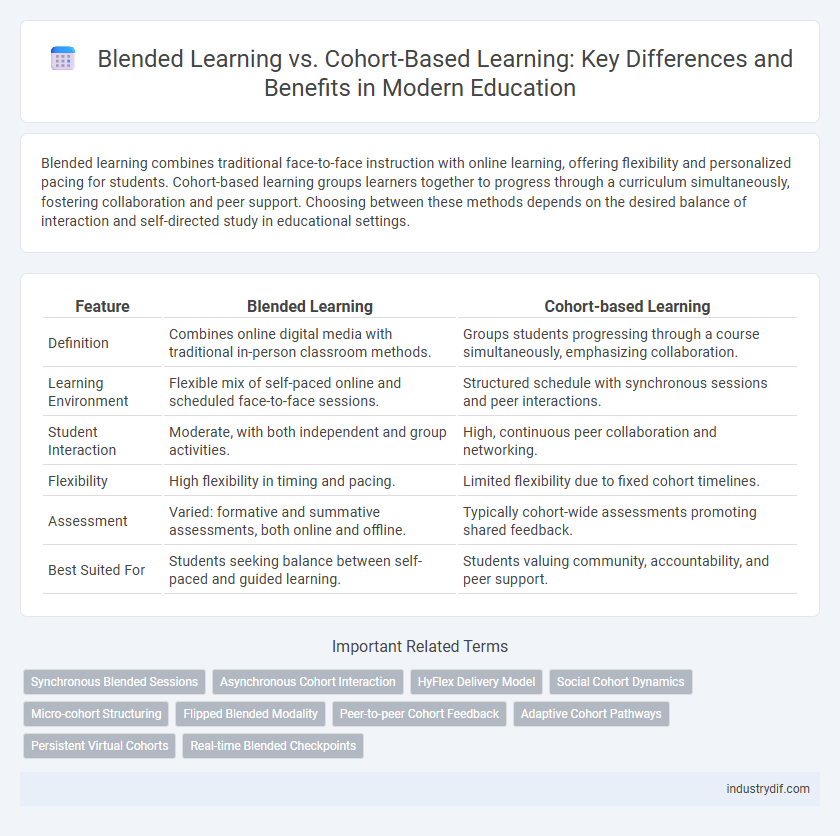
| Feature | Blended Learning | Cohort-based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional in-person classroom methods. | Groups students progressing through a course simultaneously, emphasizing collaboration. |
| Learning Environment | Flexible mix of self-paced online and scheduled face-to-face sessions. | Structured schedule with synchronous sessions and peer interactions. |
| Student Interaction | Moderate, with both independent and group activities. | High, continuous peer collaboration and networking. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in timing and pacing. | Limited flexibility due to fixed cohort timelines. |
| Assessment | Varied: formative and summative assessments, both online and offline. | Typically cohort-wide assessments promoting shared feedback. |
| Best Suited For | Students seeking balance between self-paced and guided learning. | Students valuing community, accountability, and peer support. |
Defining Blended Learning in Education
Blended learning in education combines traditional face-to-face classroom methods with online digital media, creating an integrated instructional approach that maximizes student engagement and flexibility. This model leverages technology platforms like Learning Management Systems (LMS) to facilitate personalized learning pathways, enabling scalable access to diverse resources and interactive content. Research from the Clayton Christensen Institute highlights improved retention rates and learner satisfaction as key benefits of blended learning environments.
Understanding Cohort-based Learning Models
Cohort-based learning models structure education around fixed groups of students progressing through a curriculum simultaneously, fostering collaboration and peer support. This model emphasizes shared experiences, accountability, and real-time interaction, which can enhance motivation and retention compared to individualistic approaches. Understanding these models helps optimize course design by leveraging social dynamics and synchronous engagement to improve learning outcomes.
Key Differences: Blended vs Cohort-based Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, allowing students to learn at their own pace while still engaging in face-to-face interactions. Cohort-based learning organizes students into fixed groups progressing through the curriculum together, fostering collaboration and peer support. The key differences lie in flexibility and structure: blended learning offers individualized pacing and mixed modalities, whereas cohort-based learning emphasizes synchronized progression and group dynamics.
Benefits of Blended Learning for Modern Students
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering modern students flexibility and personalized pacing to enhance engagement and retention. This approach supports diverse learning styles and enables real-time feedback, fostering deeper understanding through interactive content and collaborative activities. By integrating technology with face-to-face instruction, blended learning improves accessibility and prepares students for digital proficiency essential in today's workforce.
Advantages of Cohort-based Learning Approaches
Cohort-based learning fosters strong peer collaboration and accountability by engaging students in structured group settings throughout the course duration. This approach enhances retention and motivation through shared goals and real-time feedback, creating a dynamic and supportive learning community. Cohorts also facilitate personalized instruction and networking opportunities, which can lead to improved academic and career outcomes.
Technology’s Role in Blended and Cohort-based Education
Technology in blended learning integrates digital tools and platforms to facilitate flexible, self-paced study, enhancing personalized educational experiences through adaptive learning software and virtual classrooms. In cohort-based learning, technology primarily supports synchronous interaction and collaboration via video conferencing, discussion forums, and shared digital workspaces, fostering peer engagement and real-time feedback. Both approaches leverage learning management systems to track progress and manage resources, but blended learning emphasizes individualized access while cohort-based learning focuses on collective participation.
Flexibility and Personalization in Learning Modalities
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering flexibility for students to access content anytime and tailor their study pace, enhancing personalized learning experiences. Cohort-based learning groups students to progress together through a fixed curriculum, fostering collaboration but limiting individual pace adjustments. The blend of asynchronous digital resources with synchronous group interactions in blended learning enables a more adaptive approach compared to the structured, time-bound format of cohort-based models.
Student Engagement: Blended vs Cohort-based Strategies
Blended learning enhances student engagement by combining online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, allowing personalized pacing and interactive content that adapts to individual learning styles. Cohort-based learning fosters a strong sense of community and peer support, promoting collaboration and accountability through synchronized group progress and shared experiences. Effective educational strategies integrate these approaches to maximize engagement by balancing flexibility and structured social interaction.
Assessment Methods in Blended and Cohort-based Learning
Blended learning assessment methods integrate online quizzes, interactive assignments, and traditional in-person evaluations to provide a comprehensive understanding of student progress and adaptability across various learning environments. Cohort-based learning assessments emphasize group projects, peer evaluations, and collaborative problem-solving tasks designed to measure collective knowledge retention and interpersonal skills within a fixed learning community. Both approaches employ formative and summative assessments but differ in their focus, with blended learning prioritizing individual performance across digital and face-to-face modalities, while cohort-based learning concentrates on communal learning outcomes and group dynamics.
Choosing the Right Model: Factors for Educational Institutions
Educational institutions should consider student engagement levels, resource availability, and learning objectives when choosing between blended learning and cohort-based learning models. Blended learning offers flexibility and personalized pacing through a mix of online and in-person instruction, ideal for diverse learning needs and technology integration. Cohort-based learning fosters collaboration and peer interaction by grouping learners to progress together, supporting community building and structured timelines.
Related Important Terms
Synchronous Blended Sessions
Synchronous blended sessions combine real-time virtual instruction with in-person activities, enhancing engagement and immediate feedback in blended learning environments. Cohort-based learning benefits from these sessions by fostering collaboration and consistent pacing among group members, improving overall retention and skill development.
Asynchronous Cohort Interaction
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, allowing students to engage asynchronously while benefiting from periodic face-to-face interactions. In cohort-based learning, asynchronous cohort interaction fosters collaboration and peer support through structured discussion forums and group assignments, enhancing engagement within a fixed group timeline.
HyFlex Delivery Model
The HyFlex delivery model integrates blended learning by offering flexible participation through both in-person and online formats, enhancing accessibility and personalized education. Combining real-time cohort-based learning dynamics with self-paced elements, HyFlex supports diverse learning preferences while maintaining collaborative engagement.
Social Cohort Dynamics
Blended learning integrates online and face-to-face instruction, fostering flexible social cohort dynamics by allowing diverse interaction modalities that enhance peer engagement and collaboration. Cohort-based learning emphasizes synchronous group progression, strengthening social bonds and collective accountability through shared experiences and structured communication within fixed cohorts.
Micro-cohort Structuring
Micro-cohort structuring in blended learning combines the flexibility of online instruction with small, focused groups that enhance peer interaction and personalized feedback, optimizing student engagement and retention. Cohort-based learning organizes students into fixed groups progressing through curriculum simultaneously, promoting collaboration and accountability but potentially limiting individualized pacing.
Flipped Blended Modality
Flipped blended learning combines asynchronous pre-class study with interactive, cohort-based in-class activities to enhance engagement and deeper understanding. This modality leverages collaborative cohort structures to maximize peer interaction while allowing flexible, self-paced content absorption outside the classroom.
Peer-to-peer Cohort Feedback
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, fostering flexible and personalized education, while cohort-based learning organizes students into groups progressing through a curriculum simultaneously, enhancing peer-to-peer cohort feedback opportunities. Peer-to-peer feedback in cohort-based learning amplifies collaborative problem-solving and critical thinking by allowing learners to share diverse perspectives and receive immediate, relevant input from classmates engaged in the same learning phase.
Adaptive Cohort Pathways
Adaptive cohort pathways in blended learning integrate personalized digital content with synchronized group activities, enhancing student engagement and retention by tailoring instruction to individual learning paces within a collaborative environment. This approach leverages real-time data analytics to adjust curricular progressions dynamically, offering a scalable solution that combines the benefits of cohort-based interaction with adaptive learning technologies for improved educational outcomes.
Persistent Virtual Cohorts
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering flexibility and personalized pacing, whereas cohort-based learning emphasizes group progression through a curriculum, fostering collaboration and peer support. Persistent virtual cohorts enhance cohort-based learning by maintaining continuous online interaction, enabling sustained engagement and community building beyond scheduled sessions, which improves knowledge retention and learner motivation.
Real-time Blended Checkpoints
Real-time blended checkpoints in blended learning integrate synchronous assessments with asynchronous content, enabling immediate feedback and adaptive instruction tailored to individual student progress. Cohort-based learning, while promoting collaborative pacing, often lacks the flexibility of real-time checkpoints that blend digital and live interactions for dynamic student engagement and personalized learning paths.
Blended Learning vs Cohort-based Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com