Educational degrees provide comprehensive academic training over several years, often including theoretical knowledge and practical experience in a chosen field. Nanodegrees are short, skill-focused programs designed to quickly equip learners with specific competencies, ideal for career advancement or switching fields. Both options offer unique advantages depending on individual goals, time availability, and career aspirations within education and technology sectors.
Table of Comparison
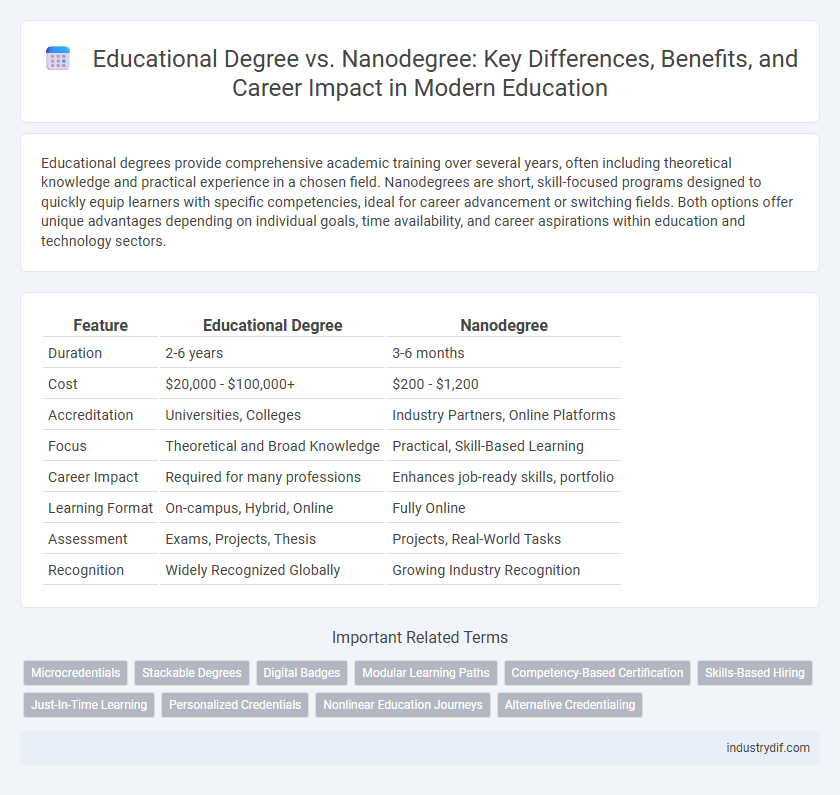
| Feature | Educational Degree | Nanodegree |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | 2-6 years | 3-6 months |
| Cost | $20,000 - $100,000+ | $200 - $1,200 |
| Accreditation | Universities, Colleges | Industry Partners, Online Platforms |
| Focus | Theoretical and Broad Knowledge | Practical, Skill-Based Learning |
| Career Impact | Required for many professions | Enhances job-ready skills, portfolio |
| Learning Format | On-campus, Hybrid, Online | Fully Online |
| Assessment | Exams, Projects, Thesis | Projects, Real-World Tasks |
| Recognition | Widely Recognized Globally | Growing Industry Recognition |
Understanding Traditional Educational Degrees
Traditional educational degrees, such as associate, bachelor's, master's, and doctoral programs, offer comprehensive curricula designed to provide foundational knowledge and critical thinking skills across various academic disciplines. These degrees typically require multi-year commitments and emphasize theoretical frameworks, research methodologies, and broad subject mastery. Employers often value traditional degrees for their rigorous accreditation and extensive academic preparation in professional fields.
What is a Nanodegree?
A Nanodegree is a short, skill-focused certification designed by industry leaders to provide practical knowledge in areas like programming, data science, and digital marketing. Unlike traditional educational degrees that cover broad academic disciplines over several years, Nanodegrees emphasize hands-on projects and real-world applications to quickly build job-ready skills. These programs are often online, flexible, and aligned with current industry demands, making them a popular choice for career advancement in tech-driven fields.
Key Differences: Degree vs Nanodegree
Traditional educational degrees typically require multiple years of study, covering broad theoretical knowledge and offering deep academic credentials recognized globally. Nanodegrees, often provided by online platforms like Udacity, focus on specific skill sets and practical, project-based learning designed to quickly prepare students for niche job markets. Degrees emphasize comprehensive education and research, while nanodegrees target rapid skill acquisition and direct employment opportunities in evolving industries.
Curriculum Structure: Degrees vs Nanodegrees
Educational degrees typically follow a comprehensive and structured curriculum spanning several years, covering foundational knowledge alongside advanced topics across multiple disciplines. Nanodegrees focus on specialized, skill-based modules designed for rapid learning and immediate application in specific fields such as technology and digital marketing. The modular format of nanodegrees allows for flexible pacing and updates aligned with industry trends, contrasting with the fixed, semester-based structure of traditional degree programs.
Duration and Time Commitment
Educational degrees typically require multiple years of full-time study, ranging from two to six years depending on the level and field, while nanodegrees are designed for accelerated learning, often completed in two to six months with flexible, part-time commitment. Traditional degrees demand consistent campus attendance and broader coursework, whereas nanodegrees focus on specific skills through online modules, offering greater adaptability for working professionals. Time investment in nanodegrees prioritizes practical application and immediate industry relevance, contrasting with the comprehensive theoretical foundations emphasized in degree programs.
Cost Comparison: Degrees vs Nanodegrees
Traditional educational degrees typically require a substantial financial investment, often amounting to tens of thousands of dollars in tuition, fees, and associated expenses over several years. Nanodegrees offer a cost-effective alternative, usually priced between $200 and $1,500, allowing learners to acquire specialized skills in a shorter timeframe. This significant cost difference makes nanodegrees accessible for budget-conscious students seeking targeted education without the long-term financial commitment of a full degree.
Employer Perceptions and Industry Value
Employers often perceive traditional educational degrees as comprehensive credentials that demonstrate a broad foundation of knowledge and critical thinking skills relevant across multiple fields. Nanodegrees, while more specialized and focused on specific skills like coding or digital marketing, are valued for their practical, industry-aligned content that enables rapid workforce readiness. In rapidly evolving industries such as technology, nanodegrees can complement traditional degrees by providing targeted expertise that meets current employer demands and enhances job market competitiveness.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Nanodegrees offer greater flexibility and accessibility compared to traditional educational degrees by providing online, self-paced courses that accommodate diverse schedules and learning speeds. Unlike conventional degree programs that often require physical attendance and fixed timelines, nanodegrees enable learners to gain specialized skills quickly without geographic or financial barriers. This approach democratizes education, making it easier for working professionals and non-traditional students to advance their careers efficiently.
Career Outcomes and Advancement
Educational degrees, such as bachelor's or master's, provide comprehensive knowledge and are widely recognized by employers, often serving as prerequisites for advanced career roles and higher salaries. Nanodegrees, offered by platforms like Udacity, focus on specialized, job-ready skills in emerging fields like AI and data science, facilitating faster career advancement and entry into tech-driven industries. Employers increasingly value nanodegrees for their practical, up-to-date skill sets, complementing traditional degrees in competitive job markets.
Choosing the Right Path: Degree or Nanodegree
Selecting between an educational degree and a nanodegree depends on career goals, time commitment, and industry demand. Educational degrees offer comprehensive knowledge and are often required for professions like medicine or engineering, while nanodegrees provide targeted skills in technology, programming, or data science with flexible timelines. Evaluating job market trends and personal learning preferences helps determine whether a traditional degree or a specialized nanodegree aligns best with professional aspirations.
Related Important Terms
Microcredentials
Microcredentials, including nanodegrees, offer targeted skills and industry-relevant knowledge emphasizing practical learning and rapid career advancement, contrasting with traditional educational degrees' broader theoretical framework. These focused digital certifications are increasingly recognized by employers for specific competencies, aligning education with evolving job market demands.
Stackable Degrees
Stackable degrees offer a flexible and modular approach to education, allowing learners to combine traditional educational degrees with nanodegrees to build specialized skill sets tailored to industry demands. This blend of credentials enhances career prospects by providing both comprehensive theoretical knowledge and practical, concise skill-based training recognized by employers.
Digital Badges
Educational degrees typically represent comprehensive academic achievements recognized by accredited institutions, while nanodegrees emphasize specialized, skill-focused learning often validated through digital badges that showcase verified competencies in specific digital skills. Digital badges serve as portable, shareable credentials that enhance employability by providing real-time proof of expertise in targeted areas such as coding, data analysis, or digital marketing.
Modular Learning Paths
Educational degrees provide comprehensive, structured curricula spanning multiple years, offering in-depth theoretical knowledge and broad foundational skills, while nanodegrees emphasize modular learning paths tailored for specific skills with flexible, shorter time commitments targeting immediate career applicability. Modular learning paths in nanodegrees allow learners to customize their education, focusing on relevant industry-demanded competencies, facilitating continuous upskilling and adaptability in a rapidly evolving job market.
Competency-Based Certification
Competency-based certification in education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and practical knowledge over traditional time-based credentials, making nanodegrees a flexible and targeted alternative to conventional educational degrees. Nanodegrees often provide specialized training aligned with industry standards, enabling learners to demonstrate job-ready competencies efficiently in contrast to broader, theory-focused degree programs.
Skills-Based Hiring
Skills-based hiring increasingly values nanodegrees for their focus on practical, job-ready skills and shorter completion times compared to traditional educational degrees. Employers prioritize candidates with verified competencies in specific areas like programming, data analysis, or digital marketing, often demonstrated through nanodegree projects and assessments.
Just-In-Time Learning
Educational degrees provide comprehensive, long-term academic foundations across various disciplines, while nanodegrees offer focused, Just-In-Time learning tailored for specific skill acquisition in rapidly evolving industries like technology and digital marketing. This targeted approach enables learners to quickly gain practical expertise and adapt to market demands without the extended time commitment of traditional degrees.
Personalized Credentials
Personalized credentials offered through nanodegrees provide targeted skill development and industry-relevant expertise tailored to current job market demands. Traditional educational degrees focus on broad theoretical knowledge and foundational concepts, while nanodegrees emphasize practical, project-based learning with flexible timelines to cater to individual career goals.
Nonlinear Education Journeys
Educational degrees offer structured, comprehensive curricula across multiple disciplines, while nanodegrees provide focused, skill-specific training designed for flexibility and rapid adaptation to industry demands. Nonlinear education journeys blend these pathways, empowering learners to customize their knowledge acquisition by combining traditional academic credentials with micro-credentialing options like nanodegrees to enhance employability and lifelong learning.
Alternative Credentialing
Nanodegrees offer specialized, skills-focused training designed for rapid workforce entry, contrasting traditional educational degrees that provide broad theoretical knowledge over several years. Alternative credentialing like nanodegrees enhances career adaptability by certifying practical competencies valued by employers in technology-driven industries.
Educational Degree vs Nanodegree Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com