Credit hours measure learning based on time spent in class, often limiting flexibility and pace. Competency-based education emphasizes mastery of skills and knowledge, allowing students to progress as they demonstrate understanding. This approach better accommodates individual learning styles and real-world application of skills.
Table of Comparison
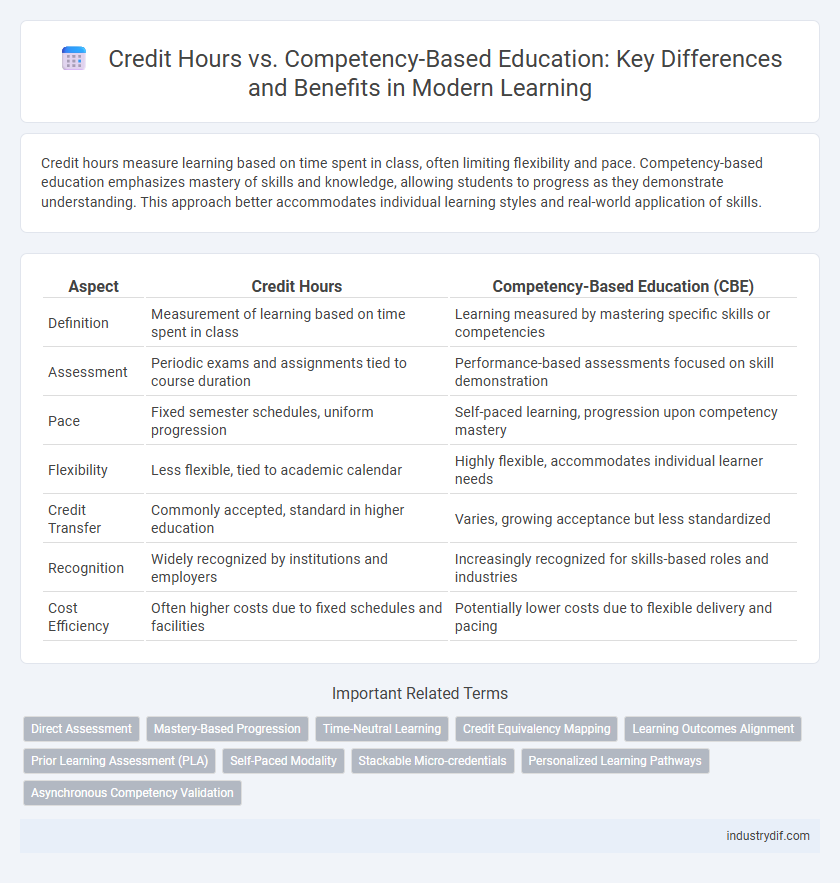
| Aspect | Credit Hours | Competency-Based Education (CBE) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement of learning based on time spent in class | Learning measured by mastering specific skills or competencies |
| Assessment | Periodic exams and assignments tied to course duration | Performance-based assessments focused on skill demonstration |
| Pace | Fixed semester schedules, uniform progression | Self-paced learning, progression upon competency mastery |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, tied to academic calendar | Highly flexible, accommodates individual learner needs |
| Credit Transfer | Commonly accepted, standard in higher education | Varies, growing acceptance but less standardized |
| Recognition | Widely recognized by institutions and employers | Increasingly recognized for skills-based roles and industries |
| Cost Efficiency | Often higher costs due to fixed schedules and facilities | Potentially lower costs due to flexible delivery and pacing |
Understanding Credit Hours in Traditional Education
Credit hours in traditional education measure the amount of time students spend in class, typically defining one credit hour as one hour of classroom instruction per week over a semester. This system emphasizes seat time and structured schedules, often requiring students to complete a set number of credit hours to earn a degree. Understanding credit hours helps clarify how academic progress is quantified through time-based benchmarks rather than demonstrated skills or competencies.
What is Competency-Based Education?
Competency-Based Education (CBE) focuses on students demonstrating mastery of specific skills or knowledge rather than accumulating credit hours through time spent in class. CBE allows learners to progress at their own pace by proving mastery through assessments and real-world applications. This approach emphasizes personalized learning outcomes and practical competencies aligned with workforce demands.
Historical Overview: Credit Hours vs. Competency Models
Credit hours have traditionally served as the standard metric for measuring student learning based on seat time and instructional hours since the early 20th century, reflecting a time-bound approach rooted in college and university accreditation systems. Competency-based education (CBE) emerged in the late 20th and early 21st centuries as a response to the limitations of credit hours, emphasizing mastery of skills and knowledge regardless of time spent, aligning educational outcomes with workforce demands. This shift highlights a historical transition from time-based to outcome-based frameworks, driven by technological advancements and evolving employer expectations for demonstrable competencies.
Measuring Student Progress: Seat Time vs. Mastery
Credit hours measure student progress based on seat time, quantifying the duration spent in classroom instruction. Competency-based education evaluates mastery by assessing a student's demonstrated knowledge and skills, regardless of time spent. This approach prioritizes learning outcomes over time, enabling personalized pacing and a focus on true competency attainment.
Flexibility: Fixed Schedules vs. Personalized Pacing
Credit hours rely on fixed schedules with predetermined class times and durations, limiting flexibility for students with varying learning speeds. Competency-Based Education (CBE) allows personalized pacing by enabling learners to progress upon mastering skills, accommodating individual learning styles and time constraints. This adaptability makes CBE a more flexible option compared to the rigid structure of credit hour systems.
Assessment Methods: Exams vs. Demonstrated Skills
Credit hour systems primarily assess student learning through timed exams and standardized testing, measuring knowledge acquisition over fixed class periods. Competency-based education evaluates demonstrated skills and real-world application, allowing students to progress by proving mastery regardless of time spent. This shift emphasizes personalized assessment methods that prioritize practical abilities over traditional exam performance.
Impact on Graduation Rates and Time-to-Completion
Credit hours focus on time spent in class, often prolonging degree completion and affecting graduation rates negatively. Competency-based education (CBE) allows students to progress by mastering skills, accelerating time-to-completion and improving graduation rates. Studies show CBE programs increase flexibility, reduce excess credits, and enhance student success outcomes compared to traditional credit hour models.
Affordability and Cost Structure in Both Models
Credit hours often lead to higher tuition costs due to fixed time requirements and resource allocation, whereas competency-based education (CBE) can lower expenses by allowing students to progress at their own pace, reducing time spent in courses. CBE models typically offer flexible payment structures tied to demonstrated skills instead of seat time, promoting affordability for learners balancing work and study. The shift to competency-based assessments minimizes unnecessary course repetition, further decreasing overall education costs compared to traditional credit hour frameworks.
Employer Perceptions and Workforce Readiness
Employers increasingly value competency-based education (CBE) over traditional credit hour models due to its emphasis on demonstrable skills and real-world readiness. Competency-based programs align learning outcomes with industry standards, enabling graduates to meet specific workforce needs more effectively. This alignment enhances employer confidence in candidate capabilities, accelerating hiring decisions and promoting career advancement.
Future Trends: The Shift Toward Competency-Based Learning
The future of education is marked by a shift toward competency-based learning, emphasizing mastery of skills over traditional credit hours. This approach enables personalized pacing and real-world application, aligning education with workforce demands. Institutions increasingly adopt competency frameworks to enhance flexibility, improve student outcomes, and address skill gaps in rapidly evolving industries.
Related Important Terms
Direct Assessment
Direct assessment in competency-based education measures student mastery through demonstrable skills and knowledge instead of credit hours, offering personalized pacing and flexibility. This approach aligns learning outcomes directly with industry standards and academic competencies, enhancing relevance and accountability in education.
Mastery-Based Progression
Mastery-based progression in competency-based education allows students to advance upon demonstrating mastery of specific skills or knowledge, contrasting sharply with the traditional credit hour system that measures learning based on time spent in class. This approach prioritizes individualized learning pace and ensures deeper understanding and application of subject matter, enhancing educational outcomes in mastery-focused programs.
Time-Neutral Learning
Credit hours measure student progress based on time spent in class, while competency-based education emphasizes mastery of skills regardless of time. Time-neutral learning allows students to advance upon demonstrating proficiency, promoting personalized pacing and flexible education pathways.
Credit Equivalency Mapping
Credit equivalency mapping translates competency-based learning outcomes into traditional credit hours, facilitating seamless student transitions and institutional recognition across education systems. This mapping ensures accurate assessment of skills mastery against standardized credit benchmarks, optimizing academic progression and degree completion timelines.
Learning Outcomes Alignment
Credit hours traditionally measure student progress through time spent in class, while competency-based education emphasizes mastery of specific skills and knowledge, directly aligning learning outcomes with real-world competencies. Aligning learning outcomes in competency-based education ensures students demonstrate practical abilities and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding beyond seat-time metrics.
Prior Learning Assessment (PLA)
Prior Learning Assessment (PLA) enables students to earn academic credit by demonstrating mastery of skills and knowledge acquired outside traditional classrooms, offering a flexible alternative to credit hours in competency-based education models. This approach accelerates degree completion, reduces education costs, and acknowledges real-world experience, aligning with personalized learning paths and workforce readiness.
Self-Paced Modality
Credit hours are traditionally used to measure time spent in class, whereas competency-based education (CBE) emphasizes mastery of skills at the learner's own pace, allowing for flexible, self-paced progression. In self-paced CBE modalities, students advance by demonstrating competency through assessments, enabling personalized learning paths that accommodate individual schedules and learning speeds.
Stackable Micro-credentials
Stackable micro-credentials enable learners to accumulate verified competencies through targeted assessments, offering a flexible alternative to traditional credit hours that measure time spent in class. This approach accelerates skill acquisition and enhances career readiness by aligning education with specific industry competencies and personalized learning pathways.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Credit hours measure education by time spent in class, whereas competency-based education (CBE) focuses on mastery of skills and knowledge, enabling personalized learning pathways tailored to individual student progress. CBE allows learners to advance at their own pace, ensuring a more flexible and efficient education aligned with specific career goals and competencies.
Asynchronous Competency Validation
Asynchronous competency validation in competency-based education enables students to demonstrate mastery at their own pace, independent of traditional credit hour constraints. This approach enhances personalized learning by allowing flexible assessment timing and reduces time-to-completion compared to fixed-semester credit hour systems.
Credit Hours vs Competency-Based Education Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com