Semester admission follows a fixed schedule with specific start and end dates, allowing students to plan their academic year in structured intervals. Rolling admission offers flexibility by accepting applications continuously, enabling students to enroll at multiple points throughout the year. Choosing between these options depends on a student's need for a predictable timeline or the ability to start studies promptly.
Table of Comparison
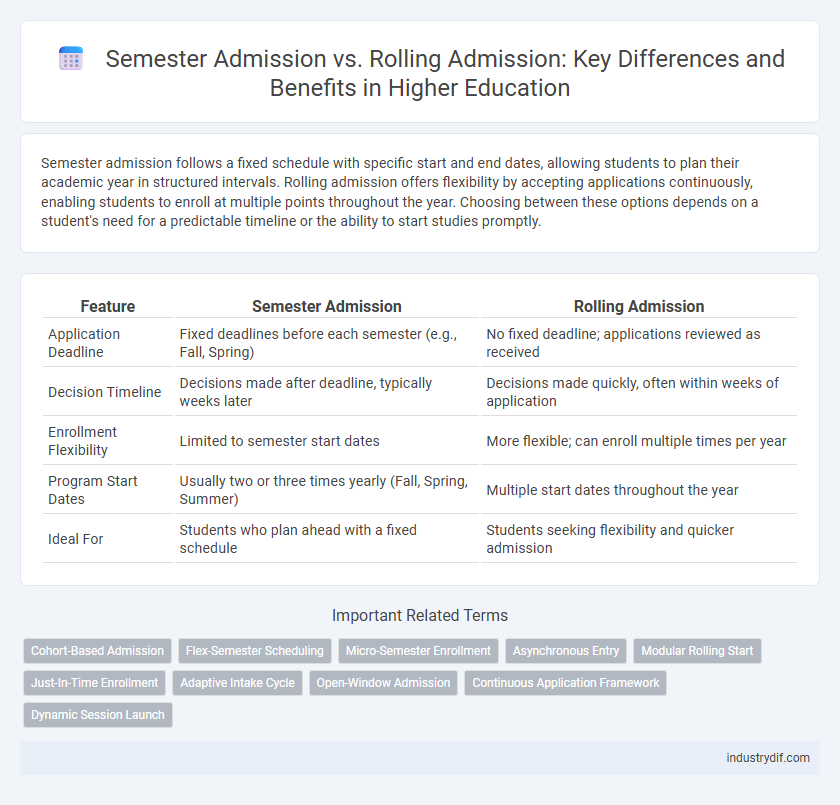
| Feature | Semester Admission | Rolling Admission |
|---|---|---|
| Application Deadline | Fixed deadlines before each semester (e.g., Fall, Spring) | No fixed deadline; applications reviewed as received |
| Decision Timeline | Decisions made after deadline, typically weeks later | Decisions made quickly, often within weeks of application |
| Enrollment Flexibility | Limited to semester start dates | More flexible; can enroll multiple times per year |
| Program Start Dates | Usually two or three times yearly (Fall, Spring, Summer) | Multiple start dates throughout the year |
| Ideal For | Students who plan ahead with a fixed schedule | Students seeking flexibility and quicker admission |
Understanding Semester Admission in Education
Semester admission divides the academic year into fixed periods, typically two or three semesters, where students enroll and begin courses simultaneously at the start of each term. This structured schedule allows institutions to manage resources efficiently and provides students with clear timelines for course completion and academic progression. Understanding semester admission helps students plan their studies effectively, aligning their academic goals with the institution's set calendar and deadlines.
What Is Rolling Admission?
Rolling admission is an application process where colleges review applications as they are received and make decisions continuously until all available spots are filled. This method offers greater flexibility compared to traditional semester deadlines, allowing students to apply at any time within the admission period. Many universities use rolling admission to accommodate a diverse range of applicants and streamline enrollment throughout the academic year.
Key Differences Between Semester and Rolling Admission
Semester admission follows fixed application deadlines and start dates, typically aligned with the academic calendar, while rolling admission allows students to apply and receive decisions continuously until programs fill. Semester systems often require earlier planning and provide structured enrollment periods, whereas rolling admission offers flexibility and faster feedback, accommodating late applicants. Understanding these distinctions helps students choose the best application strategy based on their readiness and program preferences.
Pros and Cons of Semester Admission
Semester admission provides a structured framework with fixed enrollment periods, allowing institutions to plan resources and course offerings efficiently. Students benefit from clear deadlines and a cohesive academic schedule, promoting focused study and routine. However, the rigid enrollment dates can limit flexibility, potentially delaying entry for applicants who miss deadlines and reducing opportunities for continuous enrollment throughout the year.
Pros and Cons of Rolling Admission
Rolling admission offers flexibility by allowing students to apply and receive decisions throughout the year, reducing stress associated with fixed deadlines. However, the unpredictability can complicate planning for housing and financial aid, and spots may fill up quickly, limiting availability later in the cycle. This system benefits students who need more time to prepare applications but may disadvantage those seeking a structured timeline like semester admissions.
Impact on Application Deadlines and Flexibility
Semester admission follows fixed application deadlines typically set months before the term begins, requiring students to plan their applications carefully to meet these strict cutoff dates. Rolling admission offers greater flexibility by accepting applications continuously until program capacity is reached, allowing students to apply later and receive quicker decisions. This flexibility can benefit applicants who need additional time to prepare materials or who decide to apply after traditional deadlines have passed.
How Admission Types Affect Student Planning
Semester admission requires students to apply within fixed enrollment periods, leading to structured academic timelines and defined course start dates, which can aid in long-term planning and financial preparation. Rolling admission offers flexibility by accepting applications continuously, allowing students to start their studies sooner or align enrollment with their personal circumstances, but may complicate synchronization with financial aid deadlines or housing availability. Understanding the differences between semester and rolling admission helps students strategically choose the best option to optimize their academic progression and resource management.
Suitability for Different Student Profiles
Semester admission suits students who prefer structured academic timelines and clear start and end dates, ideal for those balancing part-time work or extracurricular commitments. Rolling admission benefits applicants needing flexibility, such as career changers or international students facing visa processing variability. Each system caters to distinct student profiles by offering predictable planning versus adaptable enrollment options.
Admission Strategies: Semester vs Rolling
Semester admission follows fixed application deadlines and structured enrollment periods, enabling institutions to manage resources and class sizes effectively. Rolling admission allows continuous evaluation of applications, providing flexibility for both students and schools by accepting candidates as they apply until spots fill. Choosing between these strategies depends on institutional capacity, program demand, and the desired balance between selectivity and accessibility.
Industry Trends in Admission Processes
Industry trends in education reveal a growing shift from traditional semester-based admissions to rolling admission models, enhancing flexibility and student accessibility. Institutions adopting rolling admissions report increased application volumes and improved diversity by allowing candidates to apply throughout the year. Data indicates that rolling admission aligns with the digital transformation in higher education, offering real-time decision-making and streamlined enrollment processes.
Related Important Terms
Cohort-Based Admission
Cohort-based admission organizes students into fixed groups that start and progress through courses simultaneously, differing from semester systems with set enrollment periods or rolling admission allowing continuous entry. This model enhances peer collaboration and structured curriculum pacing, improving retention and academic performance in education programs.
Flex-Semester Scheduling
Flex-semester scheduling in education offers a dynamic alternative to traditional semester systems by allowing students to start courses at multiple points throughout the academic year, enhancing enrollment flexibility and personalized learning paths. Rolling admission complements flex-semester models by continuously accepting applications, enabling institutions to maintain steady student intake and accommodate diverse schedules without the constraints of fixed semester start dates.
Micro-Semester Enrollment
Micro-semester enrollment offers flexible, short-term courses within a traditional semester framework, enabling students to start and complete classes at multiple intervals throughout the academic year. Unlike rolling admission, which allows continuous application submission and evaluation, micro-semester structures provide condensed learning periods that enhance timely skill acquisition and improve academic scheduling efficiency.
Asynchronous Entry
Semester-based admission restricts student enrollment to fixed periods, limiting flexibility and often delaying entry, while rolling admission allows asynchronous entry throughout the academic year, enabling students to start their coursework at any time and tailor their educational journey to personal schedules. This flexibility supports diverse learning paces and enhances access to education by reducing wait times and increasing continuous enrollment opportunities.
Modular Rolling Start
Modular rolling start admission allows students to begin courses at multiple points throughout the academic year, offering greater flexibility compared to traditional semester-based enrollment that confines entry to fixed terms. This system enhances personalized learning paths and reduces waiting times, accommodating diverse schedules and improving student retention rates.
Just-In-Time Enrollment
Semester admission typically follows fixed enrollment periods aligned with academic terms, while rolling admission allows for continuous application review and acceptance. Just-in-time enrollment leverages rolling admission by enabling students to register closer to course start dates, optimizing resource allocation and accommodating late decision-makers in educational institutions.
Adaptive Intake Cycle
Semester-based admission follows fixed enrollment periods each academic term, while rolling admission allows for continuous application review and acceptance throughout the year, offering greater flexibility. An adaptive intake cycle integrates both models by adjusting enrollment windows based on demand and institutional capacity, optimizing student intake and resource allocation.
Open-Window Admission
Open-Window Admission offers continuous enrollment opportunities throughout the year, contrasting with traditional Semester Admission's fixed start dates and deadlines. This flexible admission model enhances accessibility for students by allowing applications at any time, enabling seamless entry into academic programs without waiting for specific semester periods.
Continuous Application Framework
Semester-based education structures enroll students at fixed intervals, creating distinct academic periods and deadlines, while rolling admission offers a continuous application framework that allows candidates to apply and receive decisions throughout the year, enhancing flexibility and access. Institutions adopting rolling admission benefit from a dynamic enrollment process, reducing pressure on applicants and enabling a steady influx of students aligned with course availability.
Dynamic Session Launch
Dynamic session launch in semester systems allows fixed start dates with structured academic calendars, enhancing course planning and cohort cohesion, while rolling admissions offer flexible entry points throughout the year, enabling continuous enrollment and personalized academic pacing for diverse student needs. Institutions leveraging rolling admission with dynamic session launches often increase accessibility and student retention by accommodating varying application timelines and accelerating time-to-degree completion.
Semester vs Rolling Admission Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com