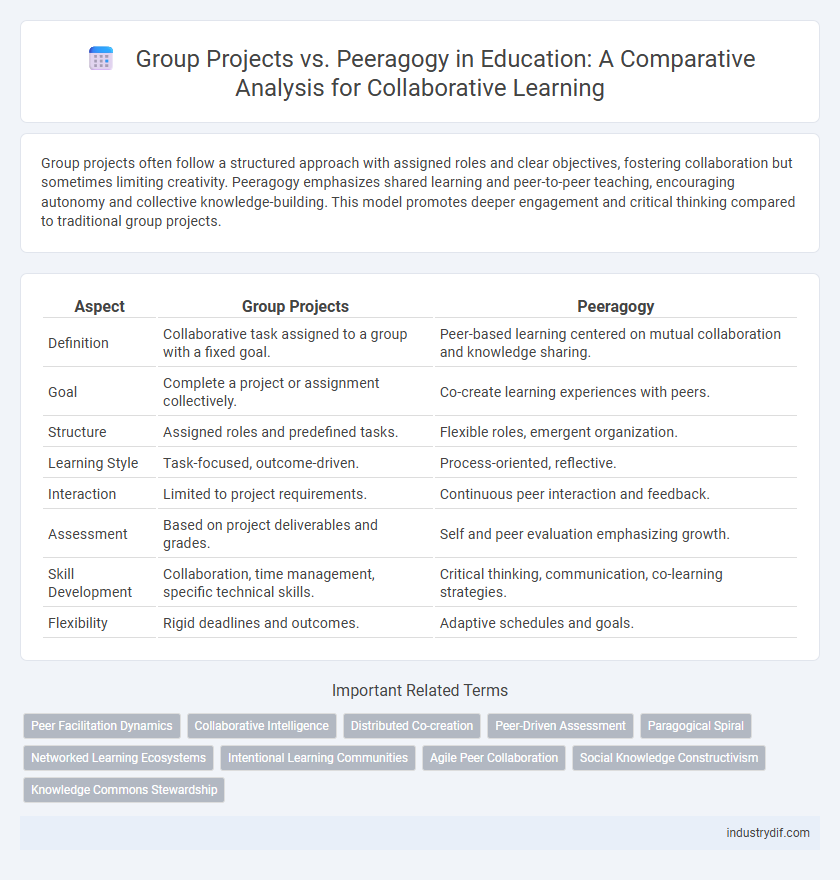
Group projects often follow a structured approach with assigned roles and clear objectives, fostering collaboration but sometimes limiting creativity. Peeragogy emphasizes shared learning and peer-to-peer teaching, encouraging autonomy and collective knowledge-building. This model promotes deeper engagement and critical thinking compared to traditional group projects.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Group Projects | Peeragogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative task assigned to a group with a fixed goal. | Peer-based learning centered on mutual collaboration and knowledge sharing. |
| Goal | Complete a project or assignment collectively. | Co-create learning experiences with peers. |
| Structure | Assigned roles and predefined tasks. | Flexible roles, emergent organization. |
| Learning Style | Task-focused, outcome-driven. | Process-oriented, reflective. |
| Interaction | Limited to project requirements. | Continuous peer interaction and feedback. |
| Assessment | Based on project deliverables and grades. | Self and peer evaluation emphasizing growth. |
| Skill Development | Collaboration, time management, specific technical skills. | Critical thinking, communication, co-learning strategies. |
| Flexibility | Rigid deadlines and outcomes. | Adaptive schedules and goals. |
Defining Group Projects in Education
Group projects in education involve students collaboratively working on a shared assignment to achieve common academic goals, often guided by instructor-defined roles and objectives. These projects emphasize teamwork, communication, and the division of tasks to foster cooperation and collective problem-solving. Structured group projects provide measurable outcomes and opportunities for peer assessment, enhancing students' critical thinking and collaborative skills within an educational setting.
Understanding Peeragogy: A Collaborative Learning Model
Peeragogy is a learner-centered collaborative model that emphasizes shared responsibility and collective knowledge creation, contrasting traditional group projects which often rely on assigned roles and hierarchical structures. This approach fosters deeper engagement through co-creation, reflection, and mutual support, enhancing the development of critical thinking and problem-solving skills. By leveraging diverse perspectives and continuous feedback loops, peeragogy transforms learning into an iterative, social process that adapts dynamically to participants' needs.
Historical Evolution: Group Projects and Peeragogy
Group projects have historically dominated educational settings as structured activities where students collaborate under authoritative guidance to complete assignments, emphasizing hierarchical roles and standardized outcomes. Peeragogy, emerging from digital and collaborative learning movements, promotes a decentralized, learner-driven approach that values mutual teaching, shared responsibility, and co-creation of knowledge. This evolution reflects a shift from traditional top-down educational models to participatory learning frameworks that harness social interaction and collective intelligence.
Key Differences Between Group Projects and Peeragogy
Group projects rely on assigned roles and structured collaboration to achieve specific outcomes, emphasizing task completion and instructor evaluation. Peeragogy fosters a self-directed learning environment where participants co-create knowledge through mutual teaching and shared responsibility, promoting continuous interaction and adaptability. Unlike group projects, peeragogy supports decentralized leadership and encourages learner autonomy, enhancing engagement and deeper understanding.
Benefits of Traditional Group Projects
Traditional group projects foster collaborative skills by distributing tasks among diverse members, enhancing communication and problem-solving abilities. They offer structured learning environments, promoting accountability and time management through clearly defined roles and deadlines. Furthermore, these projects simulate real-world teamwork scenarios, preparing students for professional challenges and collective decision-making.
Advantages of Peeragogy in Modern Classrooms
Peeragogy fosters collaborative learning by empowering students to co-create knowledge, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills beyond traditional group projects. It encourages autonomy and accountability within peer networks, leading to deeper engagement and personalized learning experiences. Modern classrooms benefit from peeragogy's adaptive framework, which supports continuous feedback and dynamic knowledge exchange critical in 21st-century education.
Challenges in Implementing Group Projects
Group projects often face challenges such as unequal participation, conflicting schedules, and difficulties in coordinating tasks, which can reduce overall learning outcomes. In contrast, peeragogy emphasizes collaborative learning through shared leadership and mutual support, addressing many issues inherent in traditional group projects. Overcoming the hierarchical structure in group projects is essential to foster engagement and equal accountability among participants.
Barriers to Effective Peeragogy
Barriers to effective peeragogy in education include lack of clear structure, uneven participation among members, and insufficient facilitation skills, which hinder collaborative learning outcomes compared to traditional group projects. Communication breakdowns and differing commitment levels often cause conflicts that reduce the quality of peer-generated knowledge. Overcoming these challenges requires designing frameworks that promote accountability, equal engagement, and continuous feedback within peeragogy environments.
Assessment Strategies: Group Projects vs Peeragogy
Assessment strategies in group projects often rely on collective grading, which can obscure individual contributions and hinder precise evaluation of student performance. In contrast, peeragogy uses collaborative, peer-driven assessment methods that promote continuous feedback and accountability among participants, enhancing skill development and critical reflection. Effective assessment in peeragogy integrates self-assessment, peer reviews, and iterative improvement, aligning more closely with learner-centered educational goals.
Future Trends in Collaborative Educational Practices
Group projects often emphasize structured roles and predefined outcomes, whereas peeragogy fosters self-directed, peer-led learning communities. Future trends indicate a shift towards hybrid models combining technology-enhanced peeragogy with traditional group collaboration to enhance critical thinking and digital literacy. Increasing adoption of AI-driven platforms supports personalized collaboration, promoting deeper engagement and adaptable skill-building in educational environments.
Related Important Terms
Peer Facilitation Dynamics
Peeragogy emphasizes collaborative knowledge creation through peer facilitation dynamics, where participants actively guide, support, and learn from each other in decentralized roles. Unlike traditional group projects, peer facilitation fosters equal engagement, shared responsibility, and adaptive learning environments that enhance critical thinking and collective problem-solving skills.
Collaborative Intelligence
Group projects often emphasize task division and individual accountability, while peeragogy fosters collaborative intelligence by encouraging co-creation of knowledge and shared problem-solving among peers. Leveraging collective expertise in peeragogy enhances critical thinking, adaptability, and deeper learning outcomes compared to traditional group project structures.
Distributed Co-creation
Group projects traditionally involve structured collaboration with defined roles, whereas peeragogy emphasizes distributed co-creation where learners collectively design, share, and refine knowledge without centralized authority. Distributed co-creation in peeragogy enhances engagement and fosters diverse perspectives by leveraging decentralized contributions and continuous peer feedback throughout the learning process.
Peer-Driven Assessment
Peer-driven assessment in peeragogy revolutionizes traditional group projects by fostering collaborative learning environments where participants actively evaluate each other's contributions, enhancing critical thinking and accountability. This approach leverages continuous feedback loops and shared responsibility, promoting deeper engagement and personalized learning outcomes compared to conventional teacher-led assessments.
Paragogical Spiral
The Paragogical Spiral emphasizes iterative, collaborative learning in peeragogy by continually reflecting, sharing, and refining knowledge within a community. Unlike traditional group projects, which often follow linear task completion, this spiral fosters emergent, participatory learning that evolves with each cycle of peer interaction and feedback.
Networked Learning Ecosystems
Group projects foster collaborative skills by dividing tasks among members, yet often suffer from uneven participation and limited knowledge exchange. Peeragogy enhances networked learning ecosystems by encouraging decentralized, peer-to-peer knowledge creation and continuous feedback loops, leading to more dynamic and scalable learning environments.
Intentional Learning Communities
Group projects foster collaboration through assigned roles and shared goals, while Peeragogy emphasizes self-directed, intentional learning communities where participants co-create knowledge and develop critical thinking skills. Intentional learning communities enhance engagement by promoting mutual accountability and continuous reflection, leading to deeper understanding and improved academic outcomes.
Agile Peer Collaboration
Agile peer collaboration in Peeragogy fosters adaptive learning environments where students co-create knowledge through iterative feedback and shared responsibility, enhancing engagement beyond traditional group projects. This approach prioritizes flexibility, mutual accountability, and dynamic role shifts, aligning with Agile principles to optimize collective problem-solving and continuous improvement in educational settings.
Social Knowledge Constructivism
Group projects facilitate collaborative learning by allowing students to co-construct knowledge through shared experiences and diverse perspectives, aligning with social knowledge constructivism principles. Peeragogy enhances this process by promoting peer-to-peer learning networks where participants actively engage in creating, refining, and applying knowledge collaboratively.
Knowledge Commons Stewardship
Group projects often centralize knowledge control within predefined roles, limiting collaborative stewardship and shared accountability; peeragogy emphasizes distributed expertise and co-creation, fostering a dynamic knowledge commons where learners collectively manage and sustain educational resources. Effective knowledge commons stewardship in peeragogy promotes transparency, adaptability, and mutual trust, enhancing learner engagement and the evolution of shared knowledge assets.
Group Projects vs Peeragogy Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com