School libraries offer vast resources for reading and research, fostering literacy and independent learning. Makerspaces provide hands-on experiences with technology and creative tools, encouraging problem-solving and collaboration. Both environments complement each other by combining traditional knowledge access with innovative, experiential learning opportunities.
Table of Comparison
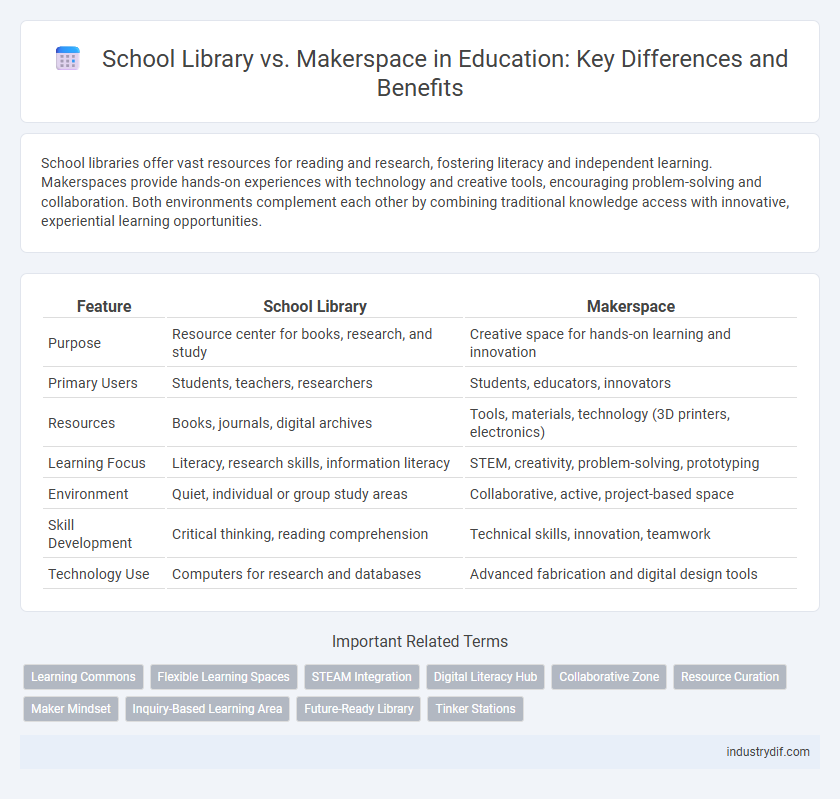
| Feature | School Library | Makerspace |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Resource center for books, research, and study | Creative space for hands-on learning and innovation |
| Primary Users | Students, teachers, researchers | Students, educators, innovators |
| Resources | Books, journals, digital archives | Tools, materials, technology (3D printers, electronics) |
| Learning Focus | Literacy, research skills, information literacy | STEM, creativity, problem-solving, prototyping |
| Environment | Quiet, individual or group study areas | Collaborative, active, project-based space |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, reading comprehension | Technical skills, innovation, teamwork |
| Technology Use | Computers for research and databases | Advanced fabrication and digital design tools |
Defining the School Library: Core Functions and Roles
The school library serves as a centralized resource hub, providing access to diverse educational materials such as books, digital media, and research databases that support curriculum goals and foster literacy development. It functions as a quiet study environment and a literacy center where students enhance their information literacy skills through guided research and critical thinking activities. By collaborating with educators, the library staff facilitates curriculum-aligned instruction and encourages lifelong learning habits essential for academic success.
What Is a Makerspace? Purpose and Key Features
A makerspace is an interactive learning environment designed to foster creativity, innovation, and hands-on skills through collaborative projects and access to diverse tools like 3D printers, electronics, and crafting supplies. Unlike traditional school libraries that primarily provide reading materials and research resources, makerspaces emphasize experiential learning and STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics) education. Key features include open work areas, technology integration, flexible resources, and support for problem-solving and critical thinking among students.
Traditional Library Services vs. Makerspace Offerings
School libraries provide traditional services such as curated book collections, reference materials, and quiet study areas that support literacy and research skills. Makerspaces offer hands-on learning environments equipped with technology like 3D printers, robotics kits, and crafting tools that encourage creativity, collaboration, and STEM exploration. While libraries emphasize information access and literacy development, makerspaces prioritize experiential learning and innovation through project-based activities.
Supporting Literacy: Libraries and Makerspaces Compared
School libraries traditionally support literacy by providing access to diverse books, fostering reading skills, and promoting information literacy through curated collections and quiet study environments. Makerspaces complement this by encouraging hands-on learning, creativity, and problem-solving, which enhance digital literacy and technical skills relevant to modern education. Both environments contribute uniquely to comprehensive literacy development by combining traditional reading with interactive, experiential learning.
Fostering Creativity and Innovation: Differentiating Approaches
School libraries provide structured access to diverse resources, promoting creativity through research, reading, and critical thinking, which nurtures innovation by expanding knowledge foundations. Makerspaces encourage hands-on experimentation and collaborative problem-solving, stimulating inventive thinking by allowing students to create prototypes and explore technology. Both environments complement each other by fostering creativity, with libraries offering intellectual depth and makerspaces enabling practical innovation.
Resource Availability: Materials and Technology in Each Space
School libraries offer extensive collections of books, digital archives, and multimedia resources that support diverse academic research and literacy development. Makerspaces provide hands-on access to cutting-edge technology such as 3D printers, microcontrollers, and crafting tools, fostering creativity and practical skills. Both spaces complement educational goals by combining traditional knowledge resources with innovative fabrication technologies.
Staffing and Expertise: Librarians vs. Makerspace Facilitators
School libraries rely on professional librarians who possess expertise in information organization, research support, and literacy development, ensuring students access credible resources and develop critical reading skills. Makerspaces require facilitators skilled in technology, design thinking, and hands-on problem solving, guiding students through experiential learning with tools such as 3D printers, coding kits, and robotics. Staffing these spaces with specialized personnel directly impacts the effectiveness of each environment in fostering educational growth and creativity.
Learning Outcomes: Research Skills vs. Hands-On Skills
School libraries primarily enhance research skills by providing access to diverse resources, fostering critical thinking, information literacy, and effective information retrieval techniques. Makerspaces cultivate hands-on skills through experiential learning, promoting creativity, problem-solving, collaboration, and technical proficiency with tools and technologies. Integrating both environments supports comprehensive learning outcomes, balancing theoretical knowledge acquisition with practical application.
Student Engagement: Passive Access vs. Active Participation
School libraries provide passive access to knowledge through books and digital resources, encouraging quiet study and research. Makerspaces promote active participation by offering hands-on activities that foster creativity, problem-solving, and collaboration among students. This shift from passive consumption to interactive learning increases student engagement and retention of educational concepts.
Integrating Libraries and Makerspaces: Trends and Best Practices
Integrating school libraries and makerspaces enhances collaborative learning by combining literacy resources with hands-on creativity, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Emerging trends emphasize flexible space design, technology integration, and interdisciplinary programming that supports STEAM education and digital literacy. Best practices include staff collaboration, student-centered activities, and continuous assessment to tailor resources that meet diverse learning needs.
Related Important Terms
Learning Commons
Learning Commons integrate the traditional resources of a school library with the creative, hands-on environment of a makerspace, fostering collaborative, interdisciplinary learning. This hybrid space supports diverse learning styles by combining digital literacy, critical thinking, and innovation through access to books, technology, and maker tools.
Flexible Learning Spaces
School libraries and makerspaces both serve as flexible learning spaces that foster creativity and collaboration, yet school libraries primarily offer access to diverse informational resources while makerspaces emphasize hands-on, experiential learning with tools and technology. Integrating these spaces supports personalized education by blending traditional research with innovative problem-solving activities, enhancing student engagement and skill development.
STEAM Integration
School libraries foster STEAM integration by providing access to diverse digital and print resources that support research, critical thinking, and creativity, while makerspaces enhance hands-on learning through interactive tools like 3D printers, robotics kits, and coding stations, promoting collaboration and innovation. Combining these environments maximizes STEAM education by blending traditional literacy with experiential, project-based activities that develop problem-solving and technical skills.
Digital Literacy Hub
School libraries serve as traditional centers for accessing curated digital and print resources, fostering foundational research and information evaluation skills. Makerspaces complement these libraries by providing hands-on opportunities with emerging technologies like 3D printers and coding kits, thereby enhancing students' practical digital literacy and innovative problem-solving abilities.
Collaborative Zone
School libraries foster collaborative zones by offering curated resources and quiet study spaces that support research and teamwork, while makerspaces emphasize hands-on learning through shared tools and creative projects, encouraging innovation and peer collaboration. Integrating both environments enhances student engagement by combining knowledge access with practical application in a dynamic educational setting.
Resource Curation
School libraries excel in resource curation by offering carefully selected books, digital databases, and reference materials that support diverse curricula and research needs. Makerspaces complement this by curating hands-on tools, technology kits, and creative resources that foster experiential learning and innovation.
Maker Mindset
School libraries foster literacy and provide access to diverse resources that develop critical thinking, while makerspaces cultivate a maker mindset by encouraging hands-on creativity, problem-solving, and innovation through collaborative, project-based learning. Emphasizing STEAM education, makerspaces empower students to experiment, prototype, and iterate, nurturing skills essential for future-ready learners.
Inquiry-Based Learning Area
School libraries provide curated resources and quiet study environments that support research and critical thinking, while makerspaces offer hands-on tools and collaborative settings designed to foster creativity and problem-solving skills essential for inquiry-based learning. Integrating both areas empowers students to engage deeply with content, experiment, and apply knowledge through exploration and innovation.
Future-Ready Library
School libraries evolve into future-ready hubs by integrating makerspaces that foster hands-on learning, critical thinking, and creativity. These dynamic environments combine digital resources with collaborative, project-based tools, preparing students for innovation-driven careers.
Tinker Stations
Tinker Stations in school libraries enhance hands-on learning by providing students with tools for creative problem-solving and STEM exploration. These interactive environments foster innovation, collaboration, and critical thinking skills beyond traditional book-based resources.
School Library vs Makerspace Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com