Synchronous learning involves real-time, interactive classes where students and teachers engage simultaneously, fostering immediate feedback and collaboration. Asynchronous learning offers flexibility by allowing students to access materials and complete assignments at their own pace, enhancing accessibility for diverse schedules. Both approaches cater to different learning styles, with synchronous learning promoting active participation and asynchronous learning supporting self-directed study.
Table of Comparison
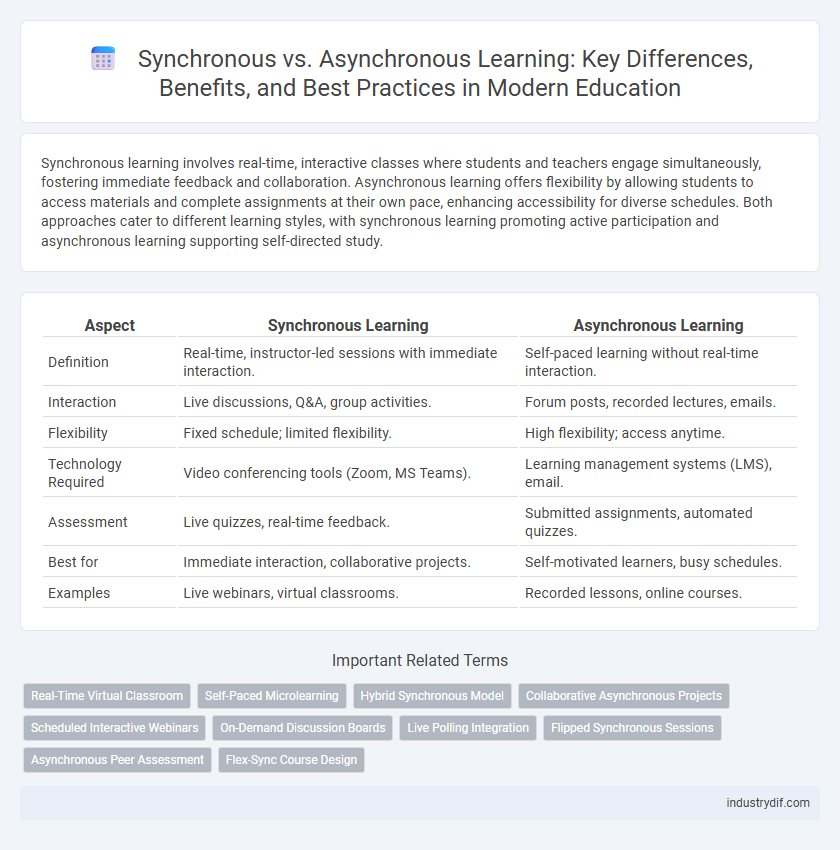
| Aspect | Synchronous Learning | Asynchronous Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time, instructor-led sessions with immediate interaction. | Self-paced learning without real-time interaction. |
| Interaction | Live discussions, Q&A, group activities. | Forum posts, recorded lectures, emails. |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule; limited flexibility. | High flexibility; access anytime. |
| Technology Required | Video conferencing tools (Zoom, MS Teams). | Learning management systems (LMS), email. |
| Assessment | Live quizzes, real-time feedback. | Submitted assignments, automated quizzes. |
| Best for | Immediate interaction, collaborative projects. | Self-motivated learners, busy schedules. |
| Examples | Live webinars, virtual classrooms. | Recorded lessons, online courses. |
Defining Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning refers to real-time, instructor-led instruction where students and teachers interact simultaneously through virtual classrooms or face-to-face settings. Asynchronous learning allows students to access course materials, complete assignments, and engage with content at their own pace without real-time interaction. Both methods offer unique benefits, with synchronous learning facilitating immediate feedback and collaboration, while asynchronous learning provides flexible scheduling and self-directed study options.
Key Differences in Delivery Methods
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between students and instructors through live video classes, chats, or webinars, enabling instant feedback and collaboration. Asynchronous learning allows students to access course materials, lectures, and assignments at their own pace without direct interaction, fostering flexibility and self-directed study. The key difference lies in timing: synchronous learning requires simultaneous participation, while asynchronous learning enables anytime, anywhere access to educational content.
Advantages of Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction, fostering immediate feedback and active participation, which enhances student engagement and understanding. It facilitates collaborative learning through live discussions, group activities, and direct communication with instructors, promoting a dynamic educational environment. This approach supports structured schedules, helping students maintain consistent study habits and stay motivated throughout the course.
Benefits of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning offers flexible scheduling, allowing students to access course materials and complete assignments at their own pace, which enhances time management and accommodates diverse learning styles. This mode supports deeper comprehension through self-directed study and repeated review of lectures, fostering improved retention and critical thinking skills. It also increases accessibility for learners across different time zones and with variable internet connectivity, promoting inclusive education opportunities.
Challenges of Synchronous Learning
Synchronous learning presents challenges such as scheduling conflicts that hinder participation across different time zones, limiting flexibility for diverse learners. Technical difficulties like unstable internet connections disrupt real-time engagement and negatively impact the learning experience. Additionally, reduced opportunities for self-paced study can increase stress and decrease comprehension for students requiring more time to process information.
Limitations of Asynchronous Learning
Asynchronous learning lacks real-time interaction, which can hinder immediate feedback and reduce student engagement. Delays in communication may lead to misunderstandings and slower problem resolution. The absence of scheduled sessions can also decrease motivation and accountability among learners.
Impact on Student Engagement
Synchronous learning fosters real-time interaction, promoting immediate feedback and active participation, which enhances student engagement through collaborative discussions and live problem-solving. Asynchronous learning offers flexibility, enabling students to engage with materials at their own pace, which can increase motivation for self-directed learners but may reduce spontaneous interaction. Research indicates that balancing synchronous sessions with asynchronous content maximizes engagement by catering to diverse learning preferences and schedules.
Flexibility and Accessibility Considerations
Synchronous learning requires students and instructors to be online simultaneously, which can limit flexibility for those with varying schedules or time zones, potentially impacting accessibility for learners with commitments or disabilities. Asynchronous learning allows students to access materials and participate at their convenience, enhancing flexibility and making education more accessible to diverse populations including working professionals and international students. Both modalities require thoughtful integration of technology to ensure equitable access and optimize learning outcomes.
Technology Requirements for Both Modalities
Synchronous learning demands stable high-speed internet, webcams, microphones, and real-time communication platforms such as Zoom or Microsoft Teams to facilitate live interaction between instructors and students. Asynchronous learning relies on robust learning management systems (LMS) like Moodle or Canvas, with requirements including reliable internet access, access to recorded lectures, digital assignment submissions, and discussion forums enabling flexible learning schedules. Both modalities necessitate compatible devices such as laptops or tablets, but synchronous learning emphasizes real-time connectivity, while asynchronous learning prioritizes content accessibility and user-friendly platforms.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Goals
Selecting between synchronous learning and asynchronous learning depends on educational goals, learner engagement, and flexibility requirements. Synchronous learning offers real-time interaction and immediate feedback, ideal for collaborative projects and discussions, while asynchronous learning provides adaptability and self-paced study, benefiting diverse schedules and promoting deeper reflection. Aligning instructional methods with desired outcomes enhances student performance, motivation, and overall learning effectiveness.
Related Important Terms
Real-Time Virtual Classroom
Synchronous learning in a real-time virtual classroom enables immediate interaction between students and instructors, fostering active participation and instant feedback. This approach leverages live video conferencing, chat tools, and real-time collaboration platforms to simulate traditional classroom dynamics in a digital environment.
Self-Paced Microlearning
Synchronous learning involves real-time interaction between instructors and students, promoting immediate feedback, while asynchronous learning supports self-paced microlearning by allowing learners to access modular content anytime, enhancing flexibility and knowledge retention. Emphasizing self-paced microlearning within asynchronous frameworks boosts engagement through concise, targeted lessons that adapt to individual learning speeds and schedules.
Hybrid Synchronous Model
The hybrid synchronous model combines real-time virtual interactions with flexible asynchronous activities, enhancing accessibility and engagement in education. This approach allows educators to leverage live discussions alongside pre-recorded materials, optimizing learning outcomes and accommodating diverse student schedules.
Collaborative Asynchronous Projects
Collaborative asynchronous projects in education enable students to engage in meaningful teamwork without the constraints of real-time interaction, fostering deeper reflection and diverse input through flexible scheduling. This approach leverages digital tools like shared documents and discussion boards, enhancing critical thinking and allowing participation across different time zones.
Scheduled Interactive Webinars
Scheduled interactive webinars in synchronous learning promote real-time engagement and immediate feedback, enhancing comprehension and collaboration among students and educators. Unlike asynchronous learning, this format fosters dynamic discussions and instant clarification, which are crucial for topics requiring active participation and timely interaction.
On-Demand Discussion Boards
On-demand discussion boards enhance asynchronous learning by providing flexible interaction opportunities, enabling students to engage deeply with course content at their own pace without the constraints of scheduled class times. These platforms foster collaborative knowledge building and critical thinking, supporting diverse learning styles and increasing accessibility in virtual education environments.
Live Polling Integration
Live polling integration enhances synchronous learning by enabling real-time student engagement and immediate feedback during virtual classes, increasing interaction and participation rates. In contrast, asynchronous learning benefits from polling tools through self-paced quizzes and opinion surveys, allowing learners to reflect and respond at their convenience while providing educators with valuable data on student understanding.
Flipped Synchronous Sessions
Flipped synchronous sessions combine the benefits of asynchronous learning, where students review instructional materials independently, with live, interactive classes that focus on discussion, problem-solving, and personalized feedback. This approach maximizes student engagement and retention by shifting content delivery outside of class and dedicating synchronous time to active learning and collaboration.
Asynchronous Peer Assessment
Asynchronous peer assessment enhances student engagement by allowing learners to evaluate and provide feedback on each other's work at their own pace, fostering deep reflection and critical thinking skills. This method supports flexible learning schedules and improves knowledge retention through iterative review processes outside real-time constraints.
Flex-Sync Course Design
Flex-Sync course design combines synchronous learning's real-time interaction with asynchronous learning's flexible access, enabling personalized pacing while maintaining structured engagement. This hybrid model enhances student autonomy and improves learning outcomes by leveraging live discussions, recorded lectures, and adaptable deadlines.
Synchronous Learning vs Asynchronous Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com