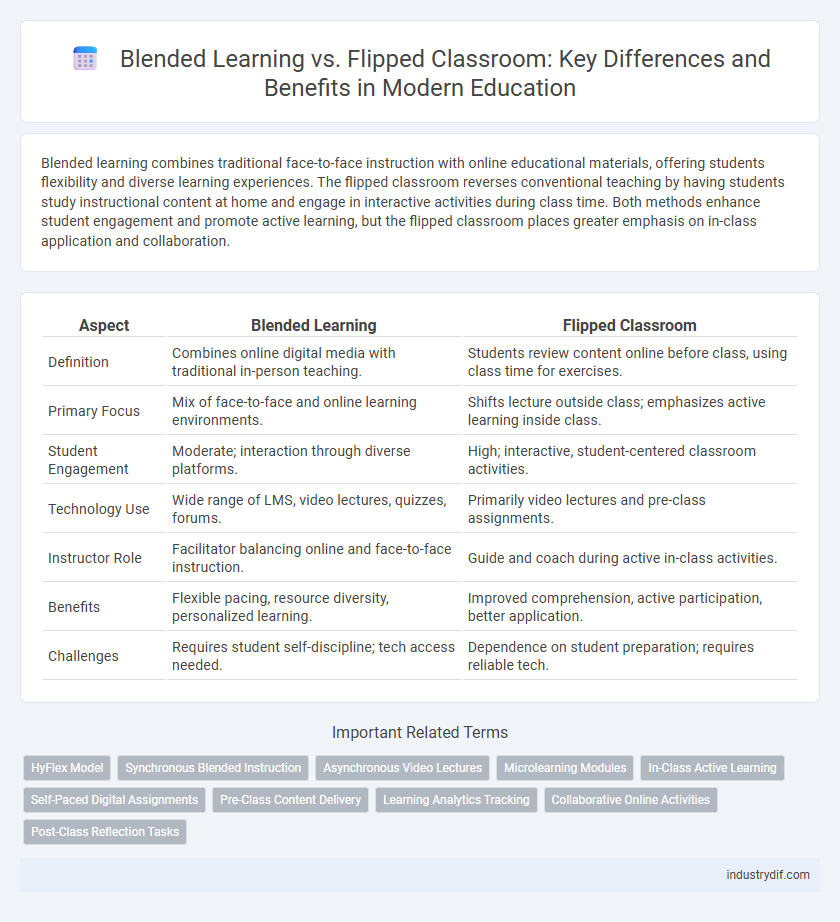
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational materials, offering students flexibility and diverse learning experiences. The flipped classroom reverses conventional teaching by having students study instructional content at home and engage in interactive activities during class time. Both methods enhance student engagement and promote active learning, but the flipped classroom places greater emphasis on in-class application and collaboration.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines online digital media with traditional in-person teaching. | Students review content online before class, using class time for exercises. |
| Primary Focus | Mix of face-to-face and online learning environments. | Shifts lecture outside class; emphasizes active learning inside class. |
| Student Engagement | Moderate; interaction through diverse platforms. | High; interactive, student-centered classroom activities. |
| Technology Use | Wide range of LMS, video lectures, quizzes, forums. | Primarily video lectures and pre-class assignments. |
| Instructor Role | Facilitator balancing online and face-to-face instruction. | Guide and coach during active in-class activities. |
| Benefits | Flexible pacing, resource diversity, personalized learning. | Improved comprehension, active participation, better application. |
| Challenges | Requires student self-discipline; tech access needed. | Dependence on student preparation; requires reliable tech. |
Introduction to Blended Learning and Flipped Classroom
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational materials, allowing for flexible, personalized learning experiences tailored to student needs. The flipped classroom reverses conventional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, enabling in-person sessions to focus on interactive, collaborative activities that reinforce understanding. Both models leverage digital technology to enhance student engagement and improve learning outcomes in modern education settings.
Core Concepts and Definitions
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online digital media, enabling flexible, personalized education through a mix of synchronous and asynchronous activities. Flipped classroom inverts the conventional model by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of class, while engaging students in interactive, problem-solving activities during in-person sessions. Both models emphasize active learning and technology integration but differ fundamentally in the timing and delivery of core instructional content.
Key Differences Between Blended Learning and Flipped Classroom
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face instruction with online components, allowing students to access content anytime while maintaining classroom interaction. The flipped classroom specifically reverses typical teaching by delivering instructional content, often online, outside of class and dedicating in-class time to exercises, projects, or discussions. Key differences include blended learning's broader application with varied online and offline methods, whereas flipped classroom focuses on shifting lecture delivery outside the classroom to enhance active, collaborative learning during class sessions.
Instructional Design Approaches
Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online digital media, emphasizing flexible instructional design that caters to diverse student needs and promotes active engagement through varied content delivery. In contrast, the flipped classroom model reverses conventional teaching by delivering instructional content online before class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive, application-based activities that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Effective instructional design in both approaches leverages multimedia resources and learner-centered strategies to optimize student outcomes and maximize classroom efficiency.
Technology Integration in Both Models
Blended learning integrates digital tools and face-to-face instruction, using learning management systems, multimedia content, and interactive apps to enhance student engagement and personalize learning paths. Flipped classrooms leverage technology by delivering instructional content online before class, enabling in-person sessions to focus on application and collaborative activities. Both models rely on robust technology infrastructure, such as high-speed internet and educational software platforms, to facilitate seamless access and effective pedagogical outcomes.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Blended learning integrates online digital media with traditional classroom methods, enhancing student engagement by offering flexible access to diverse resources and promoting interactive activities both inside and outside the classroom. The flipped classroom model shifts direct instruction to outside class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on collaborative problem-solving and active discussion, thereby increasing student interaction and deeper understanding. Both approaches leverage technology to foster participatory learning environments, but the flipped classroom specifically intensifies peer-to-peer and instructor-student interactions during face-to-face time.
Benefits and Challenges of Blended Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, offering flexibility and personalized learning experiences that cater to diverse student needs, boosting engagement and retention rates. It enables educators to leverage technology for real-time assessments and adaptive learning paths, enhancing overall educational outcomes while also promoting collaboration through varied instructional methods. Challenges include the need for reliable technology infrastructure, increased teacher training requirements, and the risk of student isolation if not properly managed, which can affect motivation and participation.
Advantages and Limitations of Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom model enhances student engagement by allowing learners to review instructional content at their own pace outside of class and participate in interactive, collaborative activities during in-person sessions. It supports personalized learning and fosters critical thinking but requires students to have reliable access to technology and a high degree of self-motivation, which can be limiting factors. Effective implementation depends on instructors' ability to design meaningful pre-class materials and facilitate dynamic classroom discussions.
Assessment and Evaluation Strategies
Blended learning integrates traditional assessments with digital tools, enabling real-time feedback and adaptive testing to enhance evaluation accuracy. Flipped classrooms emphasize formative assessments through in-class activities and peer evaluations, fostering deeper understanding and practical application. Both models benefit from diversified assessment strategies that combine self-assessment, quizzes, and project-based evaluations to measure student progress effectively.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Institution
Selecting the appropriate education model depends on institutional goals, resources, and student needs. Blended learning integrates online and face-to-face instruction, providing flexibility and diverse content delivery, while flipped classrooms prioritize active, in-class engagement by assigning lecture materials as homework. Evaluating factors such as technology access, teacher readiness, and curriculum alignment guides institutions in adopting the most effective approach for improving learning outcomes.
Related Important Terms
HyFlex Model
The HyFlex model integrates the flexibility of blended learning and the active engagement of flipped classrooms by allowing students to choose between attending sessions in-person, online synchronously, or asynchronously. This approach maximizes accessibility and personalized learning experiences, accommodating diverse student needs and promoting higher retention and participation rates.
Synchronous Blended Instruction
Synchronous blended instruction combines real-time online interaction with face-to-face classroom activities, enhancing student engagement and immediate feedback in both blended learning and flipped classroom models. This approach maximizes the effectiveness of instructional time by integrating synchronous digital tools with active, in-person learning strategies.
Asynchronous Video Lectures
Asynchronous video lectures in blended learning offer flexible access to content, allowing students to learn at their own pace and revisit materials, which enhances comprehension and retention. In flipped classroom models, these videos serve as pre-class preparation, enabling in-person sessions to focus on active learning and personalized interactions.
Microlearning Modules
Blended learning integrates microlearning modules to offer flexible, on-demand content that complements traditional in-class instruction, enhancing knowledge retention and learner engagement. Flipped classroom models leverage microlearning by delivering concise, targeted videos and interactive materials before class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on deeper discussion and application of concepts.
In-Class Active Learning
Blended learning integrates traditional face-to-face instruction with online components, enabling diverse in-class active learning strategies that promote student engagement and collaboration. The flipped classroom model specifically emphasizes shifting lecture content outside class, allowing classroom time to focus extensively on problem-solving, discussions, and hands-on activities that foster deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Self-Paced Digital Assignments
Blended learning incorporates self-paced digital assignments that allow students to progress at their own speed, enhancing individualized comprehension and retention. In flipped classrooms, these assignments are critical for pre-class preparation, enabling deeper in-class engagement and active learning activities.
Pre-Class Content Delivery
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional classroom methods, offering flexibility in pre-class content delivery by allowing students to access materials anytime, enhancing individualized learning. The flipped classroom model requires students to engage with pre-class content, such as videos or readings, to prepare for interactive in-class activities focused on application and deeper understanding.
Learning Analytics Tracking
Blended learning integrates face-to-face and online instruction, enabling real-time learning analytics tracking to assess student engagement and performance across platforms. Flipped classrooms leverage pre-class video content and in-class activities, using learning analytics to monitor video interaction and active participation, enhancing personalized feedback and instructional adjustments.
Collaborative Online Activities
Blended learning integrates collaborative online activities that foster real-time interaction and group problem-solving, enhancing student engagement across digital and face-to-face environments. Flipped classrooms emphasize pre-class content absorption, allowing in-class time to focus intensively on collaborative projects and peer discussions that deepen understanding.
Post-Class Reflection Tasks
Blended learning integrates online and face-to-face instruction, allowing post-class reflection tasks to be completed digitally, which enhances personalized feedback and self-paced analysis. Flipped classrooms emphasize pre-class content consumption, freeing up class time for active learning while post-class reflection solidifies understanding through targeted exercises and critical thinking prompts.
Blended Learning vs Flipped Classroom Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com