Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes direct transmission of knowledge from teacher to student, often through lectures and standardized testing, which can limit student engagement and critical thinking. Student-centered learning prioritizes active participation, collaboration, and personalized learning experiences that foster deeper understanding and motivation. Balancing these approaches can create a dynamic educational environment that supports diverse learning styles and maximizes pet owners' ability to educate their animals effectively.
Table of Comparison
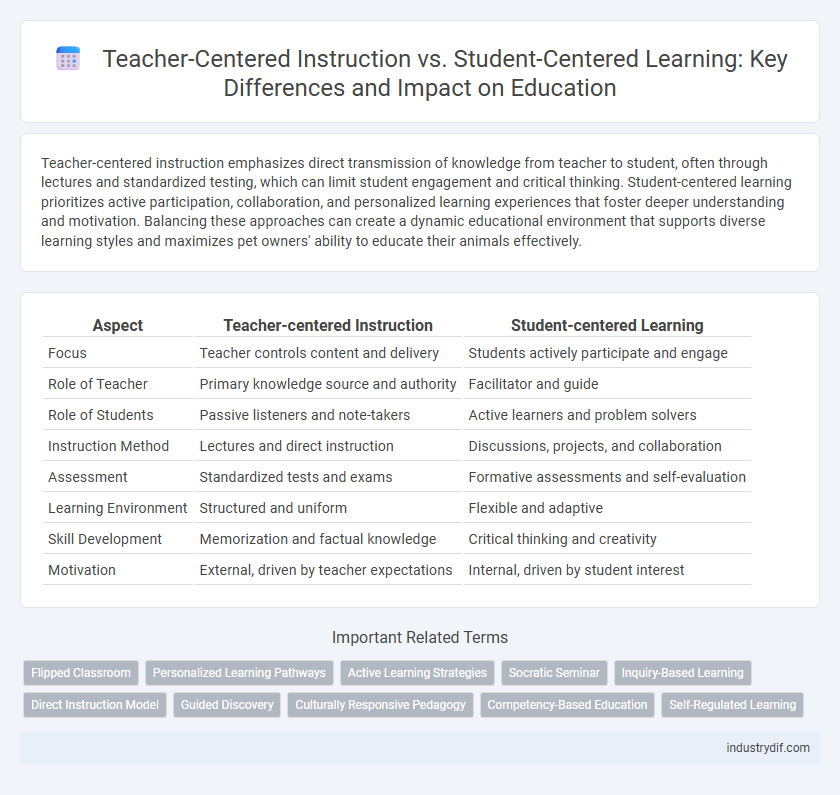
| Aspect | Teacher-centered Instruction | Student-centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Teacher controls content and delivery | Students actively participate and engage |
| Role of Teacher | Primary knowledge source and authority | Facilitator and guide |
| Role of Students | Passive listeners and note-takers | Active learners and problem solvers |
| Instruction Method | Lectures and direct instruction | Discussions, projects, and collaboration |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and exams | Formative assessments and self-evaluation |
| Learning Environment | Structured and uniform | Flexible and adaptive |
| Skill Development | Memorization and factual knowledge | Critical thinking and creativity |
| Motivation | External, driven by teacher expectations | Internal, driven by student interest |
Defining Teacher-centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction is an educational approach where the teacher directs the learning process through lectures, demonstrations, and structured lessons, emphasizing content delivery and student compliance. This method prioritizes teacher authority and knowledge transmission, often employing standardized testing to measure student performance. Its effectiveness depends on clear objectives, discipline, and the teacher's expertise in managing the classroom environment.
Key Characteristics of Student-centered Learning
Student-centered learning emphasizes active student participation, personalized instruction, and collaborative learning environments that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It prioritizes students' interests, experiences, and learning styles to enhance engagement and knowledge retention. Key characteristics include flexible pacing, formative assessment, and a focus on developing intrinsic motivation and self-regulation.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Approaches
Teacher-centered instruction, dominant in traditional education systems, emphasizes direct instruction, rote memorization, and authoritative knowledge transmission, rooted in early 20th-century pedagogical models. The shift toward student-centered learning emerged in the mid-20th century, inspired by constructivist theories from educational psychologists like Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky, promoting active engagement, critical thinking, and collaboration. This evolution reflects a broader recognition of diverse learning styles and the need to foster autonomy and lifelong learning skills in modern classrooms.
Advantages of Teacher-centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction provides a structured learning environment where educators maintain control over lesson delivery and pacing, ensuring curriculum standards are consistently met. This method facilitates efficient knowledge transfer, particularly in large classrooms, by focusing on direct instruction and clear expectations. Teacher-centered approaches often result in higher content coverage and improved mastery of foundational concepts through systematic repetition and assessment.
Benefits of Student-centered Learning
Student-centered learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills by actively engaging students in the learning process. It enhances motivation and retention through personalized instruction tailored to individual learning styles and interests. Research shows that this approach fosters collaboration, communication, and deeper understanding, preparing students for real-world challenges more effectively than teacher-centered instruction.
Challenges in Implementing Student-centered Approaches
Implementing student-centered learning faces challenges such as resistance from educators accustomed to traditional teacher-centered instruction, which emphasizes direct control and standardized assessment. Classroom management becomes more complex as students take on active roles requiring facilitation skills and adaptive lesson planning. Limited resources, insufficient teacher training, and entrenched curriculum frameworks also hinder the effective adoption of student-centered pedagogies.
Classroom Management in Both Models
Teacher-centered instruction relies on structured classroom management techniques where the teacher controls the flow, enforces rules, and directs student behavior to maintain order and ensure curriculum coverage. In contrast, student-centered learning emphasizes collaborative classroom management strategies, promoting student autonomy, engagement, and self-regulation to foster an interactive and dynamic learning environment. Effective classroom management in student-centered models often includes flexible seating, group work protocols, and conflict resolution practices that support student ownership of their learning process.
Impact on Student Engagement and Outcomes
Teacher-centered instruction often results in passive learning, limiting student engagement and critical thinking, which can negatively affect academic outcomes. In contrast, student-centered learning promotes active participation, collaboration, and personalized feedback, leading to higher motivation and improved retention of knowledge. Research shows that classrooms implementing student-centered approaches experience increased student satisfaction and better performance on assessments.
Integrating Technology in Teaching Models
Teacher-centered instruction often relies on direct technology use for presentation and content delivery, such as interactive whiteboards and educational software, to enhance clarity and engagement. Student-centered learning integrates technology as a tool for collaboration, critical thinking, and personalized learning experiences through platforms like learning management systems, digital simulations, and adaptive assessments. Effective integration balances these approaches by leveraging technology to support both structured guidance and independent exploration, optimizing educational outcomes in diverse classrooms.
Choosing the Right Approach for Educational Goals
Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes structured content delivery and authoritative guidance, ideal for foundational knowledge and large classroom management. Student-centered learning prioritizes active engagement and personalized experiences, enhancing critical thinking and collaboration skills. Selecting the right approach depends on specific educational goals, curriculum requirements, and student needs for optimal learning outcomes.
Related Important Terms
Flipped Classroom
Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes direct teaching where educators deliver content, whereas student-centered learning in a flipped classroom reverses this by having students engage with lecture materials at home and collaborate on activities in class, enhancing active learning and critical thinking. Research shows flipped classrooms improve student engagement, retention, and personalized learning by shifting the teacher's role from lecturer to facilitator.
Personalized Learning Pathways
Teacher-centered instruction often relies on standardized curricula and uniform pacing, potentially limiting the ability to tailor lessons to individual student needs. Student-centered learning emphasizes personalized learning pathways, enabling customization based on students' strengths, interests, and learning styles to enhance engagement and academic outcomes.
Active Learning Strategies
Teacher-centered instruction predominantly relies on lectures and direct teaching methods, limiting student engagement, while student-centered learning incorporates active learning strategies such as group discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities that foster critical thinking and deeper comprehension. Emphasizing active learning in student-centered settings enhances collaboration, motivation, and retention of knowledge, driving improved educational outcomes.
Socratic Seminar
Socratic seminars exemplify student-centered learning by encouraging active dialogue and critical thinking through open-ended questions, contrasting teacher-centered instruction where knowledge transmission is unilateral. This interactive approach promotes deeper comprehension and collaborative problem-solving, fostering higher-order cognitive skills essential for educational development.
Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student-centered education by encouraging learners to explore, ask questions, and develop critical thinking skills, contrasting with teacher-centered instruction which relies on direct teaching and passive knowledge absorption. Research shows inquiry-based learning improves student engagement, problem-solving abilities, and long-term retention compared to traditional teacher-led lectures.
Direct Instruction Model
The Direct Instruction Model emphasizes a teacher-centered approach where educators deliver structured, explicit lessons focusing on clear, measurable objectives that enhance student mastery of foundational skills. This model prioritizes systematic teaching sequences and frequent assessments to ensure active student engagement and consistent academic progress.
Guided Discovery
Guided discovery in student-centered learning emphasizes active exploration, enabling students to construct knowledge through carefully designed tasks that prompt critical thinking and problem-solving. Unlike teacher-centered instruction, which relies on direct explanation, guided discovery fosters deeper understanding by encouraging learners to investigate concepts independently within a supportive framework.
Culturally Responsive Pedagogy
Teacher-centered instruction often limits opportunities for culturally responsive pedagogy by emphasizing standardized content delivery, whereas student-centered learning fosters an inclusive environment that values diverse cultural backgrounds and adapts teaching strategies to meet the unique needs of each learner. Emphasizing culturally responsive pedagogy within student-centered learning enhances engagement, academic achievement, and social-emotional development by validating students' identities and experiences.
Competency-Based Education
Competency-Based Education (CBE) emphasizes student-centered learning by tailoring instruction to individual skill mastery rather than time spent in class, contrasting with teacher-centered instruction that relies on uniform pacing and direct content delivery. This approach fosters deeper understanding and practical application of knowledge, promoting active learner engagement and personalized assessment strategies.
Self-Regulated Learning
Teacher-centered instruction often limits opportunities for self-regulated learning by emphasizing direct instruction and passive knowledge absorption. Student-centered learning fosters self-regulated learning through active engagement, promoting skills like goal-setting, self-monitoring, and strategic thinking essential for academic success.
Teacher-centered Instruction vs Student-centered Learning Infographic
 industrydif.com
industrydif.com